In heat treatment, the most common furnace atmospheres are created using nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and inert gases like argon. Gases such as methane, propane, and ammonia are also used as sources for these primary active components. The specific gas or mixture is not arbitrary; it is a precisely controlled tool chosen to either protect the material's surface or intentionally change its chemical properties at high temperatures.
A furnace atmosphere is an active engineering control, not a passive environment. Its purpose is twofold: to shield the workpiece from harmful reactions like oxidation, or to serve as a reactive agent that enhances surface properties such as hardness.
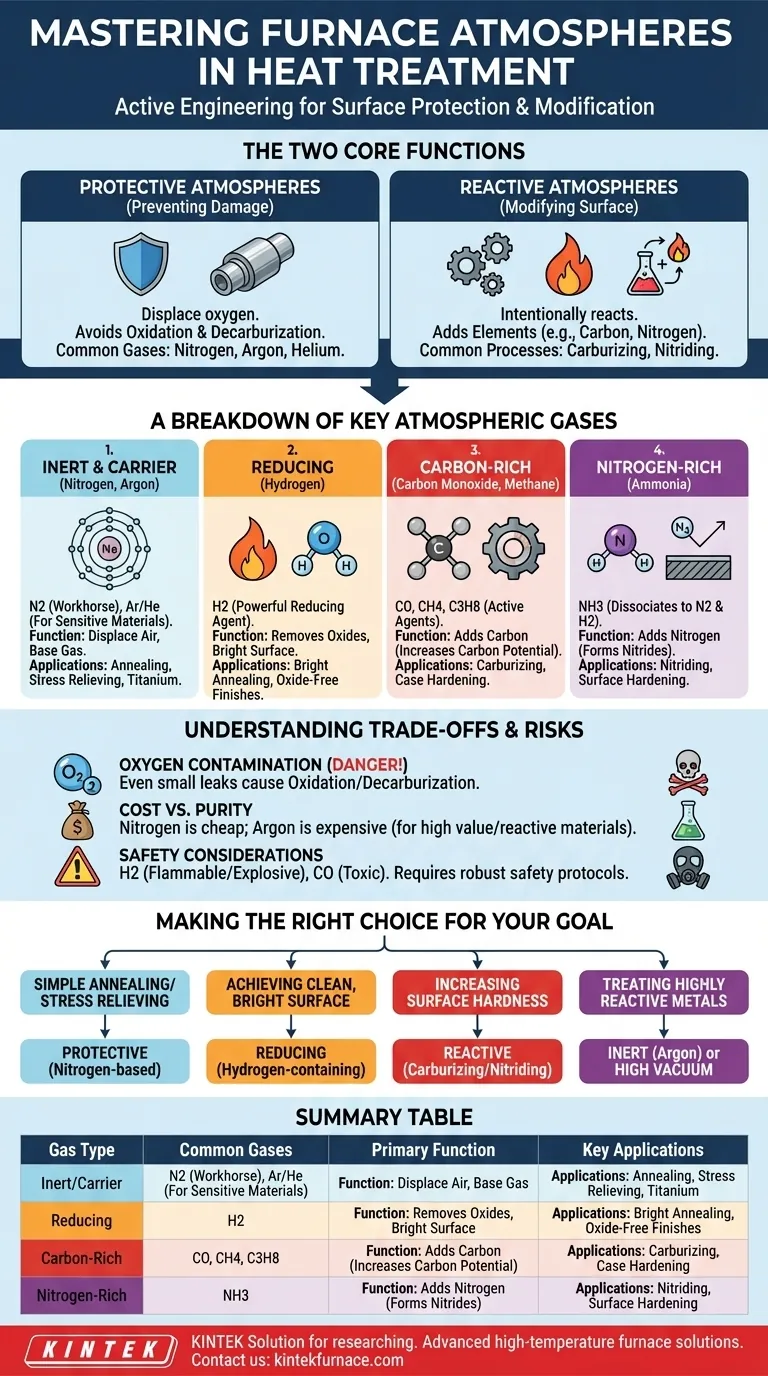
The Two Core Functions of a Furnace Atmosphere
The choice of atmosphere fundamentally depends on whether you need to protect the component or modify it. These two goals dictate entirely different chemical environments inside the furnace.
Protective Atmospheres: Preventing Damage
The primary goal of a protective atmosphere is to prevent unwanted chemical reactions between the hot metal surface and the air. The most common damaging reactions are oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon content from steel, making it softer).
These atmospheres work by displacing oxygen. They are typically composed of nitrogen, hydrogen, or inert gases, which do not react negatively with the workpiece.
Reactive Atmospheres: Modifying the Surface
In processes like case hardening, the atmosphere is intentionally designed to react with the metal's surface. The gas mixture acts as a carrier, delivering specific elements to be absorbed by the workpiece.
For example, in carburizing, carbon-rich gases add carbon to the surface of steel to increase its hardness. In nitriding, ammonia is used to introduce nitrogen for a similar hardening effect.
A Breakdown of Key Atmospheric Gases
Each gas has a distinct chemical role. Most furnace atmospheres are not a single pure gas but a carefully balanced mixture designed for a specific outcome.
Inert and Carrier Gases (Nitrogen, Argon)
Nitrogen (N2) is the workhorse of heat treatment atmospheres. It is relatively inexpensive and inert under most conditions, making it an excellent base gas for displacing air.
Argon (Ar) and Helium (He) are true inert gases. They are used for highly sensitive materials, like titanium or certain stainless steels, where even nitrogen could form undesirable nitrides at high temperatures.
Reducing Gases (Hydrogen)
Hydrogen (H2) is a powerful reducing agent. This means it actively seeks out and reacts with oxygen, removing surface oxides and preventing new ones from forming.
Atmospheres with a significant percentage of hydrogen are used for processes like bright annealing, where a clean, bright, oxide-free surface finish is critical.
Carbon-Rich Gases (Carbon Monoxide, Methane)
Carbon Monoxide (CO) is the primary active gas in carburizing processes. It efficiently transfers carbon atoms to the surface of steel, a process known as increasing the "carbon potential."
Gases like methane (CH4) or propane are often used as "enriching gases." They are added to a nitrogen-based carrier gas and break down at high temperatures to produce the desired carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
Nitrogen-Rich Gases (Ammonia)
Dissociated Ammonia (NH3) is the source for nitriding. In the furnace, ammonia breaks down into its constituent parts: 75% hydrogen and 25% nitrogen. The elemental nitrogen is then absorbed by the steel's surface to form hard nitride compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing an atmosphere involves balancing process requirements, material compatibility, cost, and safety.
The Danger of Oxygen Contamination
Oxygen (O2) is almost always an unwanted contaminant. Even small leaks that allow air (which is 21% oxygen) into the furnace can lead to significant oxidation and decarburization, compromising the quality of the final part.
Cost vs. Purity
Nitrogen is far more common than argon simply because it is much less expensive. For most applications, nitrogen is sufficiently inert. The high cost of argon is only justified when treating extremely reactive or high-value materials that demand absolute chemical purity.
Safety Considerations
Many essential atmospheric gases are hazardous. Hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive, requiring careful handling and leak detection. Carbon monoxide is extremely toxic. Facilities using these gases must have robust safety protocols, ventilation, and monitoring systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process goal directly dictates the correct atmospheric strategy.
- If your primary focus is simple annealing or stress relieving: A protective, nitrogen-based atmosphere is often the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving a clean, bright surface: An atmosphere containing hydrogen is necessary to reduce any surface oxides.
- If your primary focus is increasing surface hardness: A reactive atmosphere for carburizing (using carbon monoxide) or nitriding (using ammonia) is required.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive metals like titanium: Only a pure inert gas like argon or a high vacuum will prevent contamination.
Ultimately, mastering furnace atmospheres is about using controlled chemistry to achieve a precise metallurgical outcome.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Common Gases | Primary Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert/Carrier | Nitrogen, Argon | Displace oxygen, prevent reactions | Annealing, stress relieving, sensitive materials |
| Reducing | Hydrogen | Remove oxides, prevent oxidation | Bright annealing, oxide-free surfaces |
| Carbon-Rich | Carbon Monoxide, Methane | Add carbon for surface hardening | Carburizing, increasing carbon potential |
| Nitrogen-Rich | Ammonia | Add nitrogen for surface hardening | Nitriding, forming nitride compounds |
Struggling to select the right furnace atmosphere for your heat treatment needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















