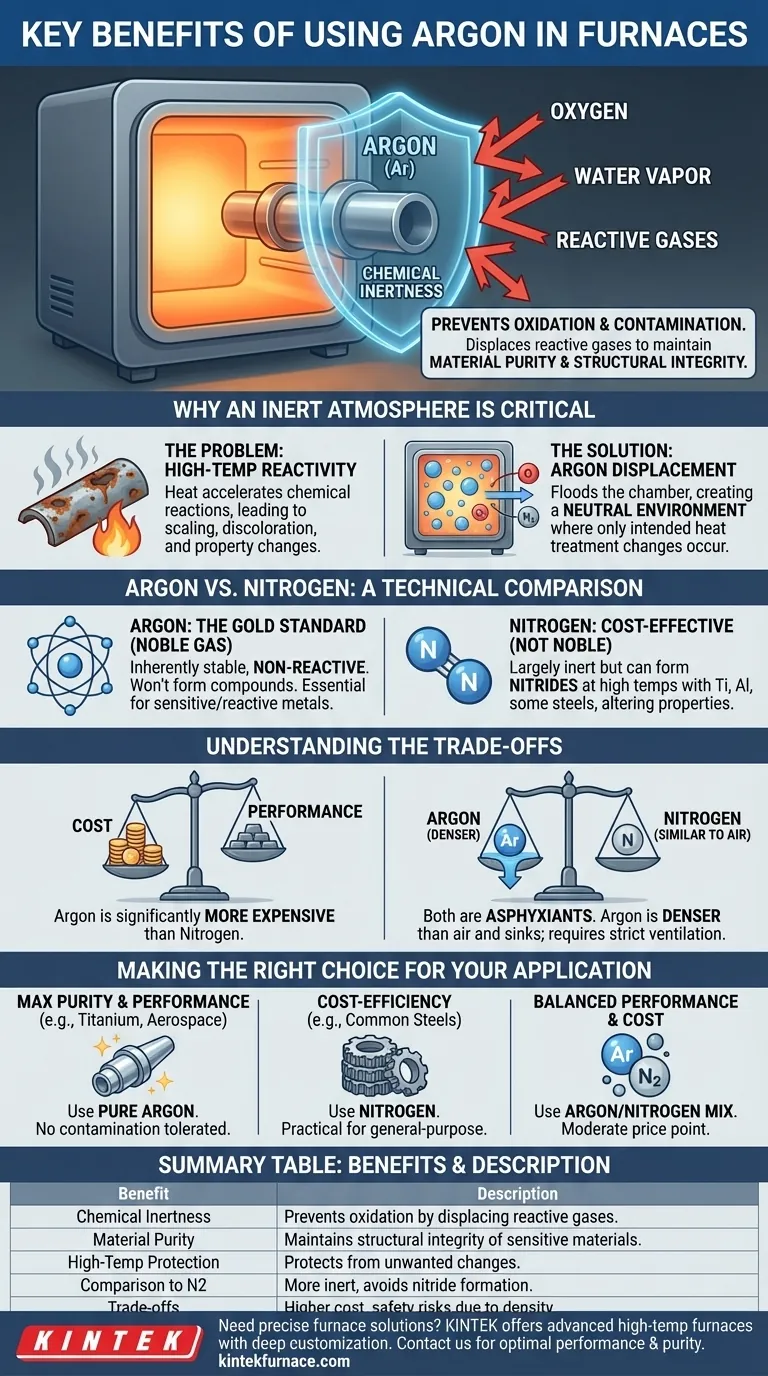
At its core, argon's primary benefit is its absolute chemical inertness. In a high-temperature furnace, it acts as a perfect protective shield, displacing reactive gases like oxygen to prevent oxidation and contamination. This ensures the final material maintains its intended purity, structural integrity, and performance characteristics, which is non-negotiable in precision industries.
Choosing a furnace atmosphere isn't just about preventing surface-level defects; it's a critical control variable for guaranteeing the fundamental properties of your material. Argon provides the highest level of inert protection, but this performance comes with distinct trade-offs in cost and handling.

Why an Inert Atmosphere is Critical
At the high temperatures found in industrial furnaces, materials become highly susceptible to unwanted chemical reactions. Understanding this vulnerability is key to appreciating the role of a gas like argon.
The Problem: High-Temperature Reactivity
Heat acts as a catalyst, dramatically accelerating chemical reactions. When exposed to ambient air, metals will rapidly react with oxygen (oxidation), nitrogen, and water vapor.
This can lead to scaling, discoloration, and, more critically, a change in the material's fundamental chemical composition and mechanical properties. The material you put into the furnace is not the same as the one you take out.
The Solution: Creating a Protective Shield
An inert gas atmosphere works by simple displacement. By flooding the furnace chamber with a non-reactive gas like argon, you physically push out the oxygen and other contaminants.
This creates a neutral environment, or a protective shield, around the workpiece. This shield ensures that the only changes occurring to the material are the ones intended by the heat treatment process itself.
Argon vs. Nitrogen: A Technical Comparison
While other gases can be used to create a furnace atmosphere, the most common alternative to argon is nitrogen. The choice between them hinges on the precise level of inertness your process demands.
The Gold Standard of Inertness
Argon is a noble gas. This means its atomic structure is inherently stable, and it will not react with other elements to form compounds, even under extreme heat and pressure.
This absolute non-reactivity makes it the "gold standard" for processes involving highly sensitive or reactive metals where even minuscule contamination cannot be tolerated.
The Critical Difference: Unwanted Reactions
Nitrogen, while largely inert and more cost-effective, is not a noble gas. At high temperatures, it can react with certain metals, such as titanium, aluminum, and some high-alloy steels.
This reaction forms nitrides on and within the material, which can alter its hardness, brittleness, and other mechanical properties. For many applications, this is an unacceptable outcome. Argon, by contrast, will never form these compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right furnace gas is a balancing act between achieving the required material quality and managing operational realities like cost and safety.
Cost: The Primary Consideration
The most significant drawback of argon is its cost. It is considerably more expensive to produce and procure than nitrogen.
For applications involving less reactive metals or where the absolute highest purity is not the primary driver, nitrogen is often the more economical and perfectly suitable choice.
Safety and Gas Behavior
Both argon and nitrogen are asphyxiants, meaning they displace oxygen and are dangerous in unventilated spaces. However, their physical behavior differs.
Argon is about 38% denser than air. This means it will sink and pool in low-lying areas, creating a serious hazard in pits or basements. Nitrogen has a density similar to air, so it tends to mix more readily throughout a space. Both mandate strict ventilation protocols and oxygen monitoring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material, process requirements, and budget will ultimately determine the optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and performance: Use pure argon, especially for reactive metals (e.g., titanium), critical aerospace parts, or medical implants where no contamination is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for general-purpose heat treating: Nitrogen is the most practical and economical choice for common steels and other less reactive materials.
- If you need a balance of performance and cost: Consider using an argon/hydrogen or argon/nitrogen mixture to achieve the necessary inertness at a more moderate price point.
Selecting the right furnace gas is a strategic decision that directly determines the quality and reliability of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents oxidation and contamination by displacing reactive gases like oxygen. |
| Material Purity | Maintains structural integrity and performance of sensitive materials, such as reactive metals. |
| High-Temperature Protection | Acts as a protective shield to ensure only intended heat treatment changes occur. |
| Comparison to Nitrogen | More inert than nitrogen, avoiding nitride formation in reactive metals like titanium. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost and safety considerations due to density and asphyxiation risks. |
Need precise furnace solutions for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we tailor solutions to meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring optimal performance and purity. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















