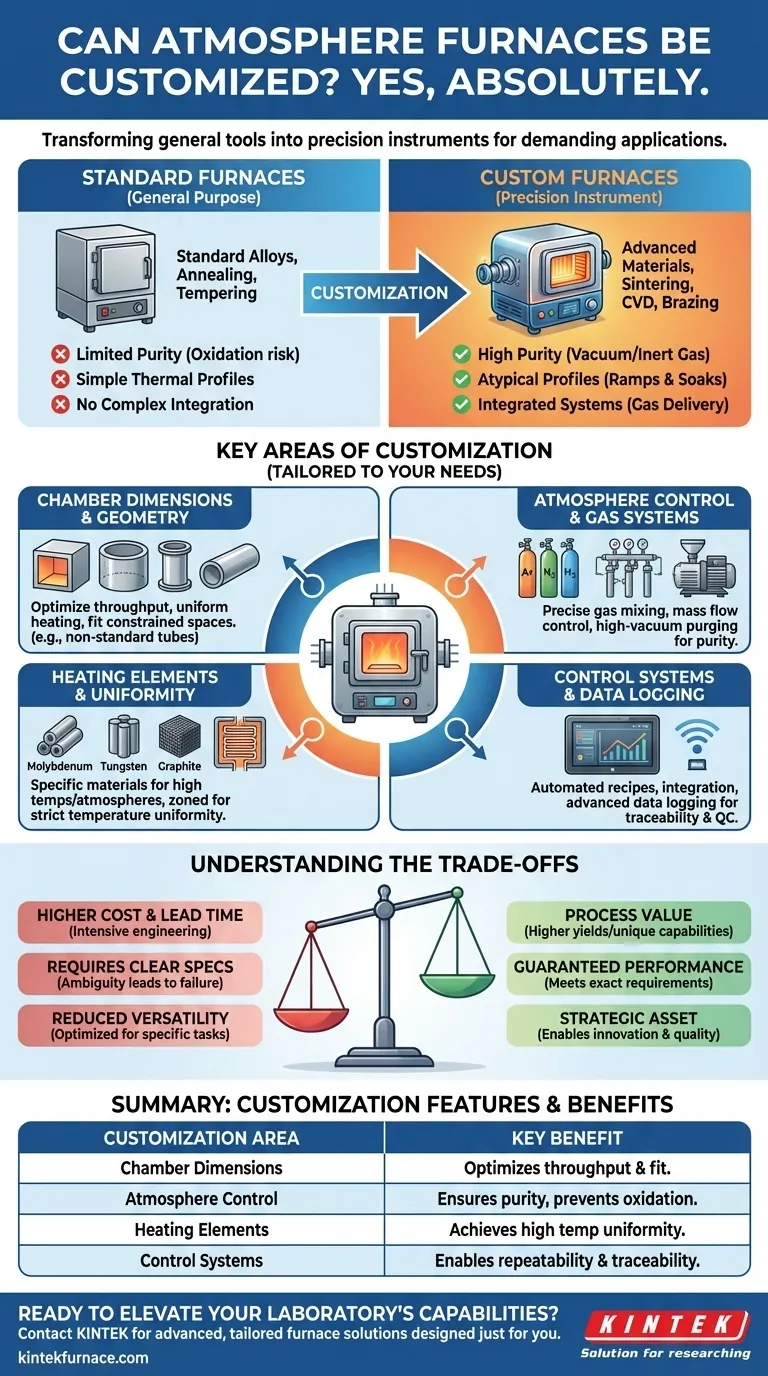
Yes, absolutely. Atmosphere furnaces are not only customizable, but they are frequently engineered for specific, demanding applications. Whether for experimental research with novel materials or high-volume production with unique process requirements, customization transforms a general-purpose tool into a precision instrument tailored to a specific outcome.
The core issue isn't whether furnaces can be customized, but understanding why a specific process demands it. While standard furnaces handle common tasks well, advanced applications require precise control over the chamber environment, thermal profile, and material handling that only a tailored solution can provide.

Why Standard Furnaces Fall Short for Specialized Tasks
A standard, off-the-shelf atmosphere furnace is designed to meet a broad range of common industrial needs like annealing or tempering standard alloys. However, they often lack the specificity required for advanced or sensitive processes.
The Challenge of Material Purity and Reactivity
Many advanced materials, such as titanium alloys, high-temperature alloys, and semiconductors, are highly reactive with oxygen and other atmospheric gases, especially at elevated temperatures.
Even trace amounts of oxygen can cause oxidation, leading to surface discoloration, compromised structural integrity, or failed electronic properties. A custom furnace ensures the required level of atmospheric purity, whether through high-vacuum purging or precise inert gas flow.
Atypical Thermal Profiles and Cycling
Standard furnaces are optimized for common heating and cooling rates. However, processes like sintering advanced ceramics or brazing complex assemblies may require unique, multi-stage thermal profiles with rapid or extremely slow ramps and soaks.
Customization allows for specialized heating elements, insulation packages, and control systems to execute these precise thermal profiles with high repeatability.
Complex Process Integration
Some applications require more than just heat in a controlled atmosphere. For example, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) involves introducing specific precursor gases into the chamber to deposit a thin film onto a substrate.
This requires a highly customized and integrated gas delivery system, exhaust management, and safety interlocks that are not part of a standard furnace design.
Key Areas of Furnace Customization
When you partner with engineers to design a custom furnace, the collaboration focuses on tailoring several critical systems to your exact process needs.
Chamber Dimensions and Geometry
The most basic customization is the furnace chamber's size and shape. This is engineered to maximize throughput for a specific part, ensure uniform heating for an unusual geometry, or simply fit within a constrained laboratory space. Components like alumina ceramic furnace tubes can be built to non-standard lengths and diameters.
Atmosphere Control and Gas Systems
This is the heart of an atmosphere furnace. Customization here includes selecting the number and type of process gases (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen, Hydrogen), designing a manifold for precise mixing, and specifying mass flow controllers for repeatable flow rates. It also involves designing the vacuum system used to purge the chamber before backfilling with the process gas.
Heating Elements and Temperature Uniformity
The maximum temperature and the chemical environment dictate the choice of heating element. Molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite elements may be required for very high temperatures or specific atmospheres where standard Kanthal elements would fail. The placement and zoning of these elements are engineered to ensure strict temperature uniformity across the entire workpiece.
Control Systems and Data Logging
A modern furnace is governed by a sophisticated control system. Customization allows for fully automated process recipes, integration with existing factory control networks, and advanced data logging for process validation and quality control. This is critical for industries that require traceability and certification.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Customization
While powerful, pursuing a custom furnace solution involves important considerations that must be weighed against the potential benefits.
Increased Upfront Cost and Lead Time
A custom-engineered solution will inherently have a higher initial cost and a longer lead time than a standard, in-stock model. The design, engineering, and fabrication process is more intensive. This investment must be justified by the value of the process it enables, such as higher yields or unique product capabilities.
The Critical Role of Clear Specifications
The success of a custom furnace depends entirely on the quality of the process requirements you provide. Ambiguous or incomplete specifications will lead to a furnace that does not perform as needed. You must work closely with the engineers to define temperatures, ramp rates, gas purity, and part handling with absolute clarity.
Potential for Reduced Versatility
A furnace highly optimized for one specific task may be less efficient or even unsuitable for others. For example, a furnace designed for a reactive gas process may have components that are not compatible with a simple air-firing process. This is the classic trade-off between a specialized instrument and a general-purpose tool.
Determining if a Custom Furnace is Your Best Solution
Your decision should be driven by the specific demands of your application and your long-term goals.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A custom build is often necessary to precisely control variables, test novel materials, and explore new process windows.
- If your primary focus is high-value production: Customization is key to ensuring the process repeatability, quality, and traceability required for sensitive applications in aerospace, medical, or electronics.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment: A standard, program-controlled atmosphere furnace will likely provide the necessary capabilities more cost-effectively.
Ultimately, a furnace tailored to your exact needs is not an expense but a strategic asset that enables innovation and guarantees quality.
Summary Table:
| Customization Area | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Dimensions | Tailored size and shape | Optimizes throughput and fit for specific parts |
| Atmosphere Control | Precise gas systems and vacuum purging | Ensures purity and prevents oxidation |
| Heating Elements | Specialized materials and zoning | Achieves high temperature uniformity |
| Control Systems | Automated recipes and data logging | Enables repeatability and traceability |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results with a custom furnace designed just for you!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















