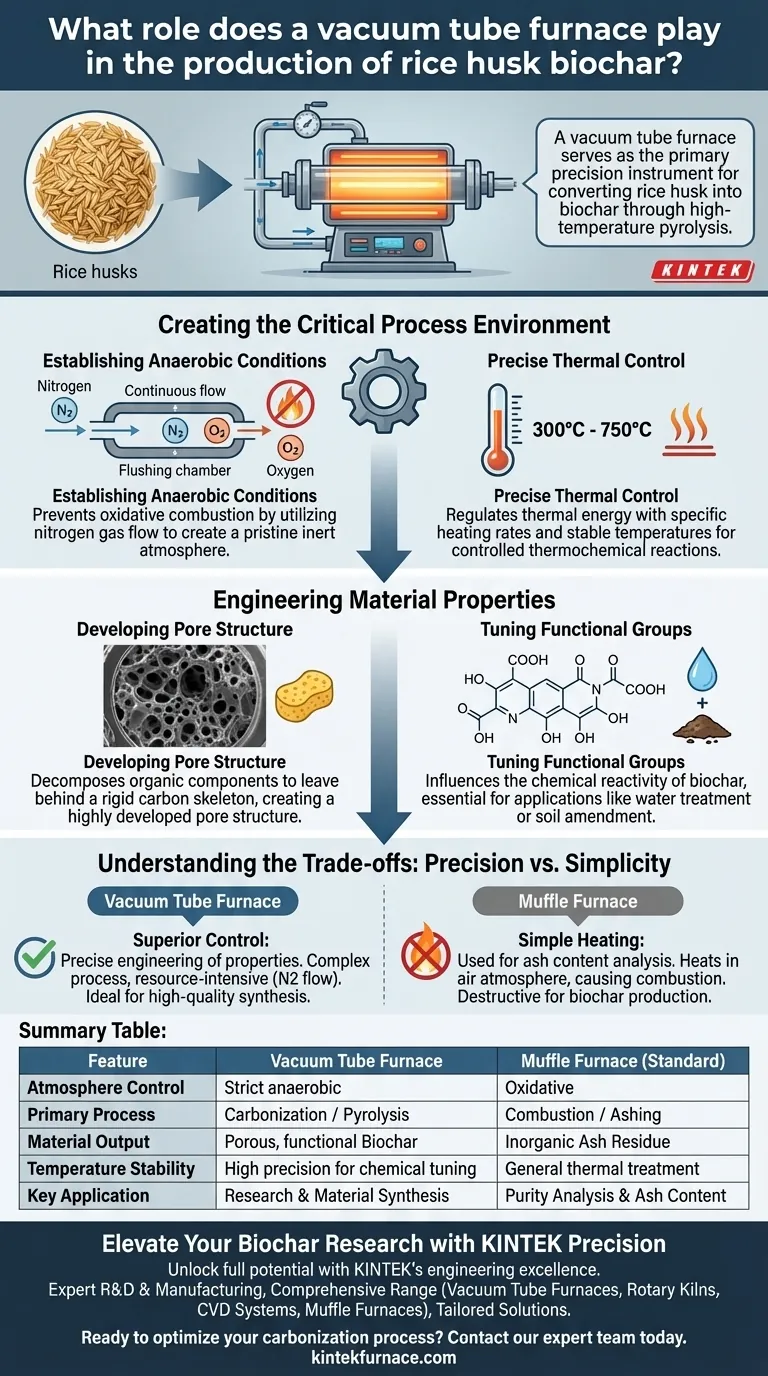
A vacuum tube furnace serves as the primary precision instrument for converting rice husk into biochar through high-temperature pyrolysis. By integrating a sealed heating chamber with a continuous flow of nitrogen gas, it creates and maintains a strictly anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment. This specific physical setup is critical to prevent the rice husk from combusting into ash, ensuring it instead undergoes the carbonization process necessary to form stable biochar.
The core function of the vacuum tube furnace is to facilitate carbonization by completely excluding oxygen. By replacing the atmosphere with inert nitrogen, the furnace enables the precise engineering of the biochar’s internal pore structure and surface chemistry, rather than simply burning the biomass.

Creating the Critical Process Environment
Establishing Anaerobic Conditions
The most vital role of the vacuum tube furnace is the prevention of oxidative combustion.
If rice husk is heated in the presence of air, it burns and leaves behind inorganic ash. The tube furnace utilizes a continuous nitrogen gas flow to flush out oxygen, creating a pristine inert atmosphere.
Precise Thermal Control
Beyond atmospheric control, the furnace provides regulation over the thermal energy applied to the biomass.
It allows operators to set specific heating rates and maintain stable pyrolysis temperatures (often between 300°C and 750°C). This stability is required to drive the specific thermochemical reactions—such as dehydration and decarbonization—without thermal shock or uneven heating.
Engineering Material Properties
Developing Pore Structure
The environment created by the furnace directly dictates the physical architecture of the final product.
Under these controlled conditions, the organic components of the rice husk decompose to leave behind a rigid carbon skeleton. This results in a highly developed pore structure, which is the defining characteristic of effective biochar.
Tuning Functional Groups
The specific "recipe" of temperature and atmosphere influences the chemical reactivity of the biochar.
The vacuum tube furnace allows for the retention or modification of specific surface functional groups. These chemical groups on the biochar surface are essential for its future applications, such as adsorption capabilities in water treatment or soil amendment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precision vs. Simplicity
While a vacuum tube furnace offers superior control, it is more complex than other thermal treatment methods.
For example, a muffle furnace is often used for simple heating or determining ash content. In a muffle furnace, biochar is heated in an air atmosphere to burn off all organic matter, leaving only inorganic residue. This is useful for testing, but destructive for biochar production unless specific "hypoxic" (oxygen-limited) methods—like compressing biomass in foil—are used.
The Cost of Quality
The tube furnace is designed for high-quality synthesis rather than bulk, crude production.
The requirement for continuous high-purity nitrogen flow and precise temperature programming makes the process more resource-intensive. However, this investment is necessary when the goal is to produce biochar with consistent, reproducible scientific properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct thermal treatment equipment, you must define the required properties of your final material.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing high-performance biochar: Use a vacuum tube furnace to ensure strict anaerobic conditions for precise pore and chemical development.
- If your primary focus is analyzing material purity: Use a muffle furnace in an air atmosphere to oxidize organic components and determine the sample's ash content.
The quality of your production environment dictates the quality of your carbon skeleton.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Tube Furnace | Muffle Furnace (Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Strict anaerobic (Inert Gas Flow) | Oxidative (Open Air) |
| Primary Process | Carbonization / Pyrolysis | Combustion / Ashing |
| Material Output | Porous, functional Biochar | Inorganic Ash Residue |
| Temperature Stability | High precision for chemical tuning | General thermal treatment |
| Key Application | Research & Material Synthesis | Purity Analysis & Ash Content |
Elevate Your Biochar Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your materials with the engineering excellence of KINTEK. Whether you are developing high-performance biochar or conducting advanced material synthesis, our thermal solutions provide the precision you need.
Why Choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems are built for consistent, reproducible results.
- Comprehensive Range: From Vacuum Tube Furnaces and Rotary Kilns to CVD Systems and Muffle Furnaces.
- Tailored Solutions: Every lab has unique challenges; we offer fully customizable high-temp systems to meet your specific thermal profiles.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact our expert team today to discuss how our lab furnaces can transform your production quality.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaotong Zhang, Qiuzhuo Zhang. Standardization and micromechanistic study of tetracycline adsorption by biochar. DOI: 10.1007/s42773-023-00299-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in h-BN preparation? Achieve Clean Surface Activation
- How does air annealing in a tube furnace enhance the performance of TiO2 nanorods? Boost Crystallinity and Conductivity
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What are some standard models of tube furnaces and their specifications? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab
- What industries commonly use vertical tube furnaces? Key Applications in Materials Science, Nanotech, and More
- What is the uniform length of a tube furnace? Maximize Thermal Stability for Reliable Results
- What are the differences between solid and split tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What are the key considerations for placing a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety, Accuracy, and Longevity



















