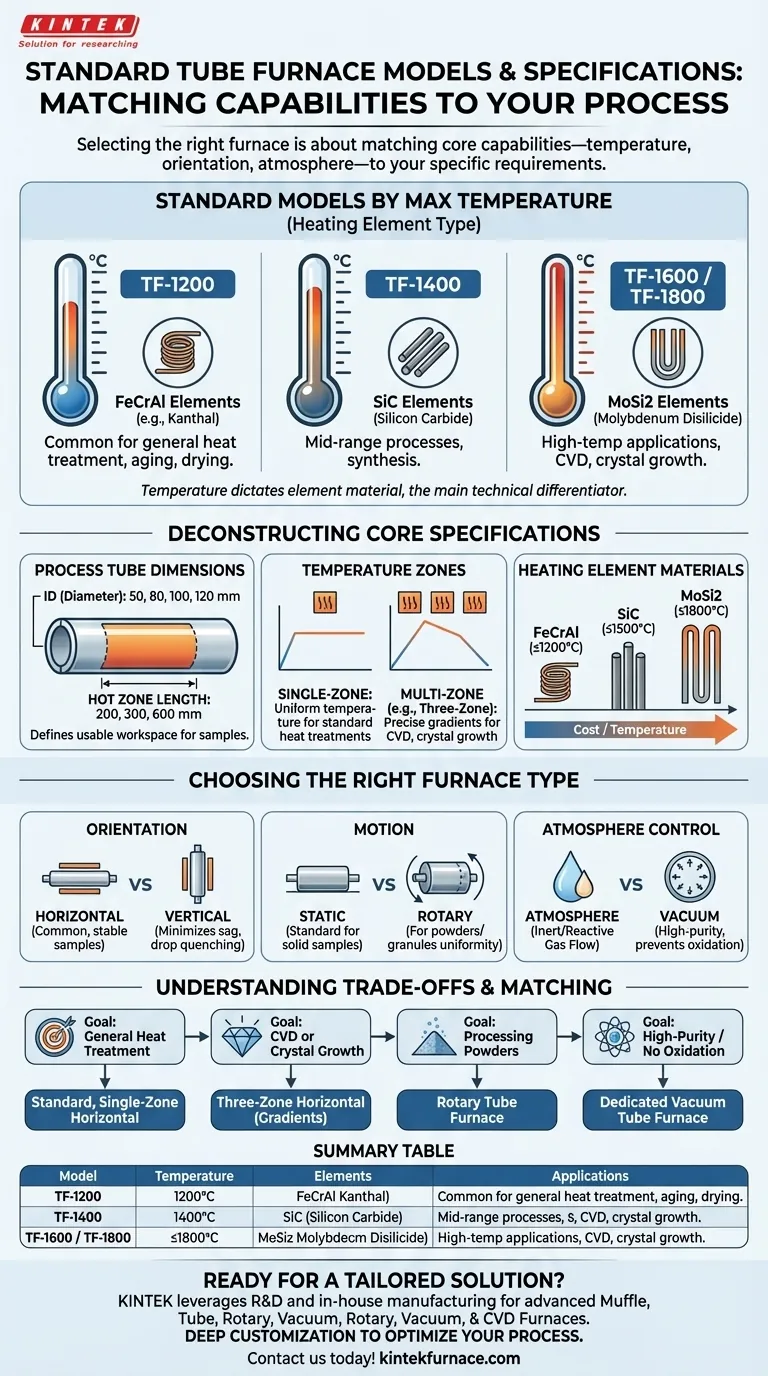
In practice, standard tube furnace models are primarily categorized by their maximum operating temperature, which dictates the type of heating element used. Common models include the TF-1200 (1200°C, FeCrAl elements), TF-1400 (1400°C, SiC elements), and the TF-1600/TF-1800 (1600-1800°C, MoSi2 elements), each available in various tube diameters and heated lengths.
Selecting the right tube furnace is not about choosing a model number. It's about matching the furnace's core capabilities—temperature, physical orientation, and atmospheric control—to the specific requirements of your scientific process or material.

Deconstructing the Core Specifications
A furnace's model number is simply a shorthand for its key performance metrics. Understanding what these metrics mean is the first step to making a sound technical decision.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the single most important specification and the primary cost driver. The temperature you need is determined entirely by your process, such as annealing, synthesis, or purification.
The Role of Heating Elements
The maximum temperature is directly tied to the material used for the heating elements. This is the main technical difference between furnace models.
- FeCrAl (e.g., Kanthal): Used for temperatures up to ~1200°C. These are common and cost-effective for general-purpose heat treatment.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Used for mid-range temperatures up to ~1400-1500°C. They offer a step up for more demanding processes.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): Required for high-temperature applications from ~1600°C to 1800°C. These are the most advanced and expensive elements for standard furnaces.
Process Tube Dimensions (Diameter & Hot Zone)
This defines the usable workspace inside the furnace.
- Tube Diameter (ID): Determines the maximum size of the sample you can place inside. Standard inner diameters (ID) are typically 50, 80, 100, or 120 mm.
- Hot Zone Length: This is the length of the tube that maintains the setpoint temperature with high uniformity. Standard lengths are often 200, 300, or 600 mm. A longer hot zone allows for larger samples or batch processing.
Temperature Zones (Single vs. Multi-Zone)
This specification determines your level of control over the temperature profile along the hot zone.
- Single-Zone: The entire hot zone is controlled by one sensor and aims for a single, uniform temperature. This is suitable for most standard heat treatments like drying or hardening.
- Multi-Zone (e.g., Three-Zone): The furnace has multiple independent heating sections. This allows you to create a precise temperature gradient across the tube, which is critical for advanced processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or specialized crystal growth.
Choosing the Right Furnace Type
Beyond the core specifications, furnaces are configured in different physical forms to suit different processes.
Orientation: Horizontal vs. Vertical
The most basic choice is the furnace's orientation.
- Horizontal: This is the most common configuration. It's easy to load and suitable for a wide range of applications involving stable samples.
- Vertical: Used to minimize the effects of gravity, such as preventing sample sag at high temperatures or for processes like drop quenching.
Motion: Static vs. Rotary
This distinction is based on whether the sample remains stationary or is in motion.
- Static (Standard): The process tube is fixed. This is used for solid samples, wafers, or crucibles.
- Rotary: The process tube slowly rotates. This is essential for processing powders or granules, ensuring every particle is uniformly heated and exposed to the process atmosphere.
Atmosphere Control: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
This determines the environment your sample is processed in.
- Atmosphere Furnace: The most common type, designed to flow inert or reactive gases (like Nitrogen or Argon) through the tube at or near ambient pressure.
- Vacuum Furnace: A specialized type designed to be sealed and evacuated to low pressures. This is crucial for high-purity processes, preventing oxidation, or for specific vacuum-dependent reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every design choice involves a compromise. Being aware of these helps in defining a realistic and cost-effective specification.
Cost vs. Temperature
The relationship is exponential. Moving from a 1200°C furnace to an 1800°C furnace involves not just more expensive heating elements (MoSi2) but also more advanced insulation and power control systems, significantly increasing the overall cost.
Uniformity vs. Hot Zone Length
Achieving high temperature uniformity (e.g., ±1°C) is more challenging and expensive over a longer hot zone. For very large samples, a multi-zone furnace may be required simply to ensure uniformity, even if a gradient isn't needed.
Standard vs. Custom
Standard models offer the best balance of cost and delivery time. Requesting custom dimensions, power requirements, or control systems provides a perfect fit for your process but will invariably increase both the cost and lead time.
Matching the Furnace to Your Application
Use your primary goal to narrow down the options and define your requirements.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment (aging, drying, hardening): A standard, single-zone horizontal furnace with a temperature rating appropriate for your material (e.g., TF-1200) is almost always the most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or crystal growth: A three-zone horizontal furnace is non-negotiable for creating the precise temperature gradients required for deposition and growth.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granules uniformly: A rotary tube furnace is essential to ensure all material is consistently heated and exposed to the process gas.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or preventing oxidation: A dedicated vacuum tube furnace is required to control the atmospheric environment with precision.
By focusing on your process requirements first, the right furnace specifications will become clear.
Summary Table:
| Model | Max Temperature (°C) | Heating Element | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| TF-1200 | 1200 | FeCrAl | General heat treatment, aging, drying |
| TF-1400 | 1400 | SiC | Mid-range processes, synthesis |
| TF-1600/1800 | 1600-1800 | MoSi2 | High-temperature applications, CVD, crystal growth |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a tailored tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and deliver reliable performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















