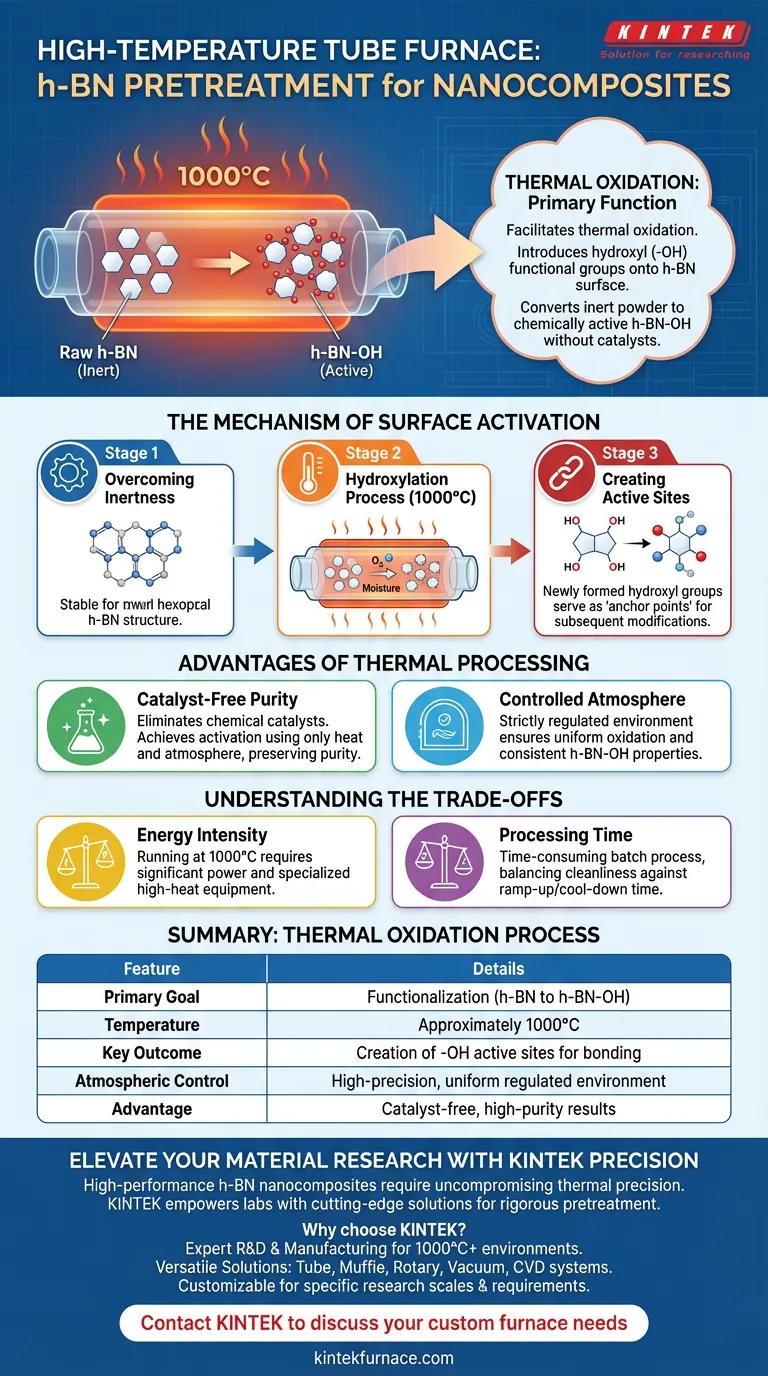
The primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in h-BN pretreatment is to facilitate thermal oxidation. By subjecting raw hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) powder to temperatures of approximately 1000°C, the furnace introduces hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups onto the material's surface. This effectively converts the powder into h-BN-OH, rendering it chemically active without the use of external chemical catalysts.
The furnace acts as a precise activation chamber, transforming the naturally inert surface of h-BN into a reactive state. This thermal hydroxylation is the foundational step that creates the necessary "anchor points" for all subsequent chemical modifications in nanocomposite preparation.

The Mechanism of Surface Activation
Overcoming Chemical Inertness
Raw hexagonal boron nitride is inherently stable and chemically inert. To make it useful for nanocomposites, its surface structure must be altered to interact with other materials.
The high-temperature tube furnace provides the extreme thermal environment needed to break this inertness. It facilitates a reaction that might otherwise require harsh chemicals.
The Hydroxylation Process
The specific goal of this heating phase is functionalization.
By maintaining a controlled atmospheric environment at 1000°C, the furnace promotes the attachment of hydroxyl (-OH) groups to the h-BN lattice. This converts the raw material into h-BN-OH.
Creating Active Sites
These newly formed hydroxyl groups serve as active sites.
Without these sites, the h-BN particles would struggle to bond with other components in a composite matrix. The furnace ensures the material is "primed" for further chemical modification.
Advantages of Thermal Processing
Catalyst-Free Purity
A major advantage of using a tube furnace for this process is the elimination of chemical catalysts.
Many chemical functionalization methods introduce impurities or require complex washing steps to remove catalysts. This thermal method achieves the same result using only heat and atmosphere, preserving the purity of the h-BN.
Controlled Atmospheric Environment
The tube furnace allows for a strictly regulated environment.
Unlike an open-air oven, a tube furnace ensures the oxidation occurs uniformly across the powder. This consistency is vital for ensuring that the h-BN-OH has uniform properties throughout the batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Energy Intensity vs. Chemical Simplicity
While this method avoids chemical catalysts, it is energy-intensive.
Running a furnace at 1000°C requires significant power and specialized equipment capable of sustaining high heat loads safely.
Processing Time
Thermal oxidation is often a time-consuming batch process.
You must balance the benefit of a "cleaner" chemical profile against the operational costs and time required to ramp the furnace up to temperature and cool it down safely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your h-BN pretreatment, consider your specific project requirements:
- If your primary focus is material purity: Rely on the high-temperature furnace method to avoid the contamination risks associated with wet chemical catalysts.
- If your primary focus is downstream reactivity: Ensure the furnace reaches and maintains the full 1000°C threshold, as insufficient heat will result in low hydroxyl density and poor bonding later.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is not just heating the material; it is chemically re-engineering the surface to enable the creation of high-performance nanocomposites.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Oxidation Process Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Functionalization (h-BN to h-BN-OH) |
| Temperature | Approximately 1000°C |
| Key Outcome | Creation of -OH active sites for bonding |
| Atmospheric Control | High-precision, uniform regulated environment |
| Advantage | Catalyst-free, high-purity results |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
High-performance h-BN nanocomposites require uncompromising thermal precision. At KINTEK, we empower labs and manufacturers with cutting-edge high-temperature solutions designed for rigorous pretreatment workflows.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems are engineered for the extreme 1000°C+ environments necessary for catalyst-free hydroxylation.
- Versatile Solutions: Whether you need Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, we provide the tools to ensure uniform surface activation.
- Customizable for Your Needs: We tailor our lab furnaces to meet your specific research scales and atmospheric requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and ensure the highest purity for your advanced material projects.
Visual Guide
References
- Seung Yeon Jang, Seong Yun Kim. Nano‐Interconnected 1D/2D Boron Nitride Hybrid Networks: Unlocking Superior Thermal Conductivity in Electrically Insulating Thermal Interface Nanocomposites Based on Hybrid Thermal Percolation Model. DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202500453
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What features ensure precise temperature control in tube furnaces? Discover the Key Components for Accuracy
- How does a horizontal electric furnace ensure precise thermal control? Achieve Superior Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace serve in the reduction smelting of batteries? Optimize Metal Migration Data
- What is the primary role of a high-temperature tube furnace in Ga2O3 annealing? Optimize Your Thin Film Quality
- What are the main advantages of an atmosphere tube furnace? Achieve Precise Control for Advanced Material Processing
- Why is a tube furnace used for Solid State Polycondensation? Master Molecular Weight Control in SSP
- What are tube furnaces used for? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing & Atmosphere Control
- What role does a high-purity quartz tube furnace play in graphene growth? Achieve Conformal Optical Resonator Coating



















