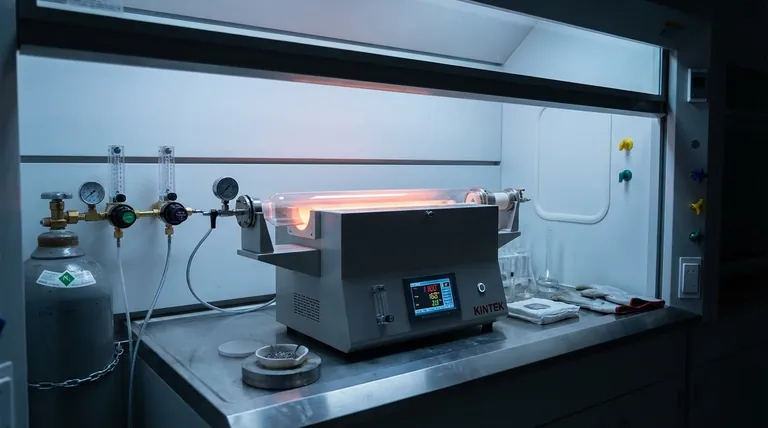
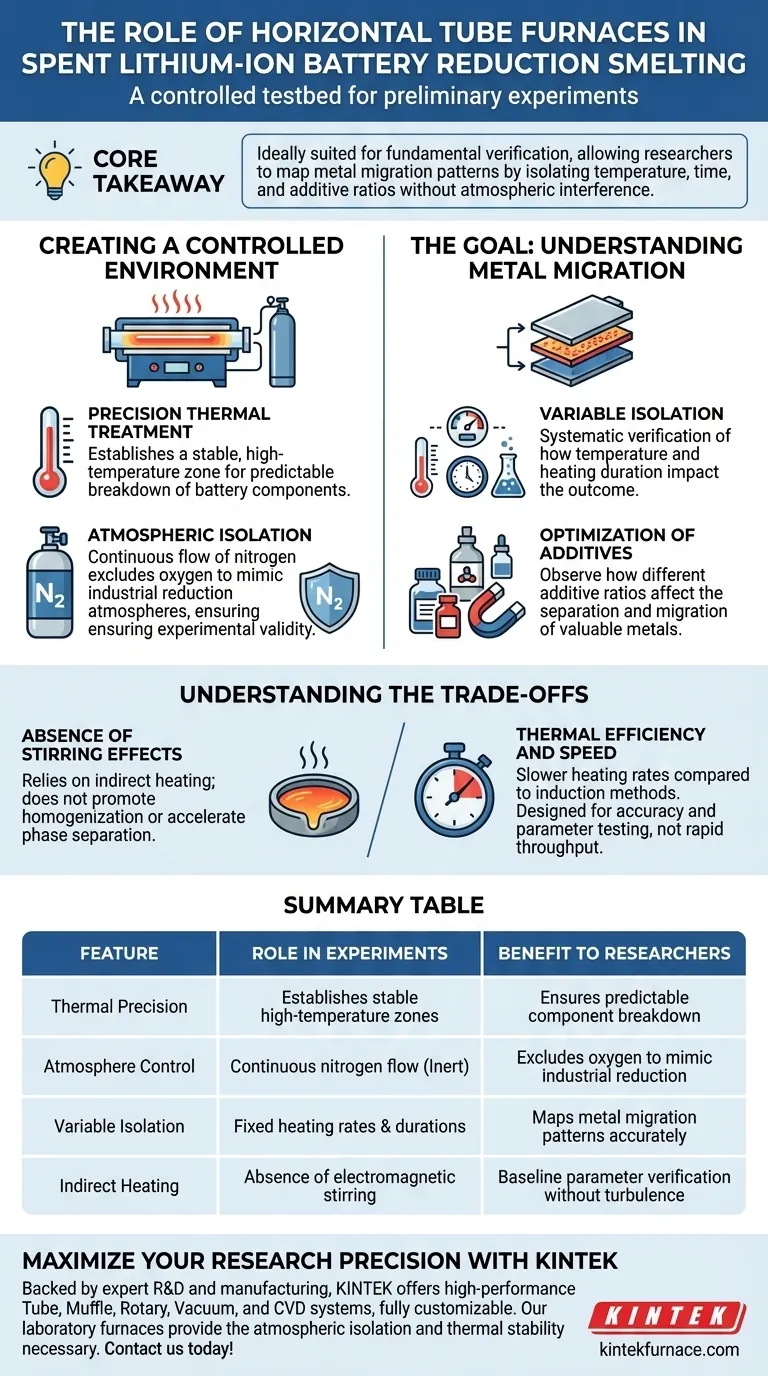
The horizontal tube furnace functions as the primary testbed for preliminary reduction smelting experiments. It provides a strictly controlled thermal environment designed to isolate specific variables during the treatment of spent lithium-ion batteries. By utilizing a continuous flow of nitrogen, it excludes oxygen to accurately simulate industrial reduction atmospheres.
Core Takeaway: Ideally suited for fundamental verification, this apparatus allows researchers to map metal migration patterns by isolating temperature, time, and additive ratios without atmospheric interference.

Creating a Controlled Environment
Precision Thermal Treatment
The horizontal tube furnace acts as the central equipment for establishing a stable, high-temperature zone. This precision is essential for the preliminary thermal treatment required to break down battery components predictably.
Atmospheric Isolation
Oxygen interference can compromise reduction smelting data. By employing a continuous flow of nitrogen, the furnace creates an inert environment. This setup effectively mimics the reduction atmospheres found in industrial processes, ensuring experimental validity.
The Goal: Understanding Metal Migration
Variable Isolation
This equipment allows for the systematic verification of process parameters. Researchers use it to determine exactly how changes in temperature and heating duration impact the outcome of the smelt.
Optimization of Additives
The furnace is critical for testing chemical inputs. It enables researchers to observe how different additive ratios affect the separation and migration of valuable metals within the spent battery material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Absence of Stirring Effects
Unlike induction furnaces, which generate an electromagnetic stirring effect, horizontal tube furnaces rely on indirect heating. This means they do not naturally promote homogenization of the melt or accelerate phase separation through movement.
Thermal Efficiency and Speed
While excellent for controlled stability, the horizontal tube furnace generally has slower heating rates compared to induction methods. It is designed for accuracy and parameter testing rather than the rapid, high-efficiency throughput typical of large-scale production equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your experiments, align your equipment choice with your specific research phase:
- If your primary focus is establishing baseline parameters: Rely on the horizontal tube furnace to isolate variables like temperature and residence time without external interference.
- If your primary focus is studying atmospheric effects: Use this setup to observe metal migration under strict nitrogen protection, verifying the reduction mechanism before scaling up.
The horizontal tube furnace is the definitive tool for converting theoretical reduction concepts into verified experimental data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Battery Smelting Experiments | Benefit to Researchers |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Precision | Establishes stable high-temperature zones | Ensures predictable component breakdown |
| Atmosphere Control | Continuous nitrogen flow (Inert) | Excludes oxygen to mimic industrial reduction |
| Variable Isolation | Fixed heating rates & durations | Maps metal migration patterns accurately |
| Indirect Heating | Absence of electromagnetic stirring | Baseline parameter verification without turbulence |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Are you looking to refine your battery recycling process or establish baseline metal migration data? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific thermal requirements.
Our laboratory furnaces provide the atmospheric isolation and thermal stability necessary to turn theoretical concepts into verified industrial data. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Chen Wang, Hongbin Ling. Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination. DOI: 10.3390/met15070732
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How have tube furnaces evolved over time? From Basic Heating to Precision Control
- How do industrial-grade tube furnaces facilitate the preparation of high-stability perovskites? Enhance Phase Purity
- What are the primary functions of a tube furnace in the thermal pre-treatment research of aluminum alloy powder?
- What special features does the quartz tube furnace have for sample handling? Unlock Visibility and Purity in High-Temp Processes
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for LNMO synthesis? Achieve Precise Fd-3m Spinel Structures
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Key Limits and Application Insights
- What is the role of a three-zone tube furnace in HPHT nanodiamond pretreatment? Unlock Precise Surface Activation
- How do vertical tube furnaces comply with environmental standards? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Operation



















