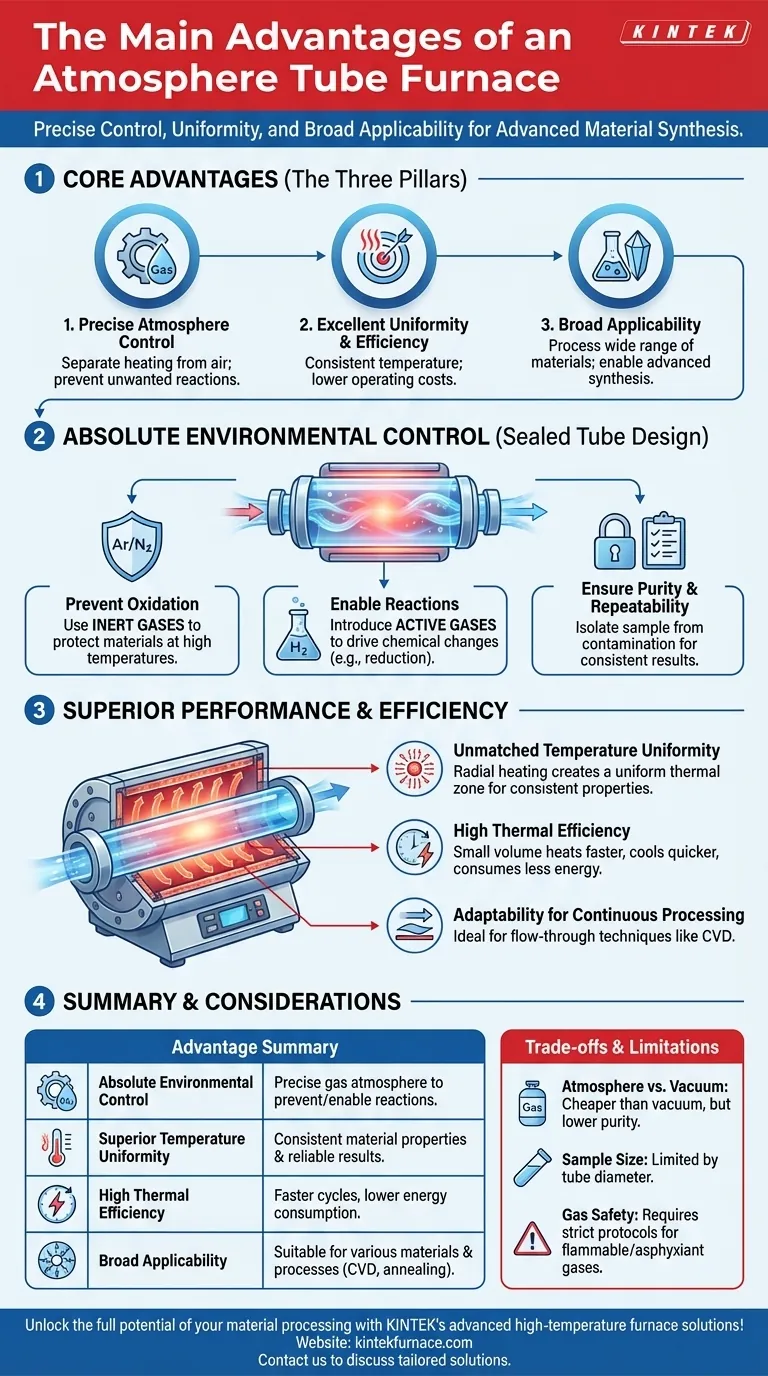
At its core, an atmosphere tube furnace offers three primary advantages: precise and flexible control over the internal atmosphere, excellent temperature uniformity and efficiency, and broad applicability for processing a wide range of materials. These capabilities allow for advanced material synthesis and treatment that would be impossible in a standard furnace that operates in ambient air.
The true value of an atmosphere tube furnace is its ability to separate the heating process from the influence of air. This control over the chemical environment is critical for preventing unwanted reactions like oxidation and enabling specific material transformations.

The Core Advantage: Absolute Environmental Control
The defining feature of this furnace is its sealed tube design, which allows you to completely replace the ambient air with a specific, controlled gas. This unlocks processing capabilities that are essential in modern materials science and engineering.
Preventing Oxidation with Inert Atmospheres
Many advanced materials, especially metals and certain ceramics, will oxidize or degrade when heated in the presence of oxygen.
An atmosphere tube furnace solves this by purging the air and filling the tube with an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This creates a stable environment that protects the material's purity and structural integrity at high temperatures.
Enabling Reactions with Active Atmospheres
Beyond simply creating a protective shield, these furnaces can introduce active or reactive gases to intentionally drive chemical changes.
For example, flowing hydrogen gas can be used to reduce metal oxides back to their pure metallic state. Other gas mixtures, like forming gas (a blend of nitrogen and hydrogen), are used for specific annealing processes.
Ensuring Process Purity and Repeatability
By isolating the sample within a sealed tube, you prevent contamination from external dust, moisture, or airborne particles.
This tight control over both atmosphere and temperature ensures that every processing run is identical, leading to highly consistent and repeatable results—a non-negotiable requirement for both research and industrial production.
Superior Performance and Efficiency
The design of a tube furnace is inherently efficient. The cylindrical heating chamber and focused insulation lead to better performance and lower operating costs compared to larger, less specialized equipment.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The heating elements typically surround the ceramic tube, creating a radially uniform thermal zone.
This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is critical for achieving consistent material properties, whether you are growing crystals, sintering powders, or annealing components.
High Thermal Efficiency
Heating a small, contained volume requires significantly less energy than heating the large chamber of a conventional box furnace.
This results in faster heat-up and cool-down times and lower overall energy consumption, reducing operational costs and improving laboratory or production throughput.
Adaptability for Continuous Processing
The tube design is uniquely suited for continuous or flow-through processes. Gases can be constantly fed in one end and vented out the other, enabling techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) where precursor gases react to form a thin film on a substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an atmosphere tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum: Cost and Purity
Compared to a vacuum furnace, an atmosphere furnace is generally less expensive and simpler to operate.
However, a vacuum furnace can achieve a higher level of purity by removing nearly all gas molecules, which is necessary for applications sensitive to even trace amounts of atmospheric elements. An atmosphere furnace only displaces the air with another gas.
Sample Size and Geometry Limitations
The primary constraint of a tube furnace is the diameter of the tube. This inherently limits the size and shape of the samples that can be processed. Large or irregularly shaped components are better suited for a controlled-atmosphere box or retort furnace.
Gas Handling and Safety Protocols
Operating an atmosphere furnace requires managing compressed gas cylinders and ensuring proper ventilation. Using flammable gases like hydrogen or asphyxiant gases like argon requires strict safety protocols, specialized equipment, and operator training.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or contamination: An atmosphere tube furnace with an inert gas flow is the ideal tool.
- If your primary focus is inducing specific chemical changes (like reduction): The ability to use active gases makes this furnace essential.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment in air with no atmospheric sensitivity: A simpler, more cost-effective muffle or box furnace is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity and outgassing materials: A vacuum furnace is the superior, albeit more complex and expensive, choice.
Ultimately, an atmosphere tube furnace empowers you to precisely control the chemical conditions of your thermal process, making it an indispensable instrument for creating and refining advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Absolute Environmental Control | Sealed tube design allows precise gas atmosphere control to prevent oxidation or enable specific reactions. |
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Radially uniform heating ensures consistent material properties and reliable results. |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Faster heat-up/cool-down times and lower energy consumption reduce operational costs. |
| Broad Applicability | Suitable for various materials and processes like CVD, annealing, and reduction reactions. |
Unlock the full potential of your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with reliable atmosphere tube furnaces, part of our product line that includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering consistent results and enhanced efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can elevate your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















