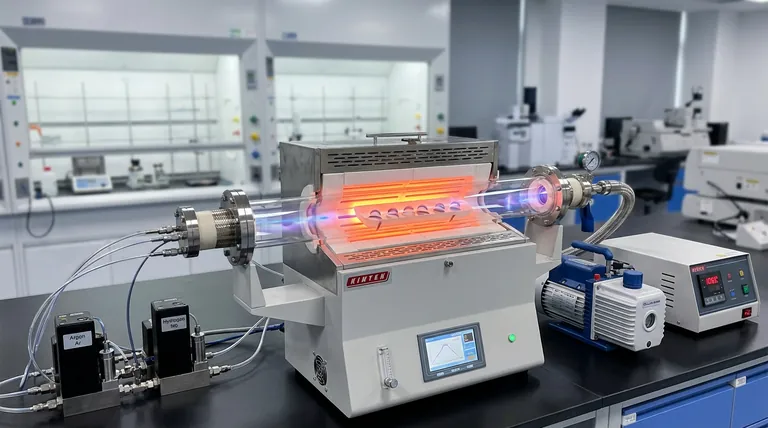
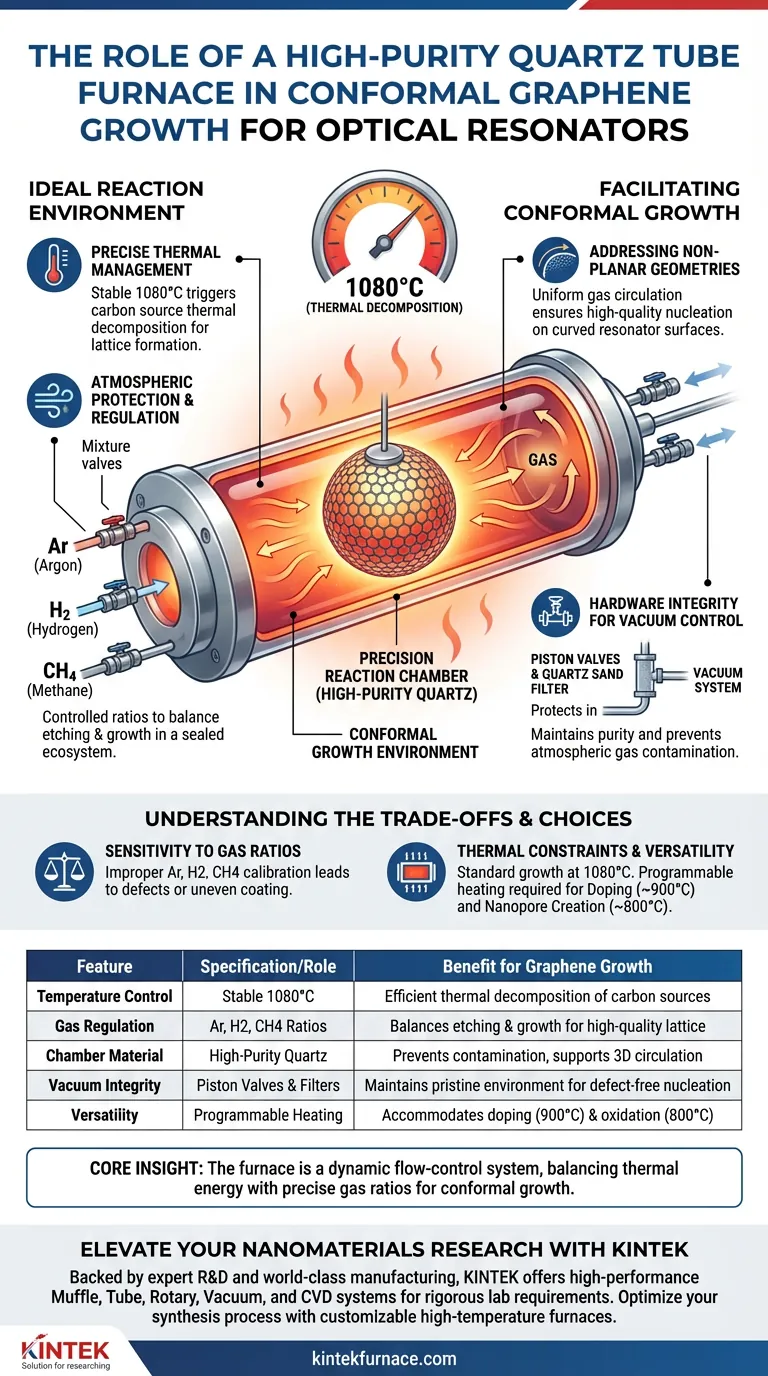
A high-purity quartz tube furnace acts as the precision reaction chamber required to synthesize graphene on complex, non-planar optical components. By maintaining a temperature of approximately 1080°C and strictly regulating gas atmospheres, it facilitates the conformal coating of microsphere resonators via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Core Insight: The furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a dynamic flow-control system. Its primary value lies in balancing thermal energy with precise gas ratios to enable the thermal decomposition of carbon sources, ensuring high-quality graphene nucleation on curved surfaces where standard planar techniques fail.

Creating the Ideal Reaction Environment
Precise Thermal Management
To grow graphene effectively, the furnace must provide a stable high-temperature environment, typically reaching 1080°C.
This specific thermal energy is required to trigger the thermal decomposition of carbon source molecules.
Without this precise heat, the chemical reaction necessary to release carbon atoms for lattice formation cannot occur efficiently.
Atmospheric Protection and Regulation
The furnace creates a sealed ecosystem that protects the reaction from external contaminants.
It precisely regulates the flow ratios of critical gases, specifically Argon (Ar), Hydrogen (H2), and Methane (CH4).
This mixture is controlled within the tube to balance the etching and growth phases of the graphene crystals.
Facilitating Conformal Growth
Addressing Non-Planar Geometries
Unlike standard substrates, optical resonators (such as microspheres) have curved, non-planar surfaces.
The quartz tube furnace facilitates conformal growth by ensuring the gas mixture circulates uniformly around the 3D structure.
This allows for the high-quality nucleation of graphene crystals across the entire surface of the resonator, rather than just on a flat plane.
Hardware Integrity for Vacuum Control
To maintain the purity of the environment, the furnace utilizes specialized hardware like piston valves and grinding mouth structures at the link ports.
A two-way piston at the rear connects to a vacuum system, ensuring the chamber remains free of unwanted atmospheric gases.
Additionally, a quartz sand filter is often positioned between the piston and the vacuum chamber to protect the system and maintain flow integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gas Ratios
While the furnace allows for precise control, the quality of the graphene is heavily dependent on the exact ratios of Ar, H2, and CH4.
Improper calibration of these flow ratios can lead to defects in the crystal lattice or uneven coating on the resonator.
Thermal Constraints
The process relies on maintaining 1080°C for standard growth, but different applications (such as doping) require different thermal profiles.
For example, heteroatom doping may require lower temperatures (around 900°C), meaning the furnace must be capable of versatile, programmable heating rates to accommodate different synthesis goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a quartz tube furnace for your specific application, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Conformal Growth on Resonators: Prioritize a furnace with high thermal stability at 1080°C and precise mass flow controllers for Argon, Hydrogen, and Methane regulation.
- If your primary focus is Graphene Doping: Ensure the furnace supports programmable heating rates to hold lower temperatures (900°C) and manage precursors like nitrogen or phosphorus.
- If your primary focus is Nanopore Creation: Verify the furnace can operate safely with corrosive or reactive atmospheres (like CO2) at temperatures around 800°C to drive controlled oxidation.
Ultimately, the quality of your optical resonator depends on the furnace's ability to maintain a pristine, stable, and chemically balanced vacuum environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification/Role | Benefit for Graphene Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Stable 1080°C | Ensures efficient thermal decomposition of carbon sources |
| Gas Regulation | Ar, H2, CH4 Ratios | Balances etching and growth for high-quality lattice formation |
| Chamber Material | High-Purity Quartz | Prevents contamination and supports 3D gas circulation |
| Vacuum Integrity | Piston Valves & Filters | Maintains a pristine environment for defect-free nucleation |
| Versatility | Programmable Heating | Accommodates doping (900°C) and oxidation (800°C) |
Elevate Your Nanomaterials Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing graphene for advanced optical resonators. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the most rigorous lab requirements. Our customizable high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal stability and atmospheric control necessary for flawless conformal growth and heteroatom doping.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact our technical specialists today to find the perfect customized solution for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Oleksiy Kovalchuk, Yong-Won Song. Non-planar graphene directly synthesized on intracavity optical microresonators for GHz repetition rate mode-locked lasers. DOI: 10.1038/s41699-024-00440-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace? Master nZVI@BC Synthesis with Precision
- What is the role of a three-zone tube furnace in HPHT nanodiamond pretreatment? Unlock Precise Surface Activation
- What is the function of a Tube Furnace in the thermal oxidation of Ti6Al4V alloy? Enhance Hardness & Wear Resistance
- What critical conditions does a tube furnace provide for Cu-Fe-NC-3 pyrolysis? Achieve Precision Catalyst Synthesis
- Why is quartz tube vacuum sealing technology utilized during the synthesis of [Pd@Bi10][AlCl4]4 cluster compounds?
- What is the recommended procedure for using a vacuum tube type experimental furnace with a specific atmosphere? Master Precise Control for Your Experiments
- How does the use of a tube furnace enhance cellulose-amine materials? Unlock Superior Porosity & Surface Area
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature vacuum tube furnace for Gr-NDs? Mastering Carbon Phase Transitions



















