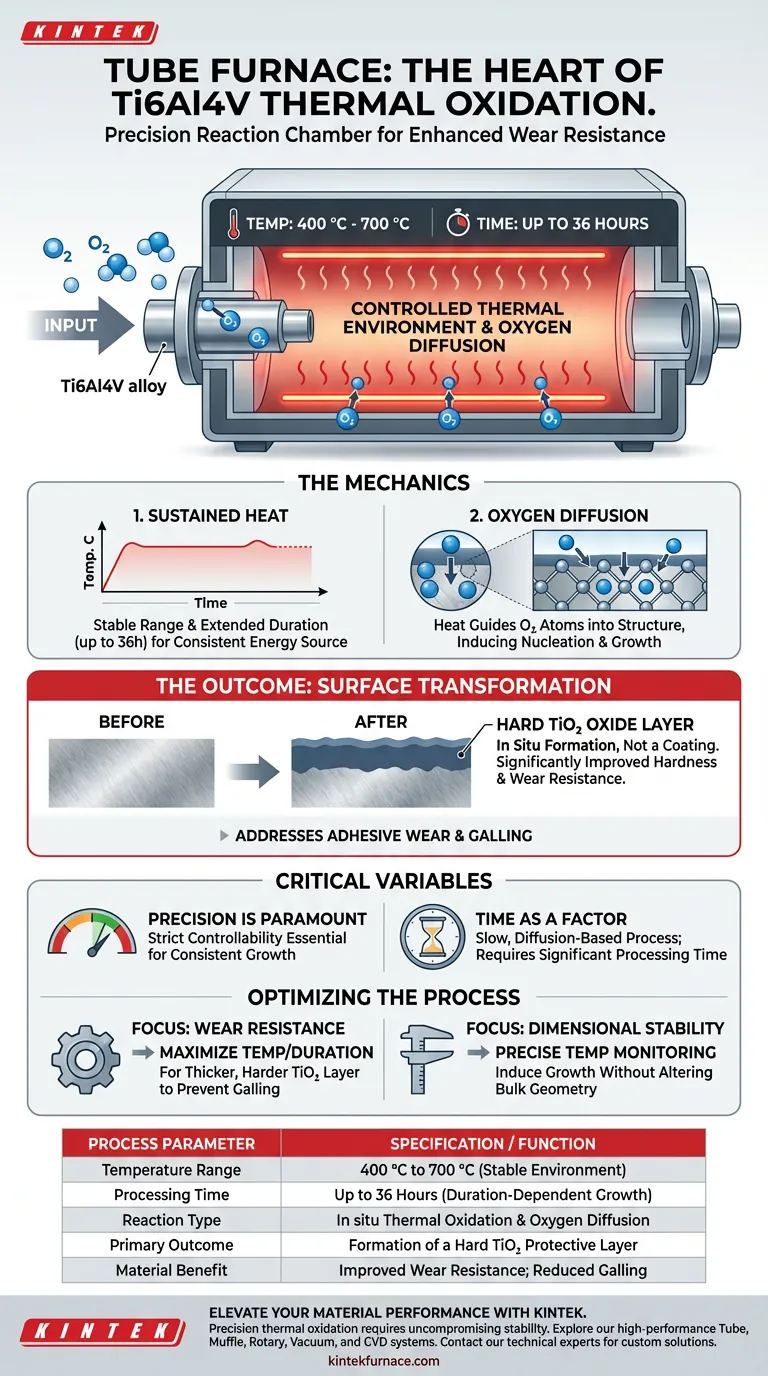
A Tube Furnace serves as the precise reaction chamber required to thermally oxidize Ti6Al4V alloy. It creates a stable, high-temperature environment that facilitates the chemical interaction between oxygen molecules and the titanium surface.
The Tube Furnace provides the sustained heat (400 °C to 700 °C) required to drive oxygen diffusion into the alloy. This process induces the nucleation and growth of a hard TiO2 oxide layer, which acts as a protective shield to significantly enhance the material's wear resistance.
The Mechanics of Thermal Oxidation
Creating a Controlled Thermal Environment
The primary function of the Tube Furnace is to maintain a specific temperature range, typically between 400 °C and 700 °C.
This stability is maintained for extended durations, often reaching up to 36 hours.
This sustained heat is critical because the surface modification is not instantaneous; it requires a prolonged, consistent energy source to facilitate the reaction.
Facilitating Oxygen Diffusion
The furnace environment promotes the thermal reaction between the atmosphere (specifically oxygen) and the titanium alloy surface.
The heat energy guides the diffusion of oxygen atoms into the material structure.
This diffusion is the catalyst for the nucleation and growth of the oxide layer, transforming the surface composition without melting the bulk material.
The Outcome: Surface Transformation
Formation of the TiO2 Layer
Through this controlled heating process, a TiO2 oxide film is grown in situ directly on the surface of the Ti6Al4V alloy.
Unlike an applied coating, this layer is chemically derived from the substrate material itself.
Enhancement of Material Properties
The presence of this oxide layer drastically changes the mechanical characteristics of the alloy's surface.
It significantly improves surface hardness and wear resistance.
This modification effectively addresses common technical failures, such as adhesive wear and galling, which are frequent issues in friction pair applications.
Critical Process Variables
Precision is Paramount
The success of the thermal oxidation process relies heavily on the controllability of the Tube Furnace.
Fluctuations outside the 400 °C to 700 °C range can lead to inconsistent oxide growth or failure to achieve the desired material properties.
Time as a Factor
This is a slow, diffusion-based process rather than a rapid surface treatment.
Operators must account for significant processing time (up to 36 hours) to achieve a sufficiently thick and robust oxide layer.
Optimizing the Process for Your Application
To maximize the benefits of using a Tube Furnace for Ti6Al4V modification, consider your specific performance goals:
- If your primary focus is Wear Resistance: Ensure the furnace maintains the higher end of the temperature spectrum or duration to maximize the thickness and hardness of the TiO2 layer to prevent galling.
- If your primary focus is Dimensional Stability: Monitor the temperature precision closely to induce oxide growth without altering the bulk geometry of the component.
The Tube Furnace is not just a heating element; it is the tool that turns oxygen into a hardening agent for titanium alloys.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Specification / Function |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 400 °C to 700 °C (Stable environment) |
| Processing Time | Up to 36 hours (Duration-dependent growth) |
| Reaction Type | In situ Thermal Oxidation & Oxygen Diffusion |
| Primary Outcome | Formation of a hard TiO2 protective layer |
| Material Benefit | Improved wear resistance; reduced adhesive wear/galling |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precision thermal oxidation of Ti6Al4V requires uncompromising temperature stability and atmospheric control. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of lab and industrial applications. Whether you need a standard setup or a customizable solution tailored to your unique research needs, our high-temp furnaces ensure consistent results every time.
Ready to optimize your alloy treatment process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Qunfeng Zeng, Xunkai Wei. Study on High-Temperature, Ultra-Low Wear Behaviors of Ti6Al4V Alloy with Thermal Oxidation Treatment. DOI: 10.3390/coatings14040416
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is high-purity quartz tube vacuum sealing required for Ag2S1-xTex? Protect Your Semiconductor Synthesis
- What are the drawbacks of induction heating tube furnaces? High Cost, Metal Tubes, and EMI Issues
- What are the process objectives of performing a secondary heat treatment in a tube furnace for Ni/NiO heterostructures?
- What are the specific requirements for quartz tubes used in fixed-bed reactors? Optimize Your CeAlOx/Ni-Foam Performance
- What is a vertical tube furnace and how does it function? Optimize Material Processing with Precision
- What is the key component of a tube furnace and how is it constructed? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What are the core functions of a tube sintering furnace in Fe3C/NC pyrolysis? Master Your Synthesis Process
- What is the primary function of a vacuum quartz tube in CVT? Grow High-Purity Bi4I4 Crystals Successfully



















