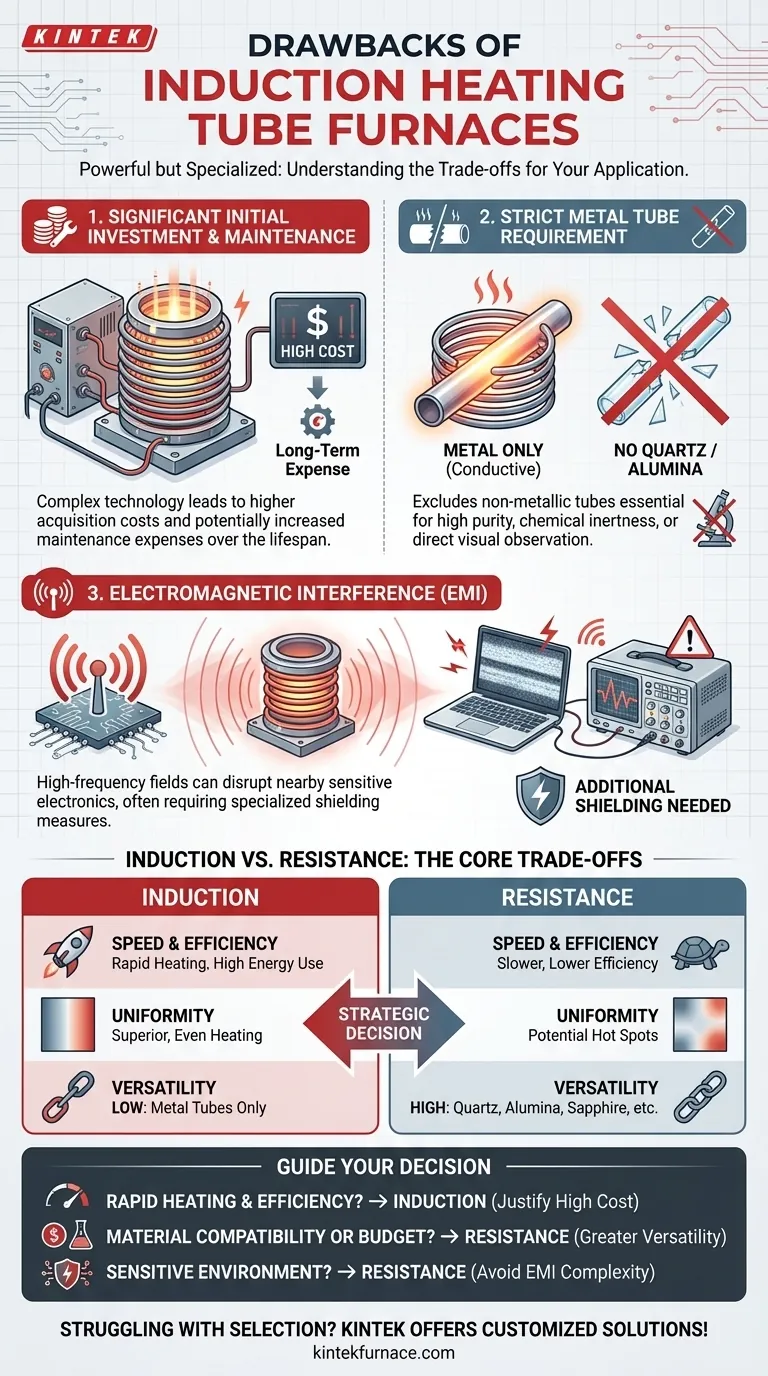
While incredibly powerful, induction heating tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Their primary drawbacks are significant equipment cost, a strict requirement for metallic furnace tubes, and the generation of electromagnetic interference that can disrupt nearby electronics. These factors make them a specialized tool rather than a general-purpose furnace.
Choosing an induction furnace is a strategic decision that trades higher initial cost and material inflexibility for unparalleled heating speed and energy efficiency. Understanding this core trade-off is essential to selecting the right technology for your specific application.

A Closer Look at the Primary Drawbacks
Induction heating offers remarkable performance, but it comes with inherent limitations that must be carefully considered before investment.
Significant Initial Investment and Maintenance
The technology behind induction heating—including high-frequency power supplies and custom-wound coils—is more complex than that of traditional resistance furnaces. This complexity translates directly into higher initial acquisition costs.
Furthermore, the specialized components can lead to increased maintenance expenses over the furnace's lifespan.
The Metal Tube Requirement
Induction heating works by inducing an electric current directly within a conductive material. This means the furnace tube itself must be made of metal to generate heat.
This requirement immediately excludes the use of non-metallic tubes like quartz or alumina. These materials are often essential for experiments requiring high purity, specific chemical inertness, or direct visual observation, making induction furnaces unsuitable for such applications.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
The high-frequency electromagnetic fields that generate the heat do not remain perfectly contained. These fields can radiate outward, creating electromagnetic interference (EMI).
EMI can disrupt or damage sensitive electronic equipment common in laboratory and industrial settings. Consequently, implementing an induction furnace often requires additional investment in specialized shielding measures to protect nearby devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Induction vs. Resistance Heating
The drawbacks of induction heating are best understood when compared to the most common alternative: resistance heating tube furnaces. The choice between them is a classic engineering trade-off.
Speed and Efficiency: The Core Advantage of Induction
Induction furnaces offer exceptionally fast heating rates. Heat is generated directly within the furnace tube wall, allowing it to reach target temperatures very quickly. This is a critical advantage for processes like rapid thermal pyrolysis.
Because only the metal tube and the sample are heated, energy utilization is very high, with minimal heat lost to the environment. In contrast, resistance furnaces are slower and have lower thermal efficiency, as heat must radiate from external elements and dissipates into the surroundings.
Temperature Uniformity: A Key Differentiator
Induction heating generally provides superior temperature uniformity compared to resistance heating. The heat is generated evenly across the entire surface of the metal tube subjected to the induction coil.
While the physical design (e.g., a long horizontal tube) can still introduce minor temperature variations, induction inherently avoids the localized "hot spots" common with resistance coil elements, leading to more reliable and repeatable results.
Material Versatility: The Advantage of Resistance
The primary advantage of a resistance furnace is its material flexibility. Since the heat source is external to the process tube, you can use tubes made from a wide variety of materials, including quartz, alumina, and sapphire.
This makes resistance furnaces the default choice for applications that are incompatible with a metallic environment.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your decision should be guided by the non-negotiable requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and energy efficiency: The performance benefits of an induction furnace in speed and reduced operational cost will likely justify the high initial investment.
- If your primary focus is material compatibility or a limited budget: A resistance furnace offers greater versatility with quartz or ceramic tubes and is a much more cost-effective solution upfront.
- If your primary focus is operating in a sensitive electronic environment: A resistance furnace is the simpler choice, as it avoids the cost and complexity of mitigating electromagnetic interference.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one whose strengths align with your priorities and whose weaknesses do not compromise your results.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Initial Cost | Complex technology leads to expensive equipment and maintenance. | Increases budget requirements and long-term expenses. |
| Metal Tube Requirement | Tubes must be metallic, excluding quartz or alumina options. | Limits material compatibility and purity in experiments. |
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) | Radiated fields can disrupt nearby sensitive electronics. | Requires additional shielding and complicates lab setup. |
Struggling with furnace selection for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're dealing with material compatibility, budget constraints, or EMI concerns, we can help you choose or customize the ideal furnace. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















