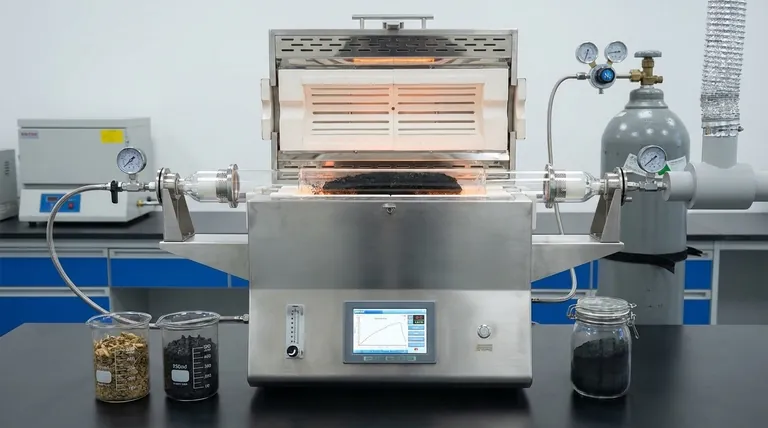
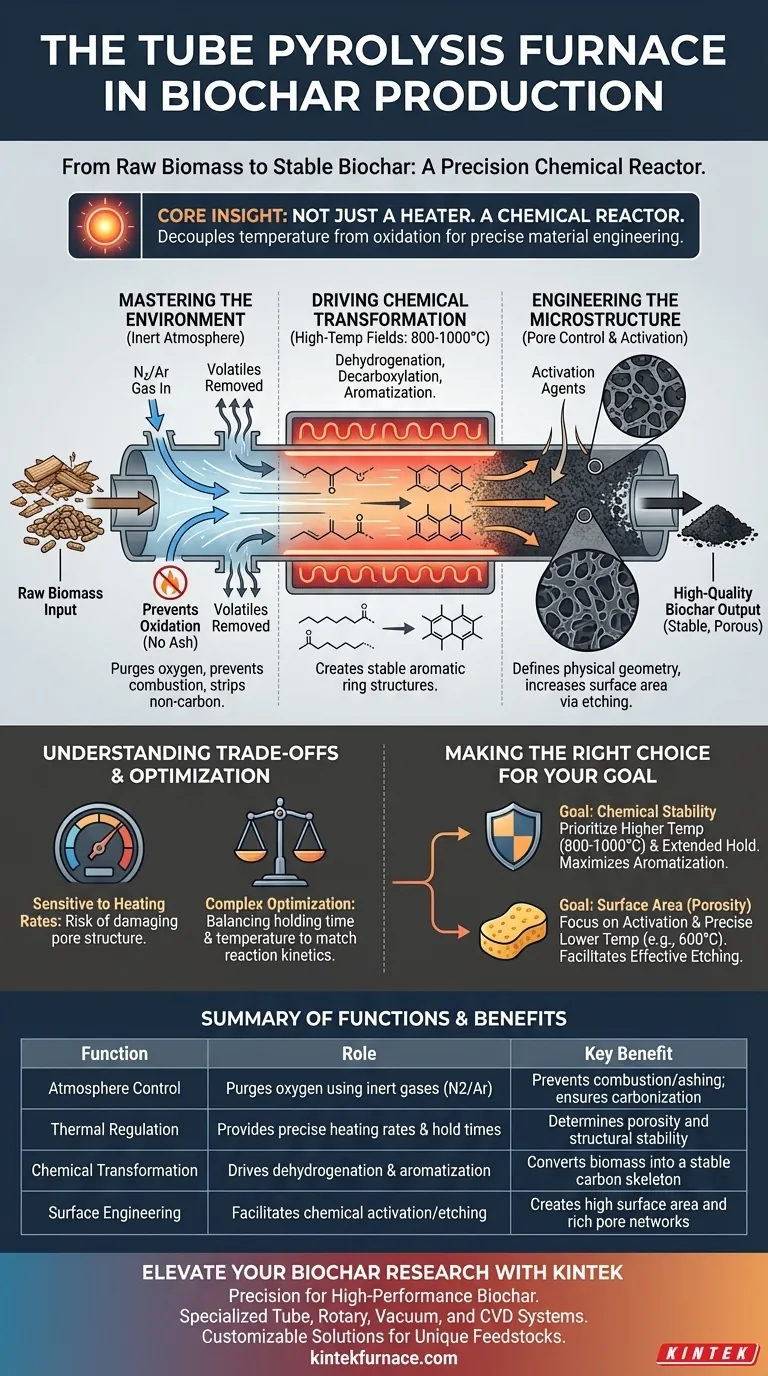
A tube pyrolysis furnace serves as the precision reaction chamber for converting raw biomass into stable biochar. It creates a strictly controlled, high-temperature environment that excludes oxygen—typically using a nitrogen atmosphere—to ensure biomass undergoes thermal decomposition rather than combustion. By regulating heating rates and holding times, the furnace drives specific chemical changes that determine the final porosity and stability of the carbon material.
Core Insight: The furnace is not merely a heater; it is a chemical reactor. Its primary value lies in decoupling temperature from oxidation, allowing you to engineer specific material properties through precise thermal profiling rather than simple burning.

Mastering the Reaction Environment
To produce high-quality biochar, you must strictly control the atmosphere surrounding the biomass. The tube furnace acts as a barrier between the sample and the outside world.
Preventing Oxidation
The fundamental role of the furnace is to maintain an inert atmosphere.
By pumping in nitrogen (or argon in specific industrial applications), the furnace purges oxygen from the chamber.
This prevents the biomass from turning into ash, allowing it to carbonize effectively.
Removing Volatile Components
During the pre-carbonization stage, the furnace creates the conditions necessary to strip away non-carbon elements.
As the temperature rises, volatile components are released and removed from the biomass matrix.
This leaves behind a concentrated carbon skeleton, ready for further structural refinement.
Driving Chemical Transformation
The tube furnace provides the high-temperature fields—often reaching 800°C or 1000°C—required to alter the chemical makeup of the biomass.
Essential Chemical Reactions
Mere drying is not enough; the biomass must undergo complex molecular changes.
The furnace facilitates dehydrogenation, decarboxylation, and aromatization.
These reactions strip away hydrogen and oxygen while rearranging the remaining carbon atoms into stable, aromatic ring structures.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
The precise control of the heat ensures these reactions complete fully.
This results in a carbonaceous material with high chemical stability, making the biochar durable and resistant to degradation.
Engineering the Microstructure
Beyond chemistry, the furnace plays a critical role in defining the physical geometry of the biochar.
Controlling Pore Structure
The "recipe" of heating rates and holding times dictates the final texture of the material.
By managing these variables, the furnace ensures the development of specific pore structures.
Facilitating Activation
In advanced applications, the furnace creates the environment for chemical activation.
It maintains precise temperatures (e.g., 600°C) that allow activators to react with the carbon matrix.
This process "etches" the surface, significantly increasing the surface area and creating a rich network of pores.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a tube pyrolysis furnace offers superior control, it requires a rigorous approach to process parameters.
Sensitivity to Heating Rates
The quality of the biochar is highly sensitive to how fast the temperature rises.
If the heating rate is not accurately controlled, you risk damaging the pore structure or failing to achieve the desired degree of aromatization.
Complexity of Optimization
Achieving the perfect balance between holding time and temperature is complex.
You cannot simply maximize heat; you must tune the furnace to the specific "kinetics" of the reaction you wish to sustain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a tube pyrolysis furnace, align your thermal protocol with your end-product requirements.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Stability: Prioritize higher temperatures (800°C–1000°C) and extended holding times to maximize aromatization and carbon density.
- If your primary focus is Surface Area (Porosity): Focus on the activation stage parameters and precise lower-temperature holds (e.g., 600°C) to facilitate effective etching of the carbon matrix.
Success in biochar production ultimately depends on using the furnace not just to heat your material, but to carefully orchestrate its molecular evolution.
Summary Table:
| Function | Role in Biochar Production | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Purges oxygen using inert gases (N2/Ar) | Prevents combustion/ashing; ensures carbonization |
| Thermal Regulation | Provides precise heating rates & hold times | Determines porosity and structural stability |
| Chemical Transformation | Drives dehydrogenation & aromatization | Converts biomass into a stable carbon skeleton |
| Surface Engineering | Facilitates chemical activation/etching | Creates high surface area and rich pore networks |
Elevate Your Biochar Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between simple ash and high-performance biochar. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to give you absolute control over your thermal profiles.
Whether you need a standard setup or a customizable solution for unique biomass feedstocks, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the stability and inert environments essential for advanced material engineering.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process?
Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Ganesh Zade, Malhari Kulkarni. Development of Biochar-Based Sustainable Corrosion-Resistant Coating. DOI: 10.3390/engproc2025105005
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of vacuum tube furnaces based on? Key Classifications for Your Lab
- What are the technical specifications of a Drop Tube Furnace? Optimize Your High-Temperature Conversion Experiments
- Why is an industrial tube furnace required for the heat treatment of SiCN(Ni)/BN ceramics? Master Precise Pyrolysis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in the annealing of low carbon steel? Precision Heat for Nanocomposites
- What is the application of a high-temperature tube resistance furnace in studying HEA coatings? | KINTEK
- What is the significance of expanding raw material applicability in tube furnaces? Unlock Versatility and Cost Savings
- What makes fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces environmentally friendly? Discover Efficient Green Tech Solutions
- What features ensure precise temperature control in tube furnaces? Discover the Key Components for Accuracy



















