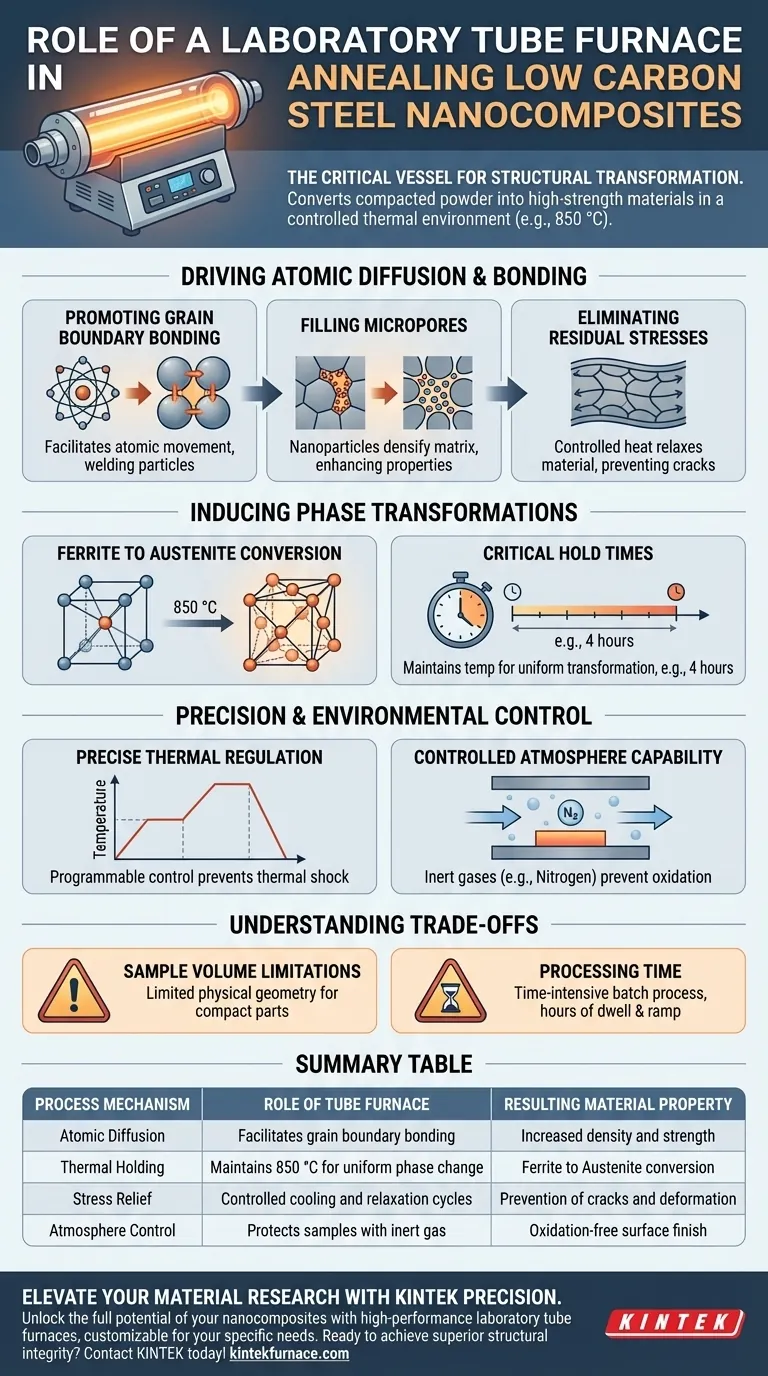
A laboratory tube furnace functions as the critical vessel for structural transformation. It provides a highly controlled thermal environment that converts compacted powder samples into solid, high-strength materials. Specifically, for low carbon steel nanocomposites, it maintains precise high temperatures—such as 850 °C—to drive the atomic mechanisms necessary for sintering and strengthening.
The furnace does more than simply heat the material; it orchestrates atomic diffusion and phase changes. By maintaining a stable thermal environment, it eliminates processing stresses and bonds particles at the granular level, directly dictating the final mechanical integrity of the nanocomposite.

Driving Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
The primary role of the tube furnace is to facilitate the transition from a pressed powder state to a unified solid.
Promoting Grain Boundary Bonding
At high temperatures, the furnace promotes atomic diffusion. This allows atoms to move across the boundaries of the powder particles, effectively welding them together.
Filling Micropores
During this thermal hold, nanoparticles within the composite matrix become active. They fill the micropores between the steel particles, densifying the material and significantly enhancing its ultimate mechanical properties.
Eliminating Residual Stresses
The pressing stage used to create the initial sample shape creates significant internal stress. The controlled heat of the annealing process relaxes the material, eliminating these residual stresses to prevent future cracking or deformation.
Inducing Phase Transformations
Beyond bonding, the tube furnace acts as a catalyst for changing the fundamental crystal structure of the steel.
Ferrite to Austenite Conversion
By maintaining a specific temperature (e.g., 850 °C), the furnace induces a phase transformation. The low carbon steel matrix shifts from a ferrite structure to an austenite structure.
Critical Hold Times
This transformation is not instantaneous. The furnace must maintain this temperature for an extended period, often around four hours, to ensure the transformation is uniform throughout the sample.
Precision and Environmental Control
While the primary mechanism is heat, the quality of that heat is why a tube furnace is selected over other heating methods.
Precise Thermal Regulation
Tube furnaces offer programmable temperature control. This allows for specific heating ramps and hold times, ensuring the sample does not experience thermal shock or uneven heating.
Controlled Atmosphere Capability
Although the annealing of steel focuses on heat, the tube furnace's design allows for the introduction of inert gases, such as nitrogen. This creates a controlled atmosphere that protects the sample from unwanted oxidation during the long heating cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for high-quality nanocomposites, the use of a laboratory tube furnace presents specific constraints.
Sample Volume Limitations
Tube furnaces are designed for compact samples. The physical geometry of the tube limits the size and quantity of nanocomposite parts that can be processed simultaneously.
Processing Time
The process is time-intensive. Achieving full atomic diffusion and phase transformation requires hours of dwell time (e.g., four hours) plus ramping time, making it a batch process rather than a continuous one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your annealing process for low carbon steel nanocomposites, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Ensure the furnace temperature is high enough (850 °C) to maximize grain boundary bonding and allow nanoparticles to fill micropores effectively.
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Prioritize the duration of the hold time (e.g., 4 hours) to guarantee a complete phase transformation from ferrite to austenite throughout the entire matrix.
Ultimately, the laboratory tube furnace is the bridge that transforms a fragile, pressed powder compact into a robust, high-performance nanocomposite.
Summary Table:
| Process Mechanism | Role of Tube Furnace | Resulting Material Property |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Diffusion | Facilitates grain boundary bonding at high temps | Increased density and strength |
| Thermal Holding | Maintains 850 °C for uniform phase change | Ferrite to Austenite conversion |
| Stress Relief | Controlled cooling and relaxation cycles | Prevention of cracks and deformation |
| Atmosphere Control | Protects samples with inert gas (e.g., Nitrogen) | Oxidation-free surface finish |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your low carbon steel nanocomposites with KINTEK’s high-performance laboratory tube furnaces. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide customizable Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your specific temperature ramps and atmosphere requirements.
Whether you need to optimize grain boundary bonding or ensure uniform phase transformations, our engineering team is ready to design the perfect thermal solution for your lab.
Ready to achieve superior structural integrity? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Abbas Ali Diwan, Mohammed J. Alshukri. Characterization of the mechanical properties for mild steel alloyed reinforcement with nanomaterials using powder technology. DOI: 10.1007/s43939-025-00280-0
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab Needs
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is the purpose of pre-treating quartz tube reactors? Achieve High-Purity CVT Crystal Growth with Precision
- How do split tube furnaces provide access to the chamber? Unlock Easy Sample Handling for Your Lab
- What industries commonly use High Temperature Tube Furnaces? Essential for Material Science, Electronics, and More
- What task is performed by industrial high-temperature tube or atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Carbon Aerogel Synthesis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace combustion system function in food waste analysis? Master Ultimate Analysis
- How do horizontal furnaces support the ceramics industry? Boost Performance with Precision Heat Treatment



















