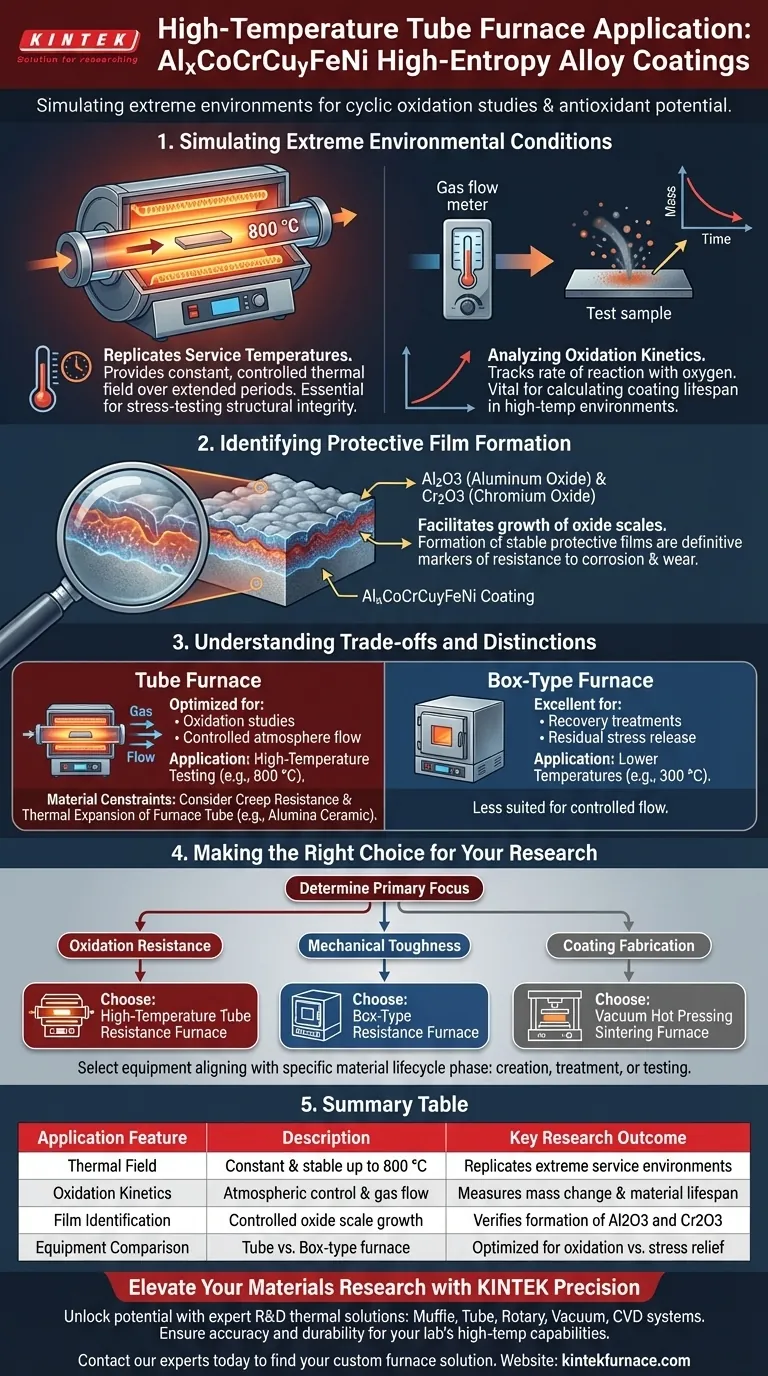
In the study of AlxCoCrCuyFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings, the high-temperature tube resistance furnace serves as a critical simulation tool for replicating extreme service environments. Its primary application is to provide a constant, controlled thermal field for cyclic oxidation experiments, enabling researchers to quantify how the material withstands degradation at temperatures as high as 800 °C.
The core value of this equipment lies in its ability to reveal the material's antioxidant potential. By subjecting coatings to precise thermal cycling, researchers can track oxidation kinetics and verify the formation of essential protective films, which are the primary indicators of a coating's long-term durability.

Simulating Extreme Environmental Conditions
Replicating Service Temperatures
The tube resistance furnace is designed to maintain a constant thermal field over extended periods.
This stability allows researchers to expose the alloy coatings to the exact temperatures they would face in real-world applications.
For example, experiments are frequently conducted at 800 °C to stress-test the material's structural integrity under heat.
Analyzing Oxidation Kinetics
A key application of this furnace is the study of oxidation kinetics, which measures the rate at which the material reacts with oxygen.
By controlling the temperature and environment within the tube, scientists can record how mass changes over time.
This data is vital for calculating the lifespan of the coating in high-temperature environments.
Identifying Protective Film Formation
The furnace environment facilitates the growth of oxide scales on the coating surface.
Researchers use these experiments to observe the formation of protective phases, specifically Al2O3 (aluminum oxide) and Cr2O3 (chromium oxide).
The presence and stability of these films are the definitive markers of a high-entropy alloy's resistance to corrosion and wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
Specificity of Furnace Type
It is crucial to distinguish the tube furnace from other laboratory thermal equipment.
While a box-type resistance furnace is excellent for recovery treatments and releasing residual stresses at lower temperatures (e.g., 300 °C), it is less suited for controlled atmosphere flow.
The tube furnace is specifically optimized for oxidation studies where gas flow and atmospheric control are necessary variables.
Material Constraints of the Equipment
The performance of the furnace relies heavily on the quality of its components, particularly the furnace tube (often alumina ceramic).
One must evaluate the creep resistance of the tube to ensure it does not deform under prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Additionally, the thermal expansion coefficient of the tube must be compatible with the sample holder to prevent mechanical failure during heating cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To select the appropriate thermal processing method for your high-entropy alloy project, consider your specific analytical goals:
- If your primary focus is Oxidation Resistance: Utilize a high-temperature tube resistance furnace to simulate service conditions and analyze the formation of protective Al2O3 and Cr2O3 films.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Toughness: Choose a box-type resistance furnace to perform recovery treatments at lower temperatures for residual stress release and grain refinement.
- If your primary focus is Coating Fabrication: Employ a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace to achieve densification and strong metallurgical bonding through combined heat and pressure.
Select the equipment that aligns with the specific phase of the material lifecycle you are investigating, whether it is creation, treatment, or environmental testing.
Summary Table:
| Application Feature | Description | Key Research Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Field | Constant & stable up to 800 °C | Replicates extreme service environments |
| Oxidation Kinetics | Atmospheric control & gas flow | Measures mass change & material lifespan |
| Film Identification | Controlled oxide scale growth | Verifies formation of Al2O3 and Cr2O3 |
| Equipment Comparison | Tube vs. Box-type furnace | Optimized for oxidation vs. stress relief |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your high-entropy alloy studies with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all precision-engineered to provide the stable thermal fields required for critical oxidation and sintering experiments.
Whether you need to simulate extreme 800 °C environments or require customizable laboratory high-temp furnaces for unique material specifications, our equipment ensures accuracy and durability for global researchers and manufacturers.
Ready to optimize your lab’s high-temperature capabilities? Contact our experts today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Ling Zhou, Yueyi Wang. Effect of Al/Cu Ratio on Microstructure and High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of AlxCoCrCuyFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. DOI: 10.3390/jmmp9010013
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is environmental control in a high-temperature tube furnace necessary during NVP/C synthesis? Key to Success
- Why is a tantalum tube encapsulated in a vacuum quartz tube? Prevent Oxidation & Embrittlement in High-Temp Calcination
- How is a Pulse Ignition device used for coal cloud explosions? Master MAIT Testing with Godbert-Greenwald Furnaces
- Why is a tube furnace with precise temperature control required for CuSbSe2 thin films? Achieve High Phase Purity
- What function does the annealing treatment in a high-temperature quartz-tube furnace serve? Optimizing Glass Ceramics
- What is the technical significance of a horizontal tube furnace with a sliding rail for NiOx annealing? Enhance Control
- How does a tube furnace facilitate the activation of xylan-derived carbon spheres? Precision Surface Engineering
- How do sealed flanges improve oxygen annealing for superconducting joints? Enhance Purity and Precision



















