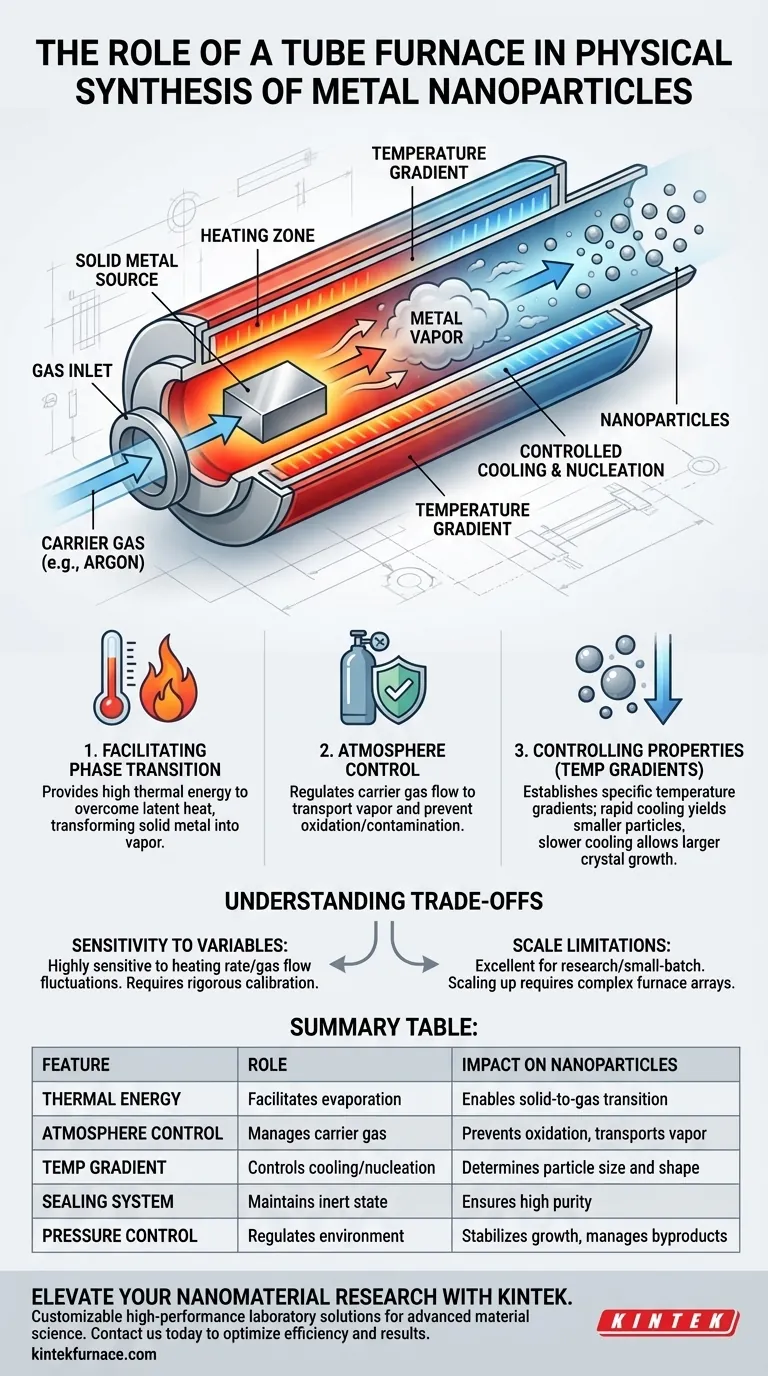
In the realm of physical nanoparticle synthesis, particularly the physical vapor condensation method, the tube furnace acts as the central thermal reactor that drives phase transformation. Its primary function is to generate a controlled, high-temperature environment that forces the solid source metal to evaporate into a gas phase within a regulated carrier gas atmosphere.
The tube furnace enables the transition from bulk metal to nanoparticle by creating precise thermal zones for evaporation and condensation. Its ability to maintain specific temperature gradients directly dictates the size, shape, and yield of the final nanomaterial.

The Mechanism of Physical Synthesis
Facilitating Phase Transition
The fundamental role of the tube furnace is to provide enough thermal energy to overcome the latent heat of vaporization of the source metal. By regulating the heating elements, the furnace transforms the solid metal located at the center of the heating zone into a vapor.
Atmosphere Control
Physical synthesis relies heavily on a clean, controlled environment to prevent unwanted oxidation or contamination. The tube furnace system includes a gas handling subsystem that introduces a carrier gas (often inert, like Argon). This gas acts as the transport medium, carrying the metal vapor away from the source.
Controlling Particle Properties
Regulating Temperature Gradients
Creating nanoparticles is not just about heating; it is about controlled cooling. The tube furnace allows researchers to establish specific temperature gradients along the length of the tube. As the metal vapor moves from the hot zone to cooler regions, it loses energy and undergoes nucleation.
Determining Size and Shape
The rate at which the vapor cools determines the crystal growth. By manipulating the furnace's internal layout and the steepness of the temperature gradient, researchers can fine-tune the nucleation rate. Rapid cooling typically yields smaller particles, while slower cooling allows for larger crystal growth.
Regulating Internal Pressure
In specific setups, such as vertical configurations, the tube furnace positioning helps manage pressure. By extending part of the tube outside the heating zone, the system creates a natural cooling area where byproducts can condense. This prevents overpressure and ensures a stable reaction environment for the metal vapor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Process Variables
While tube furnaces offer precision, they are highly sensitive to minor fluctuations. A slight deviation in the heating rate or gas flow can significantly alter the particle size distribution. Achieving high uniformity requires rigorous calibration of the temperature profile.
Scale Limitations
Tube furnaces are excellent for research and small-batch production due to their precise control. However, the physical vapor condensation method within a tube furnace often faces yield limitations. Scaling up typically requires larger, more complex furnace arrays rather than simply increasing the size of a single tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage a tube furnace effectively for physical synthesis, you must align the furnace capabilities with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is precise particle sizing: Prioritize a furnace with multi-zone heating control to create highly specific temperature gradients for uniform nucleation.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation: Ensure the furnace has a high-integrity sealing system and robust gas flow controls to maintain a pristine inert atmosphere.
Success in physical nanoparticle synthesis relies less on maximum temperature and more on your ability to control the thermal profile across the entire tube length.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Physical Synthesis | Impact on Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Energy | Facilitates evaporation of bulk metal | Enables transition from solid to gas phase |
| Atmosphere Control | Manages carrier gas flow (e.g., Argon) | Prevents oxidation and transports vapor |
| Temp Gradient | Controls cooling and nucleation rates | Determines particle size and shape |
| Sealing System | Maintains high-integrity vacuum/inert state | Ensures high purity and prevents contamination |
| Pressure Control | Regulates internal reaction environment | Stabilizes particle growth and manages byproducts |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Research with KINTEK
Precise nanoparticle synthesis demands flawless thermal profiles and absolute atmospheric purity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory solutions tailored for advanced material science. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique synthesis requirements.
Whether you are fine-tuning nucleation rates or scaling up production, our furnaces deliver the uniformity and stability your research deserves. Contact us today to discuss how our expert-engineered high-temp furnaces can optimize your laboratory’s efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What maintenance is required for a vacuum tube furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety in Your Lab
- Why is a laboratory tube furnace necessary for BiVO4/RGO synthesis? Achieve Precise Nano-Structure Control
- What features enable precise temperature control in a vertical tube furnace? Unlock Superior Thermal Accuracy for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of combining an online mass spectrometer with a fixed-bed reactor? Boost Kinetic Precision
- What critical conditions do laboratory tube furnaces provide for VLS growth of ZnO nanowires? Master Nanoscale Synthesis
- What are the key features of a 70mm tube furnace? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- How does a programmable tube furnace facilitate Al/SiC material transformation? Precision Heat for Ceramic Coatings
- What are the heating zone options for Tube Furnaces? Choose Single or Multi-Zone for Optimal Thermal Control



















