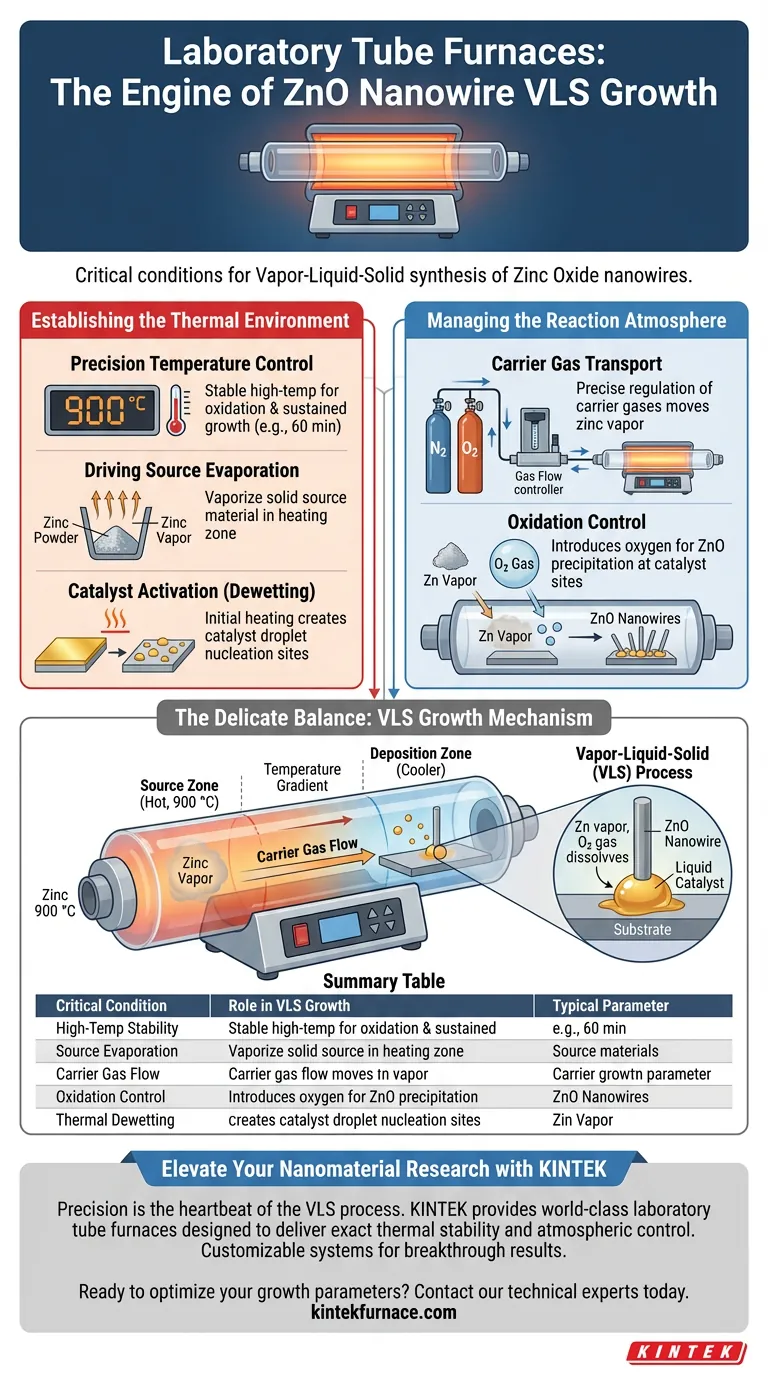
Laboratory tube furnaces are the critical enabler for the Vapor-Liquid-Solid (VLS) growth of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) nanowires because they create a strictly controlled thermal and chemical environment. These devices precisely manage high-temperature zones—often reaching 900 °C—to evaporate zinc source material while simultaneously regulating the flow of carrier gases to transport that vapor to the growth substrate.
The tube furnace does not merely heat the material; it orchestrates the delicate balance between source evaporation, vapor transport, and final precipitation. By synchronizing temperature distribution with gas flow rates, the furnace ensures that zinc vapor condenses smoothly at catalyst sites to form a dense, high-quality nanowire network.

Establishing the Thermal Environment
Precision Temperature Control
The fundamental requirement for VLS growth is a stable, high-temperature environment. Laboratory tube furnaces provide the capacity to reach and maintain temperatures up to 1000 °C.
For ZnO specifically, the furnace is typically heated to approximately 900 °C. This specific thermal energy is required to initiate the oxidation reaction and sustain the growth process over long reaction times, such as 60 minutes.
Driving Source Evaporation
The furnace must generate enough heat to vaporize the solid source material. In this process, zinc powder is placed in the heating zone where the high temperature converts it into zinc vapor.
Without this controlled evaporation phase, there is no source material available to feed the growth of the nanowires.
Catalyst Activation (Dewetting)
Before growth begins, the thermal environment plays a secondary, critical role on the substrate. The heat causes thin films of catalyst material (typically gold) to break apart into tiny droplets.
This process, known as dewetting, creates the spherical "seeds" that serve as the nucleation sites where the nanowires will eventually grow.
Managing the Reaction Atmosphere
Carrier Gas Transport
Temperature alone is insufficient; the vapor must be moved. The tube furnace allows for the precise regulation of carrier gases, such as nitrogen.
The flow rate of these gases determines how effectively the evaporated zinc species migrate from the source zone to the cooler deposition zone where the substrate lies.
Oxidation Control
To form Zinc Oxide (ZnO) rather than pure metallic zinc, oxygen must be introduced into the system. The furnace controls the introduction of oxygen gas alongside the carrier gas.
This ensures that the oxidation reaction occurs at the right rate and location, allowing the zinc vapor to precipitate as ZnO specifically at the catalyst sites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Distribution Risks
While high heat is necessary, the distribution of that heat is equally critical. If the temperature gradient between the source zone (hot) and the substrate zone (cooler) is not managed correctly, the vapor may precipitate prematurely or not at all.
Gas Flow Sensitivity
There is a delicate balance in flow rates. If the carrier gas flow is too high, the zinc vapor may be swept past the substrate before it can react.
Conversely, if the flow is too low, the transport of vapor becomes inefficient, leading to sparse or uneven nanowire growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve specific growth outcomes, you must adjust the furnace parameters to favor certain mechanisms.
- If your primary focus is Nanowire Density: Prioritize the precise control of temperature distribution to ensure maximum vapor precipitation occurs exactly at the substrate location.
- If your primary focus is Crystalline Quality: Ensure the furnace maintains a constant temperature over the full reaction time (e.g., 60 minutes) to allow for stable, uninterrupted crystal lattice formation.
The tube furnace is the engine of VLS growth, translating raw thermal energy and gas flow into the precise conditions required for atomic-scale assembly.
Summary Table:
| Critical Condition | Role in VLS Growth | Typical Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Stability | Initiates oxidation and sustains reaction | ~900 °C to 1000 °C |
| Source Evaporation | Converts solid zinc powder into vapor phase | 900 °C zone heating |
| Carrier Gas Flow | Transports zinc vapor to the growth substrate | Precision N2 regulation |
| Oxidation Control | Ensures precipitation of ZnO over metallic zinc | Regulated O2 introduction |
| Thermal Dewetting | Creates catalyst droplet nucleation sites | Initial heating phase |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Research with KINTEK
Precision is the heartbeat of the Vapor-Liquid-Solid (VLS) process. KINTEK provides world-class laboratory tube furnaces designed to deliver the exact thermal stability and atmospheric control required for high-quality ZnO nanowire synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and advanced manufacturing, our Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems are fully customizable to meet your unique research specifications. Whether you need multi-zone temperature control or specialized gas delivery systems, KINTEK empowers your lab with the tools for breakthrough results.
Ready to optimize your growth parameters? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace solution for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Clémence Badie, Sang Sub Kim. Selective Detection of H<sub>2</sub> Gas in Gas Mixtures Using NiO‐Shelled Pd‐Decorated ZnO Nanowires. DOI: 10.1002/admt.202302081
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a Split Tube Furnace (Single Zone)? Unlock Easy Access and Uniform Heating
- What are the benefits of stainless steel tube furnaces? Discover Durability, Cost Savings & Precision
- What is the mechanism of the drive-in process in a tube furnace? Master Dopant Redistribution with Nitrogen Shielding
- Why is a tube furnace with high-purity Ar protection necessary for LiFePO4 calcination? Ensure Fe2+ Phase Purity
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene? Boost Your Lab Results
- What factors should be considered when selecting a horizontal electric furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency for Your Lab
- How was the uneven heating problem in tubular furnaces solved? Achieve Perfect Heat Uniformity with Advanced Designs
- How is solid-gas phase conversion achieved in a tube furnace? Master Fe-CoP/CW Catalyst Phosphatization



















