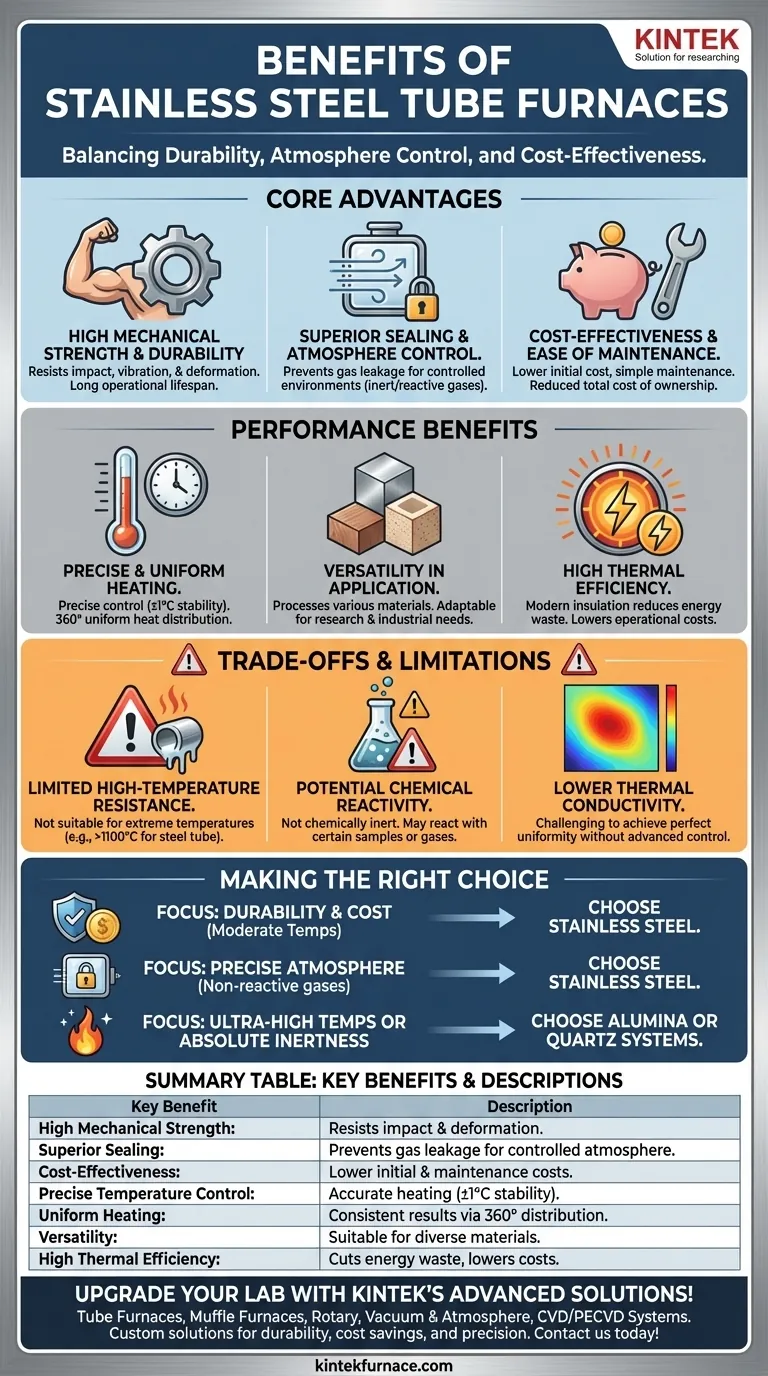
At their core, stainless steel tube furnaces offer a compelling combination of high mechanical strength, excellent process atmosphere control, and overall cost-effectiveness. Their robust construction resists physical deformation, while their superior sealing capabilities prevent gas leakage, making them a reliable workhorse for many laboratory and industrial heating applications.
The decision to use a stainless steel tube furnace is a practical one. It represents a trade-off where you gain exceptional durability and precise atmospheric control at a lower cost, but in exchange for limitations in maximum operating temperature and chemical inertness compared to specialized ceramic or quartz systems.

The Core Advantages of Stainless Steel Construction
The material properties of stainless steel are central to the furnace's primary benefits. This choice of material directly impacts its durability, ability to contain specific atmospheres, and long-term value.
High Mechanical Strength and Durability
Stainless steel provides exceptional mechanical strength. This makes the furnace highly resistant to physical impact, vibration, and deformation that can occur in busy lab or production environments.
This inherent toughness ensures a long operational lifespan and reliable performance, as the furnace structure maintains its integrity over time.
Superior Sealing for Atmosphere Control
One of the most significant benefits is the ability to create a tightly sealed system. The ductility and strength of steel allow for high-quality welds and fittings.
This prevents gas leakage, which is critical for experiments and processes that require a controlled atmosphere, such as inert gas purging (e.g., with argon or nitrogen) or reactive gas environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Ease of Maintenance
Compared to furnaces built from more exotic or specialized materials, stainless steel models are generally less expensive to manufacture and acquire.
They are also relatively simple to maintain and clean, which lowers the total cost of ownership over the furnace's lifetime.
Performance and Operational Benefits
Beyond its physical construction, a stainless steel tube furnace is engineered for reliable and efficient thermal processing.
Precise and Uniform Heating
Modern tube furnaces offer exceptionally precise temperature control, often with a stability of ±1°C.
The cylindrical design subjects the entire sample to heat from a 360° axis, promoting uniform heat distribution along its length. This consistency is crucial for sensitive processes like annealing or chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Versatility in Application
These furnaces are highly versatile. Horizontal models, for example, often provide a larger working volume, allowing for the processing of bigger samples or batch production.
They can effectively process a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and various components, making them adaptable to diverse research and industrial needs.
High Thermal Efficiency
Quality construction using modern insulation materials ensures high thermal efficiency. This means less energy is wasted, reducing operational costs and improving the system's overall sustainability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single solution is perfect for every application. To make an informed decision, you must understand where stainless steel falls short.
Limited High-Temperature Resistance
The primary limitation of using a stainless steel process tube is its temperature ceiling. While a furnace body can house a ceramic tube rated for 1700°C or higher, the steel tube itself is not suitable for such extreme temperatures.
Potential for Chemical Reactivity
Stainless steel, while resistant to many substances, is not chemically inert. At high temperatures, it can react with certain samples or process gases.
This potential for reaction can contaminate the sample or damage the tube, making it unsuitable for experiments where absolute purity is required. In these cases, quartz or alumina tubes are superior.
Lower Thermal Conductivity
Compared to materials like quartz or corundum, stainless steel has inferior thermal conductivity. This can make it slightly more challenging to achieve perfect temperature uniformity across the sample without a sophisticated and well-calibrated control system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct tube furnace requires matching the equipment's capabilities to your specific processing goals.
- If your primary focus is durability and cost-effectiveness for moderate temperatures: Stainless steel is an excellent choice due to its unmatched mechanical strength and lower price point.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control in a robust system: The superior sealing of a stainless steel furnace makes it a reliable option, provided the process gases are not reactive with the steel.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperatures (above ~1100°C) or absolute chemical inertness: You must opt for a system using a high-purity alumina or quartz process tube instead of stainless steel.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial task.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High Mechanical Strength | Resists impact, vibration, and deformation for long lifespan. |
| Superior Sealing | Prevents gas leakage, ideal for controlled atmosphere processes. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower initial cost and easy maintenance reduce total ownership expenses. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Stability of ±1°C ensures accurate heating for sensitive applications. |
| Uniform Heating | 360° heat distribution promotes consistent results in processes like annealing. |
| Versatility | Suitable for metals, ceramics, and various materials in diverse settings. |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Modern insulation cuts energy waste, lowering operational costs. |
Upgrade your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable options like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for durability, cost savings, and precision. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















