Historically, the solution was to move beyond a single heating method and design tubular furnaces with distinct radiation and convection sections. By separating the intense, direct heat of the radiation chamber from the more uniform, gentle heat of a convection chamber, designers were able to overcome the persistent problem of uneven heating.
The core challenge in furnace design is not just delivering heat, but controlling its transfer. The innovation was to adopt a two-stage process: a rapid heating (radiation) stage followed by a temperature-equalizing (convection) stage, ensuring uniformity across the entire material.
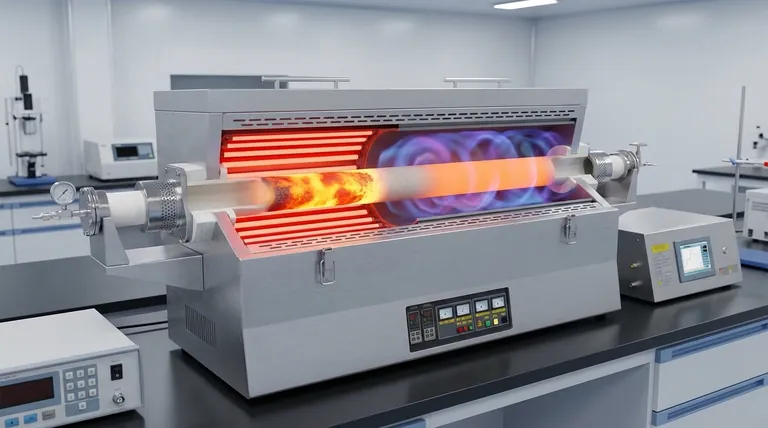

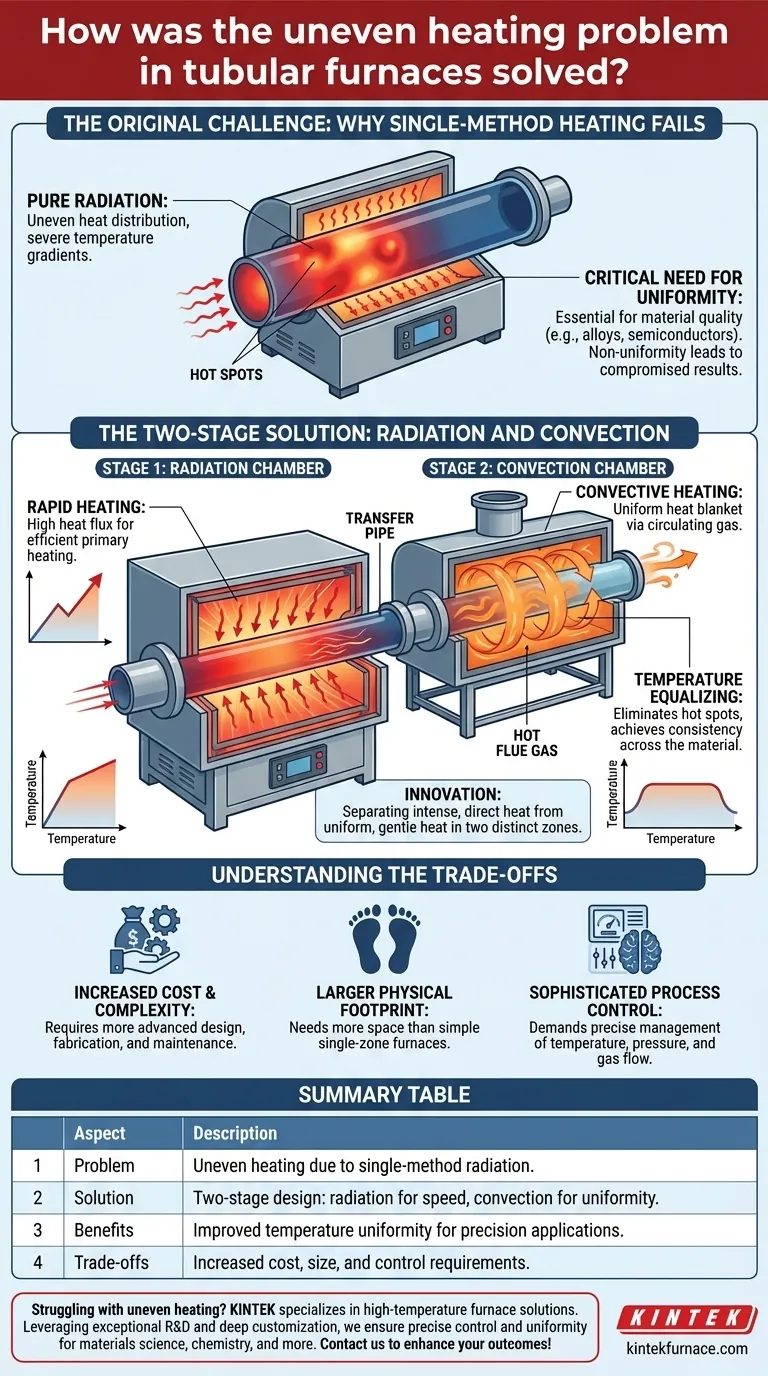
The Original Challenge: Why Single-Method Heating Fails
Early or simplistic tubular furnace designs often struggled to maintain a consistent temperature across the diameter of the tube. This limitation stems from the fundamental nature of heat transfer.
The Problem with Pure Radiation
When a furnace relies solely on radiant heat, the side of the tube directly facing the heating elements gets significantly hotter than the side facing away. This creates hot spots and severe temperature gradients.
These heating elements, often made of materials like Kanthal or silicon carbide, transfer heat very effectively via line-of-sight radiation, but this directness is also the source of the non-uniformity.
The Critical Need for Uniformity
For many modern applications, such as metal alloy treatments, semiconductor manufacturing, or chemical synthesis, temperature consistency is not a luxury—it is a strict requirement.
Even minor temperature variations can compromise the material's structural integrity, chemical properties, or overall quality, rendering the process a failure.
The Two-Stage Solution: Radiation and Convection
The breakthrough came from mimicking the design of larger, highly efficient box furnaces and applying the principles to a tubular format. This involves creating two distinct zones within the furnace.
Stage 1: The Radiation Chamber
This is the primary heating zone where the tubes are exposed to direct radiation from the heating elements. Its purpose is to rapidly and efficiently bring the material up to its target temperature range.
This section is optimized for high heat flux and speed, getting the bulk of the heating work done quickly.
Stage 2: The Convection Chamber
After the initial intense heating, the material moves to a convection section. Here, there are no direct line-of-sight heating elements.
Instead, hot flue gases from the radiant section are circulated around the tubes. This convective heating is less intense but far more encompassing, wrapping the tubes in a uniform blanket of hot gas.
This "soaking" stage allows the temperature to equalize around the entire circumference of the tube, eliminating the hot spots created in the radiation chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the dual-chamber design is highly effective, it introduces complexities that are important to acknowledge.
Increased Cost and Complexity
A furnace with both radiation and convection sections is inherently more complex to design, fabricate, and maintain than a simple single-zone radiant furnace.
Larger Physical Footprint
Separating the two heating zones requires more physical space, making these furnaces larger and potentially more difficult to integrate into existing facility layouts.
Sophisticated Process Control
Managing the temperature, pressure, and gas flow between two distinct zones requires a more advanced process control system to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this design principle helps you select, operate, and troubleshoot furnaces more effectively.
- If your primary focus is high-precision material processing: A furnace with dedicated radiation and convection zones is essential to achieve the required temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating where some non-uniformity is acceptable: A simpler, radiation-dominant design might be a more cost-effective solution.
- If you are troubleshooting an existing furnace: Uneven heating often points to an imbalance between the radiant and convective sections, such as a blocked flue gas path preventing proper convective heat transfer.
By mastering the interplay of different heat transfer modes, furnace technology provides the precise control essential for modern material science.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem | Uneven heating in tubular furnaces due to reliance on single-method radiation, causing hot spots and temperature gradients. |
| Solution | Two-stage design: radiation chamber for rapid heating and convection chamber for uniform temperature equalization. |
| Benefits | Improved temperature uniformity, essential for applications like metal treatments and semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Trade-offs | Increased cost, larger footprint, and need for sophisticated process control systems. |
Struggling with uneven heating in your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in materials science, chemistry, or semiconductor research, our advanced designs ensure precise temperature control and uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your experimental outcomes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















