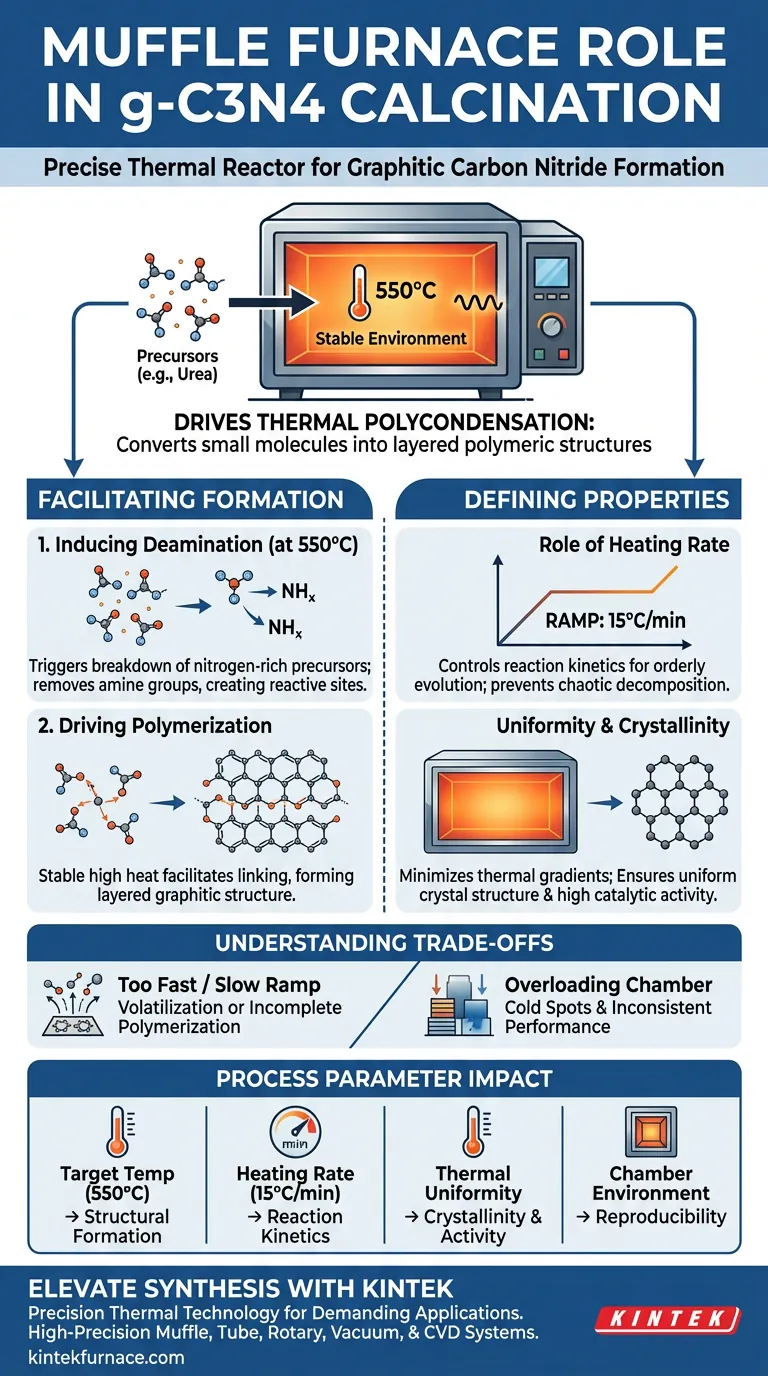
A muffle furnace acts as the precise thermal reactor necessary to drive the formation of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) from precursors. By establishing a stable environment at approximately 550°C with a controlled heating rate (commonly 15°C/min), it initiates the thermal polycondensation reaction required to convert small molecules into a layered polymeric structure.
The muffle furnace is not merely a heater; it is the regulator of the polymerization mechanism. Its ability to maintain strict thermal uniformity directly determines the crystallinity, structural integrity, and eventual catalytic activity of the g-C3N4 nanosheets.
Facilitating Thermal Polycondensation
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this context is to provide the energy required to bridge the gap between simple precursors and complex polymers.
Inducing Deamination
At the target temperature of 550°C, the furnace triggers the chemical breakdown of nitrogen-rich precursors like urea.
This heat forces the precursor molecules to undergo deamination. This removes specific amine groups, creating reactive sites necessary for the next stage of formation.
Driving Polymerization
Once deamination occurs, the stable high heat facilitates polymerization.
The small, destabilized molecules begin to link together. This forms the specific, layered graphitic structure that defines g-C3N4 and gives it its semiconductor properties.
Defining Material Properties
The quality of the final material is heavily dependent on how the heat is applied, not just the maximum temperature reached.
The Role of Heating Rate
The muffle furnace controls the "ramp" of the temperature, such as the referenced 15°C/min.
This specific rate is critical. It ensures that the reaction proceeds at a pace that allows for orderly structural evolution rather than chaotic decomposition.
Uniformity and Crystallinity
The furnace chamber is designed to minimize thermal gradients.
Temperature uniformity is the deciding factor for crystallinity. If the heat is consistent throughout the chamber, the resulting nanosheets will possess a uniform crystal structure, which correlates directly to higher catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While muffle furnaces are essential for this synthesis, there are variables that must be managed to avoid failure.
Sensitivity to Ramp Rates
If the heating rate is too fast, the precursors may volatilize before they can polymerize effectively.
Conversely, a rate that is too slow might alter the thermodynamics of the reaction, leading to incomplete polymerization or unwanted amorphous phases.
Thermal Gradients in Large Batches
While muffle furnaces aim for uniformity, overloading the chamber can disrupt airflow and heat distribution.
This results in "cold spots" where the calcination is incomplete, yielding a product with inconsistent catalytic performance across the batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the formation of g-C3N4, you must configure the furnace based on your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is High Catalytic Activity: Ensure your furnace creates a highly uniform thermal field at 550°C to maximize crystallinity.
- If your primary focus is Process Reproducibility: Strictly calibrate the heating rate (e.g., 15°C/min) to standardize the deamination and polymerization kinetics.
Precise thermal management is the difference between a high-performance photocatalyst and an inert powder.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Role in g-C3N4 Synthesis | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temp (550°C) | Triggers deamination & polycondensation | Determines basic structural formation |
| Heating Rate (15°C/min) | Controls reaction kinetics | Prevents precursor volatilization & chaos |
| Thermal Uniformity | Eliminates thermal gradients | Enhances crystallinity & catalytic activity |
| Chamber Environment | Provides stable thermal reactor | Ensures consistent batch-to-batch reproducibility |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a high-performance photocatalyst and an inert powder. KINTEK provides the advanced thermal technology required for demanding applications like g-C3N4 calcination. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to your specific heating rates and uniformity requirements.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace solution for your research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Guangying Zhou, Jianzhang Fang. Copper-Copper Oxide Heterostructural Nanocrystals Anchored on g-C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Visible-Light-Driven Photo-Fenton-like Catalysis. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30010144
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace utilized for primary heat treatment at 250 °C? Optimize Your Perovskite Catalyst Structure
- How is a muffle furnace utilized during the raw material preparation stage? Optimize Your Lab Results Today
- Why is the temperature control capability of a muffle furnace critical during the preparation of Ba2M0.4Bi1.6O6?
- What safety precautions should be taken when using a Muffle furnace? Ensure Lab Safety with Expert Guidelines
- What are the primary functions of industrial muffle furnaces in the thermal stabilization of metal-lignin complexes?
- How long does heating take on a muffle furnace? From 25 Minutes to Hours Explained
- What is the purpose of the muffle chamber in a muffle furnace? Ensure Clean, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- Why is high-temperature calcination necessary for the modification of boron-doped porous carbon? Expert Insights



















