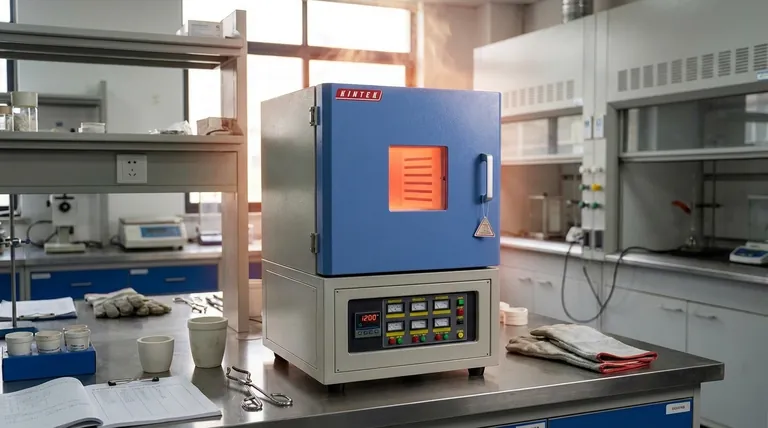
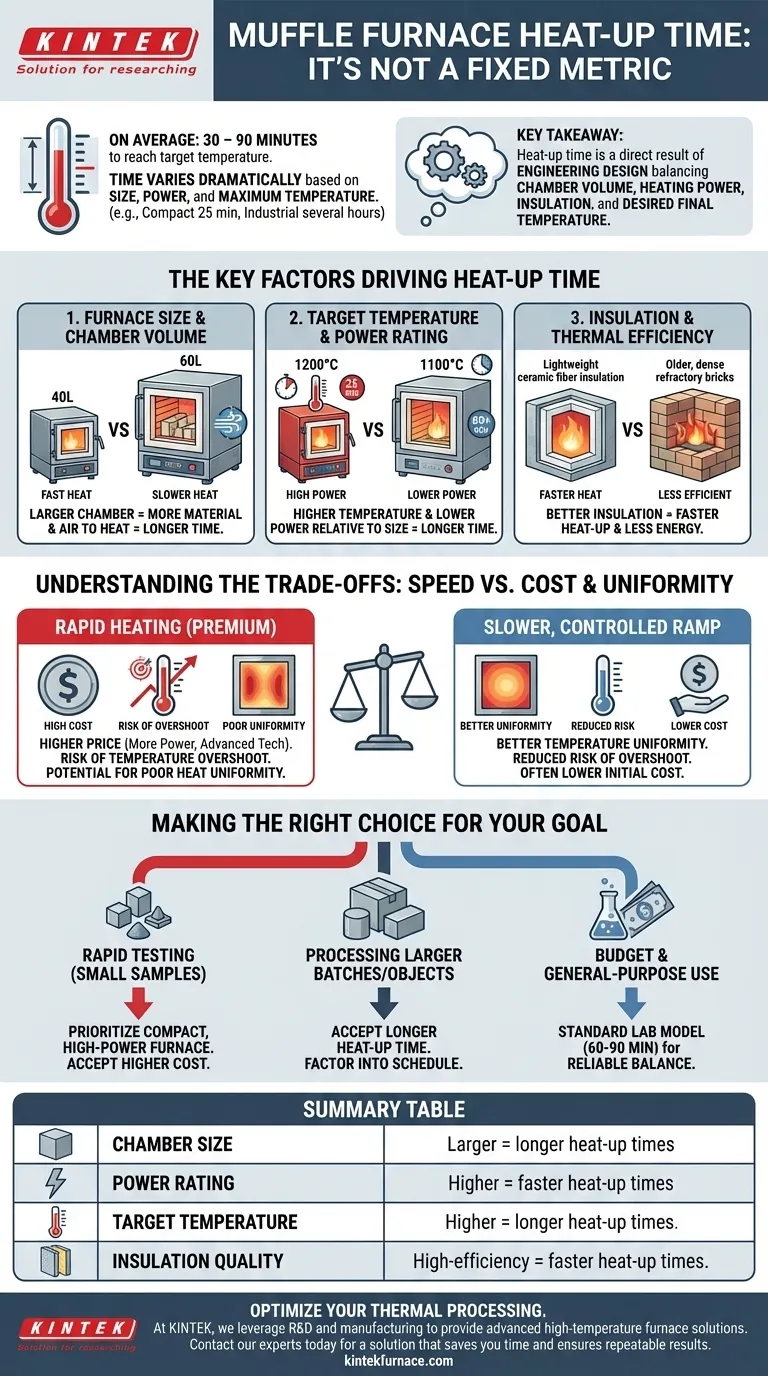
On average, a standard laboratory muffle furnace takes between 30 and 90 minutes to reach its target temperature. However, this time varies dramatically based on the furnace's size, power, and maximum temperature, with some compact models heating in as little as 25 minutes and large industrial units requiring several hours.
The most important takeaway is that heat-up time is not a fixed metric. It is a direct result of the furnace's engineering design, balancing factors like chamber volume, heating power, insulation quality, and the desired final temperature.

The Key Factors Driving Heat-Up Time
Understanding why heat-up times differ is crucial for planning experiments, managing production workflows, and selecting the right equipment. The time specified on a data sheet is a result of several interconnected design choices.
Furnace Size and Chamber Volume
The internal volume of the furnace is one of the most significant factors. A larger chamber simply contains more air and refractory material that must be brought to temperature.
For example, a furnace with a 60-liter chamber will almost always take longer to heat than a 40-liter model, even if both are rated to the same maximum temperature.
Target Temperature and Power Rating
It is intuitive that reaching a higher temperature requires more time and energy. A run to 1100°C will be faster than a run to 1200°C on the same furnace.
However, the furnace's power rating (in watts or kilowatts) is the other side of this equation. A furnace with more powerful heating elements relative to its size can achieve its target temperature much more quickly. This is why a small, high-power 1200°C furnace might heat up in 25 minutes, while a larger, lower-power 1100°C model could take 80 minutes or more.
Insulation and Thermal Efficiency
The quality and type of insulation dictate how effectively the furnace retains the energy produced by its heating elements.
Modern furnaces often use lightweight, high-efficiency ceramic fiber insulation. This allows them to heat up faster and consume less energy compared to older models that rely on heavier, denser refractory bricks, which absorb more heat during the ramp-up phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Cost and Uniformity
Choosing a furnace based solely on the fastest heat-up time can lead to unintended consequences. It is critical to understand the associated trade-offs.
The Cost of Speed
Rapid heating is a premium feature. Furnaces that achieve high temperatures quickly typically command a higher price due to the need for more powerful heating elements, advanced insulation, and sophisticated temperature controllers.
The Risk of Temperature Overshoot
Very aggressive heating ramps can cause the chamber temperature to exceed the desired setpoint before the controller can react and stabilize it. This "overshoot" can be damaging to thermally sensitive materials or ruin a precisely controlled process.
Heat Uniformity Concerns
A furnace that heats too quickly may struggle to distribute the heat evenly throughout the chamber. This can result in hot and cold spots, compromising the uniformity and repeatability of your results, especially when processing multiple samples at once. A slower, controlled ramp often produces better temperature uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always consult the manufacturer's specific data sheet for any furnace you are considering. Use these guidelines to interpret that data based on your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is rapid testing of small samples: Prioritize a compact, high-power furnace and accept the higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is processing larger batches or objects: You must accept a longer heat-up time as a function of physics and factor it into your daily schedule.
- If your primary focus is budget and general-purpose use: A standard laboratory model with a 60-90 minute heat-up time offers a reliable balance of performance and cost.
By understanding the factors that govern heating performance, you can move from simply asking "how long" to confidently controlling your thermal processing operations.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Heat-Up Time |
|---|---|
| Chamber Size | Larger chambers = longer heat-up times |
| Power Rating | Higher power = faster heat-up times |
| Target Temperature | Higher temperatures = longer heat-up times |
| Insulation Quality | High-efficiency insulation = faster heat-up times |
Optimize your thermal processing with a furnace tailored to your exact needs. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether you need rapid heating for small samples or consistent uniformity for large batches, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Let's discuss your application – contact our experts today for a solution that saves you time and ensures repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















