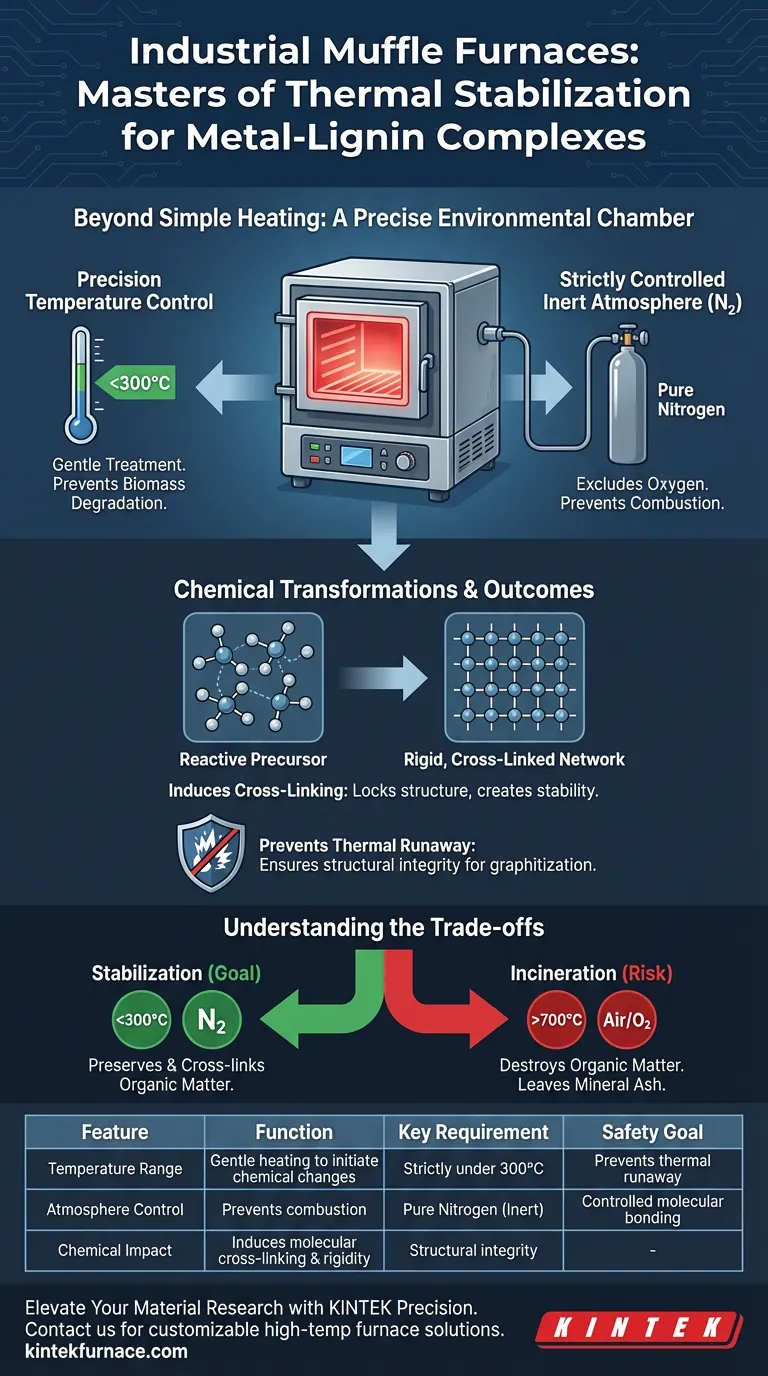
Industrial muffle furnaces act as precise environmental chambers regarding the thermal stabilization of metal-lignin complexes, functioning well beyond simple heating units. Their primary role is to provide a strictly controlled nitrogen atmosphere and regulate gentle heating, typically below 300°C, to induce specific chemical modifications without destroying the organic structure.
The core function of the muffle furnace in this context is to facilitate controlled oxidation and cross-linking reactions. By locking the material structure in an inert environment, it prevents thermal runaway during the subsequent, more aggressive graphitization stages.
The Mechanics of Thermal Stabilization
Precision Temperature Control
The stabilization process requires a "gentle thermal treatment" rather than aggressive heating. Muffle furnaces are calibrated to operate effectively in lower temperature ranges, specifically under 300°C for this application.
This specific thermal window is critical for metal-lignin complexes. It provides enough energy to initiate chemical changes but remains low enough to prevent the degradation of the biomass.
Strictly Controlled Inert Atmosphere
A defining feature of the muffle furnace in this process is its ability to maintain a pure nitrogen atmosphere. By excluding oxygen and replacing it with inert nitrogen, the furnace creates a safe environment for chemical transformation.
This isolation is necessary to prevent uncontrolled combustion. If the lignin complex were exposed to air at these temperatures, it would simply burn rather than stabilize.
Chemical Transformations and Outcomes
Inducing Cross-Linking
Inside the controlled environment of the furnace, the heat induces oxidation and cross-linking reactions within the lignin structure. This rearranges the molecular bonds to create a more rigid, interconnected network.
This networking effect effectively "locks" the structure in place. It transforms a reactive organic material into a stable precursor ready for higher thermal loads.
Preventing Thermal Runaway
The ultimate goal of this stabilization is safety and structural integrity during later processing stages. Without this furnace treatment, the material would suffer from "thermal runaway" when subjected to high-temperature graphitization.
Thermal runaway leads to rapid, uncontrolled heat release and structural failure. The muffle furnace ensures the material is chemically robust enough to withstand future heat stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Incineration
It is vital to distinguish between stabilization and incineration. As noted in other applications, muffle furnaces are capable of reaching 700°C to completely incinerate biomass into mineral-rich ash.
If the temperature is not strictly capped below 300°C, the process shifts from stabilization to destruction. You risk removing the organic matter entirely rather than preserving and cross-linking it.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The success of the process relies entirely on the integrity of the nitrogen atmosphere. While muffle furnaces can facilitate homogenization of alloys at extreme temperatures (over 1000°C) over long periods, lignin stabilization is far more sensitive to atmospheric composition.
A breach in the inert atmosphere triggers immediate oxidation. This compromises the cross-linking process and degrades the metal-lignin complex before it can be stabilized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your thermal processing, align your furnace parameters with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is Thermal Stabilization: Maintain a strictly inert nitrogen atmosphere and cap temperatures below 300°C to induce cross-linking without combustion.
- If your primary focus is Ash/Mineral Extraction: Operate the furnace at significantly higher temperatures (approx. 700°C) to fully incinerate organic matter and isolate mineral components.
Correctly utilizing the muffle furnace ensures your metal-lignin precursors are robust enough to endure the transition to high-performance graphitized materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Thermal Stabilization | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Gentle heating to initiate chemical changes | Strictly under 300°C |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents combustion and uncontrolled oxidation | Pure Nitrogen (Inert) |
| Chemical Impact | Induces molecular cross-linking and rigidity | Structural integrity |
| Safety Goal | Prevents thermal runaway in graphitization | Controlled molecular bonding |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let uncontrolled oxidation compromise your thermal stabilization process. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the delicate requirements of metal-lignin complex processing. Our lab high-temp furnaces provide the precise atmosphere control and temperature uniformity needed to prevent thermal runaway and ensure successful cross-linking.
Ready to optimize your thermal treatment? Contact us today to discuss your customizable furnace solution and see how our expertise can bring reliability to your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Qiangu Yan, Zhiyong Cai. Tuning thermal and graphitization behaviors of lignin <i>via</i> complexation with transition metal ions for the synthesis of multilayer graphene-based materials. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra05881f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What temperature capabilities do modern Muffle Furnaces have? Achieve Precision Up to 1800°C
- What is the purpose of the port at the rear of the chamber in a muffle furnace? Unlock Precision Control for Your Lab
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play in FTO thin film PDA? Optimize Your Optoelectronic Performance
- Why is a muffle furnace required for sodium-ion cathode heat treatment? Engineering P2/P3 Crystal Phase Structures
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for defect engineering in delta-MnO2? Precision Thermal Treatment for Optimal Defects
- How is a high-temperature muffle furnace utilized to evaluate the oxidation resistance of Cr2AlC ceramics?
- What are the common applications of box furnaces? Versatile Heat Treatment for Metals, Ceramics, and Research
- What maintenance practices are recommended for a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety in Your Lab



















