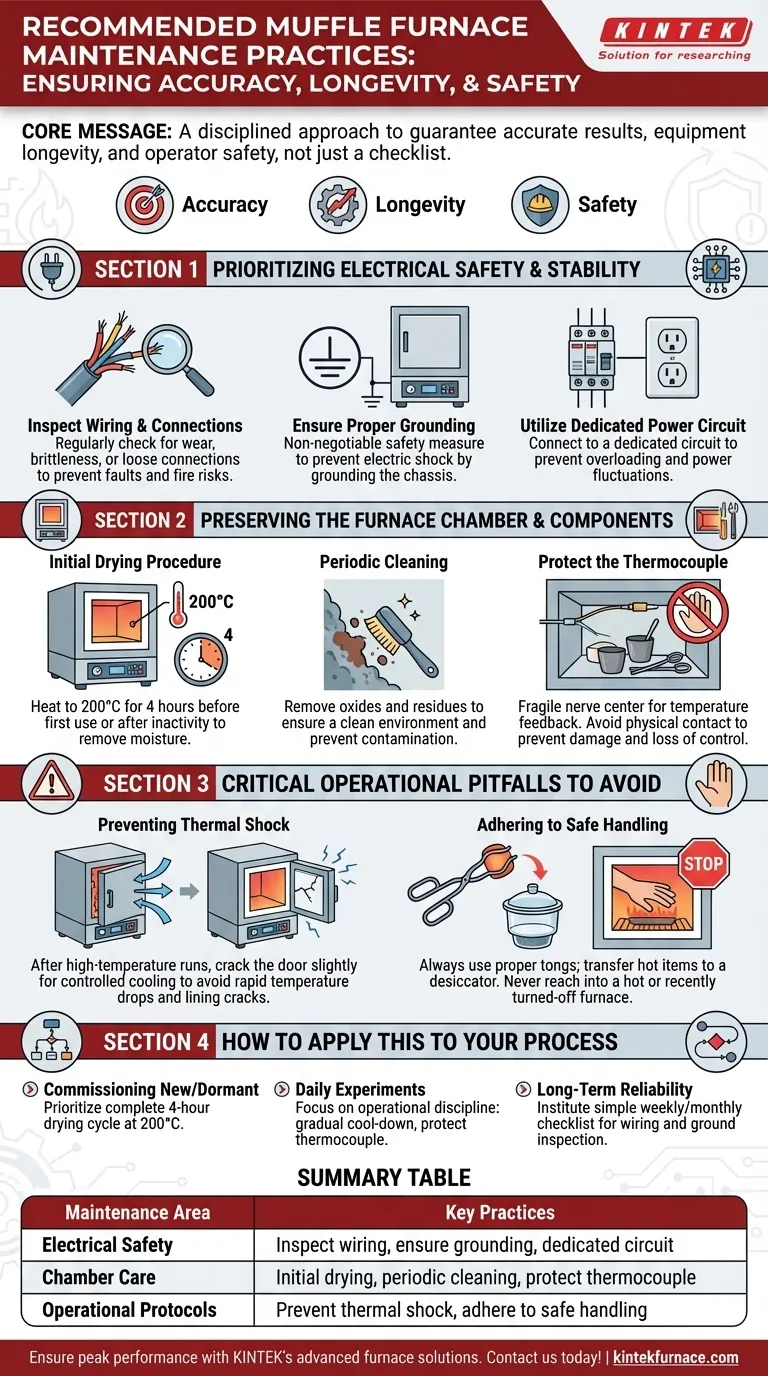
Proper muffle furnace maintenance is a systematic process of inspection, cleaning, and adherence to specific operational protocols. The key practices involve regularly checking all wiring, keeping the furnace chamber clean of oxides, performing an initial drying cycle to remove moisture, and following strict procedures for heating and cooling to prevent damage and ensure operator safety.
At its core, muffle furnace maintenance is not about a simple checklist. It is a disciplined approach to guaranteeing three critical outcomes: the accuracy of your results, the longevity of the equipment, and the safety of the operator.

Prioritizing Electrical Safety and Stability
Your furnace's performance and safety begin with its electrical foundation. Neglecting this area can lead to operational failures, inaccurate readings, and significant safety hazards.
Inspect Wiring and Connections
Regularly inspect all wiring on both the furnace and the external controller. Look for signs of wear, brittleness from heat exposure, or loose connections that could cause intermittent faults or create a fire risk.
Ensure Proper Grounding
The furnace must be properly grounded to a reliable earth ground. This is a non-negotiable safety measure to prevent the chassis from becoming live in the event of an electrical fault, protecting operators from electric shock.
Utilize a Dedicated Power Circuit
Always connect the furnace to a dedicated electrical circuit controlled by its own breaker or gate. This prevents overloading the circuit, which can cause power fluctuations that affect performance and create a fire hazard.
Preserving the Furnace Chamber and Components
The furnace chamber and its internal components are susceptible to damage from moisture and extreme temperature changes. Proactive care is essential for a long service life.
The Initial Drying Procedure
Before its first use, or after any long period of inactivity, the furnace must be dried to remove absorbed moisture from the refractory materials. Heat the furnace to 200°C and hold it at that temperature for four hours to gently drive off any moisture.
Periodic Cleaning
Over time, oxides and other residues can build up on the chamber walls. These should be removed periodically to ensure a clean operating environment and prevent sample contamination.
Protect the Thermocouple
The thermocouple is the furnace's nerve center, providing temperature feedback. It is extremely fragile, especially when hot. Never allow crucibles, racks, or tools to touch the thermocouple, as a slight bump can break it, leading to a total loss of temperature control.
Critical Operational Pitfalls to Avoid
Many maintenance issues arise not from component failure, but from improper operational procedures. Avoiding these common mistakes is as critical as any scheduled inspection.
Preventing Thermal Shock
The refractory materials that line the furnace are vulnerable to thermal shock—damage caused by rapid temperature changes. After a high-temperature run, turn off the power but do not open the door immediately.
Instead, crack the door open just a small amount. This allows the temperature to drop more rapidly but in a controlled manner, preventing the sudden influx of cool air that can cause the chamber lining to crack.
Adhering to Safe Handling
Always use proper crucible tongs to place or remove items from the furnace. When removing hot items like crucibles, transfer them to a designated desiccator to cool, which protects both the sample and the operator.
Never reach into a furnace, even when it is turned off, as it retains heat for a very long time.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your maintenance focus will shift slightly depending on the furnace's status and your primary goal.
- If you are commissioning a new or long-dormant furnace: Your first priority is performing the complete four-hour drying cycle at 200°C to prevent moisture damage.
- If you are running daily experiments: Your focus should be on operational discipline—enforcing the gradual cool-down procedure and ensuring operators never touch the thermocouple.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Institute a simple weekly or monthly checklist to visually inspect wiring and confirm a solid ground connection.
Ultimately, consistent, disciplined operation is the most effective form of maintenance you can perform.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Area | Key Practices |
|---|---|
| Electrical Safety | Inspect wiring, ensure proper grounding, use dedicated power circuit |
| Chamber Care | Perform initial drying cycle, periodic cleaning, protect thermocouple |
| Operational Protocols | Prevent thermal shock, adhere to safe handling procedures |
Ensure your muffle furnace operates at peak performance with KINTEK's advanced solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















