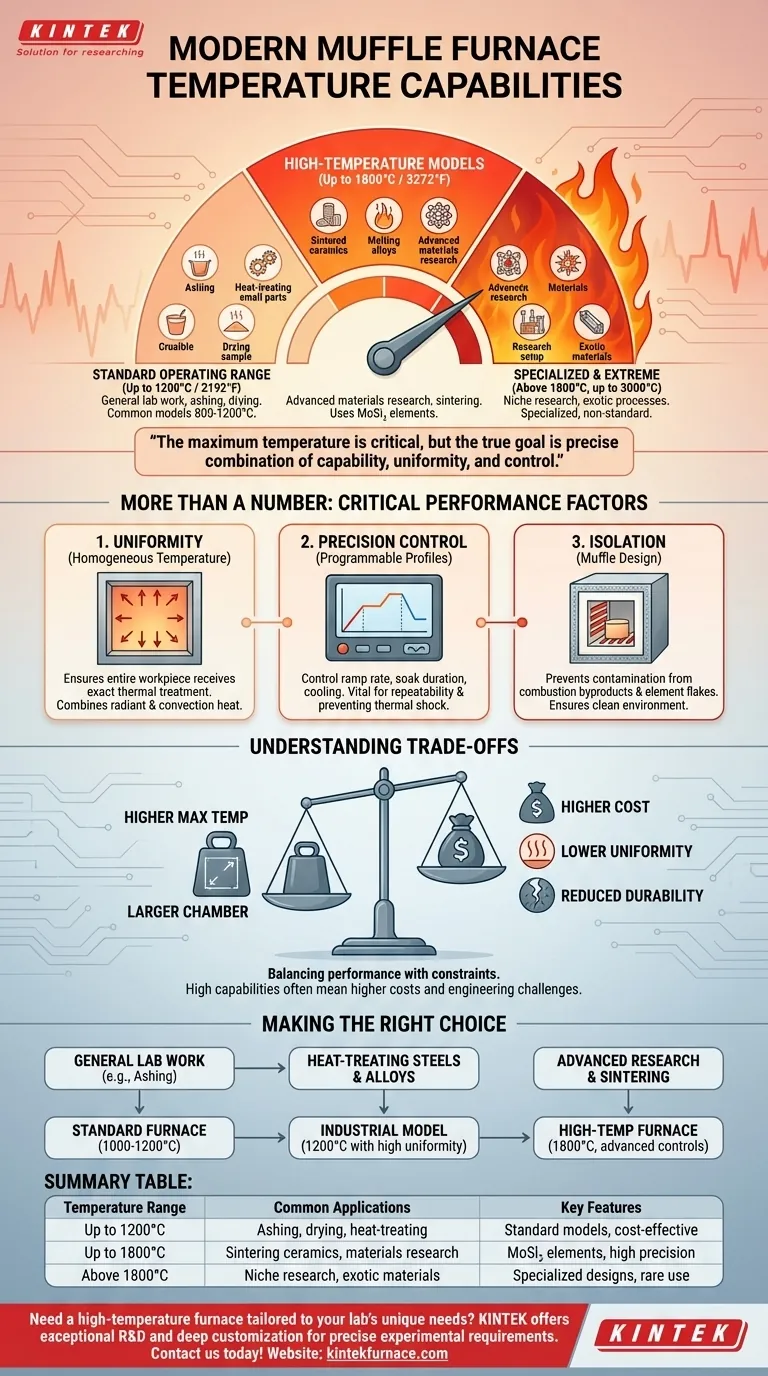
In short, modern muffle furnaces can achieve working temperatures up to 1,800°C (3,272°F). While many standard laboratory models operate in the 1000°C to 1200°C range, advancements in heating element and insulation materials have pushed the upper limits for sophisticated metallurgical and materials science applications.
The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace is a critical specification, but it is not the only one that matters. The true goal is to select an instrument that provides the right combination of temperature capability, uniformity, and atmospheric control to ensure the precision and repeatability your process demands.
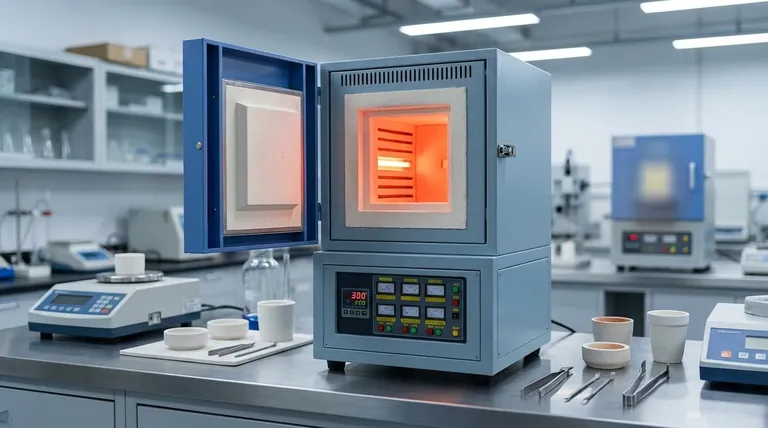

Deconstructing Muffle Furnace Temperature Capabilities
A muffle furnace is fundamentally a high-temperature oven that isolates the material being heated from the direct radiation and potential contamination of the heating elements. This design is what allows for its precision.
The Standard Operating Range (Up to 1200°C)
Most general-purpose laboratory and light industrial muffle furnaces operate in a range of approximately 800°C to 1200°C (2192°F).
This range is sufficient for a vast number of common applications, including ashing organic materials, heat-treating small steel parts, drying samples, and conducting various chemical analyses.
High-Temperature Models (Up to 1800°C)
Furnaces capable of reaching 1800°C (3272°F) are built for more demanding tasks. Reaching these temperatures requires specialized heating elements, often made from materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂).
These models are essential for advanced materials research, sintering high-performance ceramics, melting certain alloys, and other sophisticated metallurgical processes that require extreme heat.
Specialized and Extreme Temperatures (Above 1800°C)
While rare, some highly specialized models can push beyond 1800°C, with certain designs reportedly capable of reaching up to 3000°C.
These are not standard instruments. They are typically designed for niche research or industrial processes involving exotic materials and require very specific operating conditions and infrastructure.
Why Temperature Is More Than Just a Number
Focusing solely on the maximum temperature overlooks other critical features that define a furnace's performance and suitability for a given task.
The Critical Role of Temperature Uniformity
A furnace's ability to maintain a homogeneous temperature throughout the entire processing chamber is paramount. High uniformity ensures that the entire workpiece receives the exact same thermal treatment.
Muffle furnaces achieve this through a combination of radiant and convection heat transfer within an enclosed chamber, minimizing the hot and cold spots that can ruin sensitive processes.
Precision Temperature Control
Modern furnaces use advanced programmable controllers to execute precise heating profiles. This allows an operator to control the rate of temperature increase (ramp), the duration at a specific temperature (soak), and the cooling rate.
This level of control is vital for achieving repeatable results and preventing thermal shock that could damage the material or the furnace itself.
Isolation from Contaminants
The core feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle"—an interior chamber, often ceramic, that separates the workload from the heating elements.
This design prevents combustion byproducts or flakes from the elements from contaminating the sample, ensuring a clean heating environment essential for high-purity applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with practical constraints. Higher capabilities almost always come with compromises.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
The cost of a furnace increases significantly with its maximum temperature rating. The materials required for high-temperature heating elements and insulation are far more expensive than those used in standard models.
Chamber Size vs. Uniformity
As the internal chamber size increases, it becomes more difficult and expensive to engineer a system that maintains excellent temperature uniformity across the entire volume. A large industrial furnace requires more sophisticated design than a compact benchtop unit.
Durability and Efficiency
While built from heat-resistant materials, all furnace components, especially the heating elements and ceramic muffle, are subject to wear. Aggressive heating cycles or operating constantly at the maximum rated temperature can reduce the instrument's lifespan and efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choose a furnace based on the specific demands of your process, not just the highest number on the specification sheet.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work (e.g., ashing, drying): A standard furnace with a maximum temperature of 1000°C to 1200°C is cost-effective and perfectly suitable.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating common steels or alloys: An industrial model capable of reaching at least 1200°C with excellent temperature uniformity is the appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or sintering exotic ceramics: You will require a high-temperature furnace capable of reaching 1800°C, likely with advanced atmospheric controls.
By understanding these factors, you can move beyond a simple temperature rating to select a furnace that delivers the precise, reliable results your work demands.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Ashing, drying, heat-treating steels | Standard models, cost-effective |
| Up to 1800°C | Sintering ceramics, advanced materials research | MoSi₂ elements, high precision |
| Above 1800°C | Niche research, exotic materials | Specialized designs, rare use |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and achieve reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















