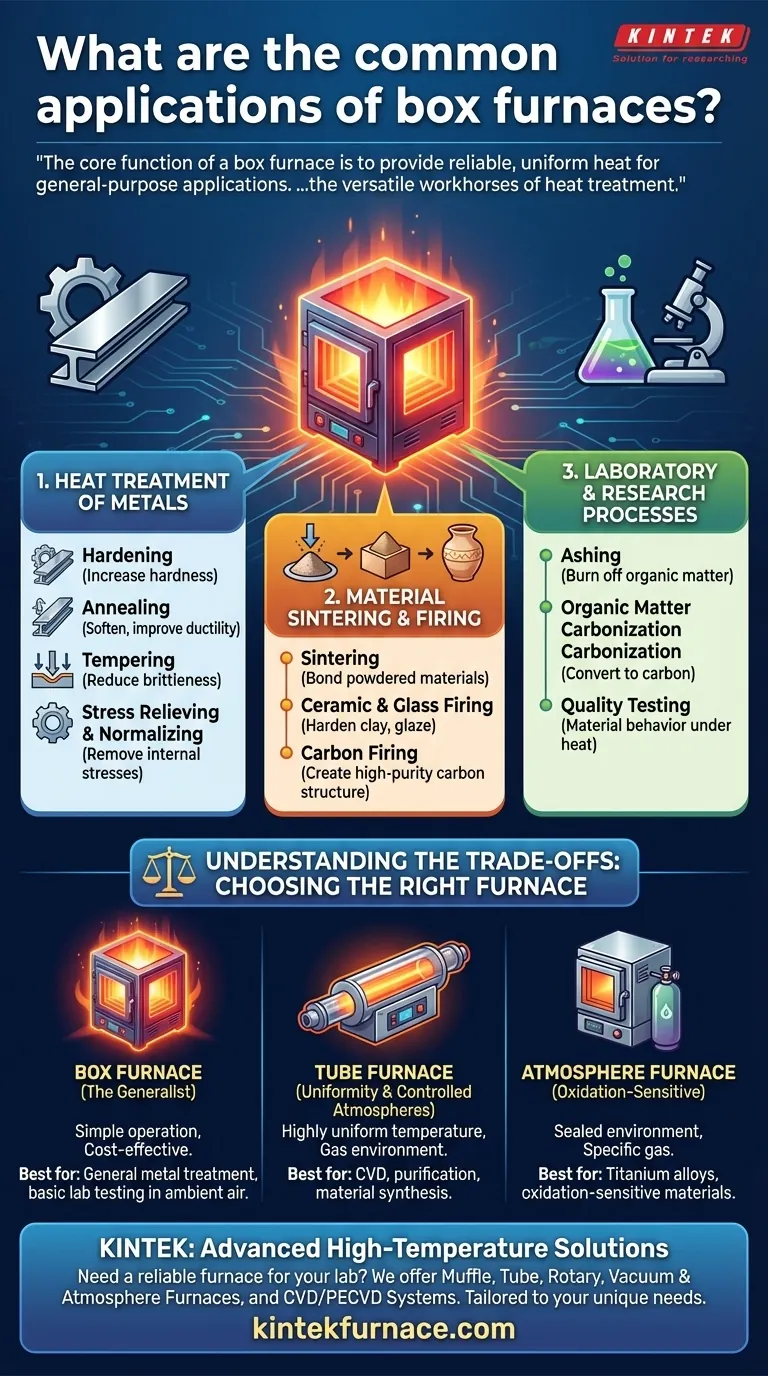
In short, box furnaces are the versatile workhorses of heat treatment, used for a wide range of thermal processes in both industrial and laboratory settings. Their primary applications include modifying the properties of metals, firing ceramics, sintering powdered materials, and conducting various research experiments that require high temperatures in a controlled environment.
The core function of a box furnace is to provide reliable, uniform heat for general-purpose applications. While specialized furnaces exist for niche requirements, the box furnace is the go-to tool for most foundational heat treatment tasks across metallurgy, materials science, and research.

The Core Functions: What Box Furnaces Excel At
A box furnace's simple, robust design makes it ideal for a set of fundamental thermal processes. These applications generally fall into three main categories.
Heat Treatment of Metals
This is the most common industrial use, where heat is applied to alter the physical and chemical properties of a metal part.
- Hardening: This process heats steel to a high temperature and then rapidly cools it to increase its hardness and wear resistance.
- Annealing: By heating and slowly cooling a material, annealing softens metals, relieves internal stresses, and improves ductility.
- Tempering: Performed after hardening, tempering is a lower-temperature treatment that reduces brittleness and improves the overall toughness of the steel.
- Stress Relieving & Normalizing: These processes use precise heating and cooling cycles to remove internal stresses caused by manufacturing and to create a more uniform internal structure.
Material Sintering and Firing
Box furnaces are essential for creating solid objects from powders or raw materials.
- Sintering: This involves heating powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) to a temperature just below their melting point, causing the particles to bond together and form a solid, dense piece.
- Ceramic & Glass Firing: Widely used in art studios, labs, and industrial production, box furnaces provide the controlled heat needed to fire clay, glazes, and glass into their final, hardened state.
- Carbon Firing: This is a specialized process used to heat materials in a way that creates a high-purity carbon structure.
Laboratory and Research Processes
In a research setting, the box furnace is a fundamental tool for material testing and development.
- Ashing: This involves burning off organic matter from a sample at a high temperature to determine its inorganic content.
- Organic Matter Carbonization: Box furnaces are used in experiments to convert organic materials into carbon through controlled heating.
- Quality Testing: They provide a stable thermal environment for testing how new materials, components, and samples behave under extreme heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Box Furnace vs. Specialized Furnaces
While versatile, the standard box furnace is not the right tool for every job. Understanding its limitations clarifies when a more specialized furnace is necessary.
The Box Furnace: The Generalist
The standard box furnace is designed for heating materials in ambient air. Its strengths are its simple operation, versatility for common tasks, and cost-effectiveness. It is the default choice for basic metal treatments and sample heating.
The Tube Furnace: For Uniformity and Controlled Atmospheres
A tube furnace is used when a sample needs a highly uniform temperature zone or must be processed within a specific gas environment. It is ideal for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), purification, and material synthesis where atmospheric control is critical.
The Atmosphere Furnace: For Oxidation-Sensitive Materials
An atmosphere furnace is essentially a sealed box furnace that allows the air to be replaced with a specific gas. It is required for processing materials that would be damaged by oxygen at high temperatures, such as titanium alloys or certain metal powders.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose metal heat treatment, ceramic firing, or basic lab testing: A standard box furnace is the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is processing oxidation-sensitive materials like titanium or certain powdered metals: You require an atmosphere furnace to prevent material degradation.
- If your primary focus is achieving a highly uniform temperature profile or processing a sample in a specific gas flow: A tube furnace is the appropriate tool for the task.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the tool's capabilities to the specific requirements of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment of Metals | Hardening, Annealing, Tempering, Stress Relieving | Industrial metalworking, improving material properties |
| Material Sintering and Firing | Sintering, Ceramic/Glass Firing, Carbon Firing | Manufacturing solid parts from powders, art and production |
| Laboratory and Research | Ashing, Carbonization, Quality Testing | Material testing, research experiments, sample analysis |
Need a reliable furnace for your lab? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong R&D and deep customization, we tailor our products to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?



















