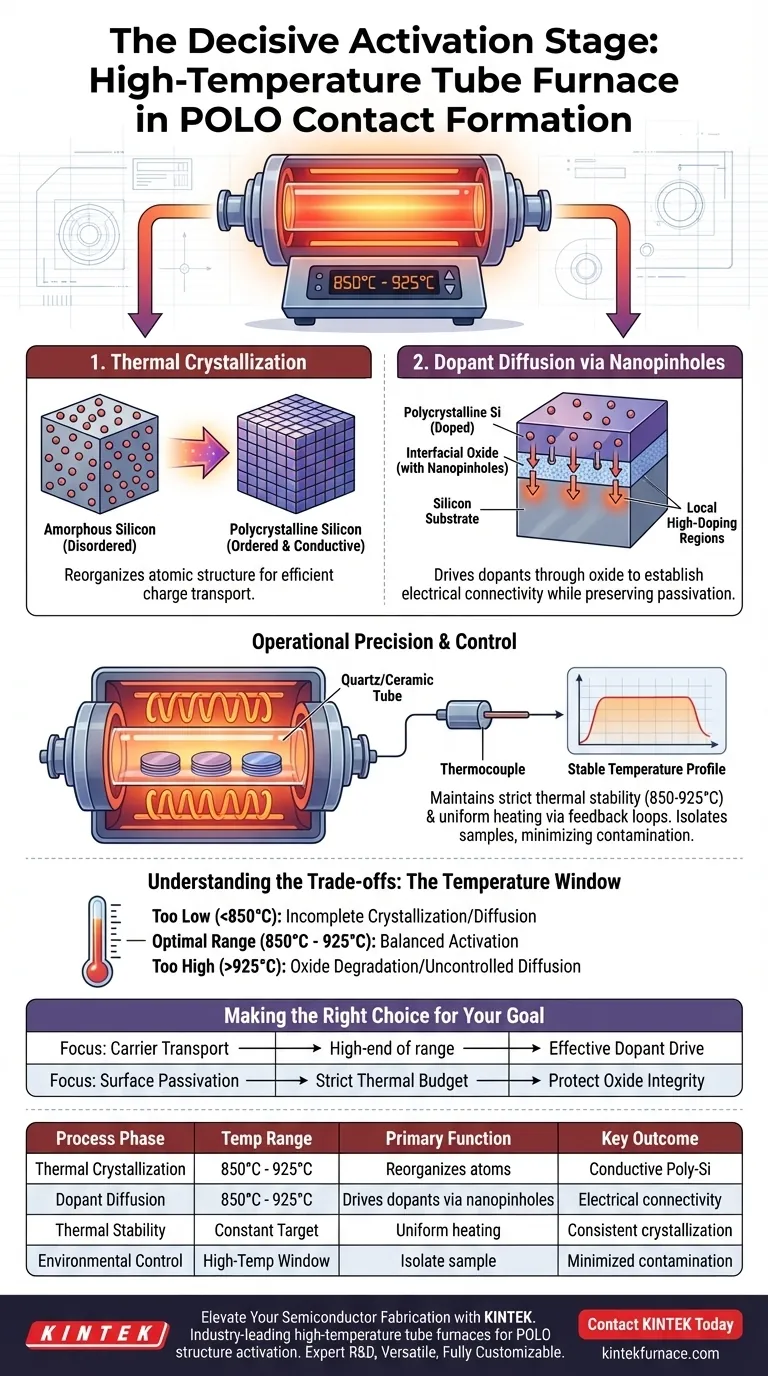
The high-temperature tube furnace acts as the decisive activation stage in the fabrication of Poly-Si on Oxide (POLO) contact structures. Its primary function is to provide a strictly controlled thermal annealing environment, typically ranging between 850°C and 925°C, which triggers the essential physical and chemical changes required to turn deposited layers into functional electronic contacts.
The furnace performs a dual function: it converts amorphous silicon into conductive polycrystalline silicon and drives dopants through oxide nanopinholes to establish electrical connectivity with the substrate.
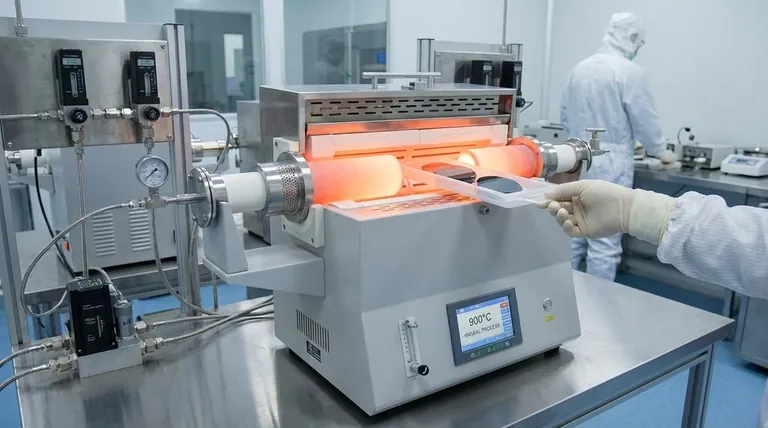

The Mechanics of the Annealing Process
Thermal Crystallization of Silicon
The initial layers deposited for POLO structures often consist of amorphous silicon. This material lacks the ordered structure necessary for optimal electrical performance.
The tube furnace applies high heat to drive thermal crystallization.
This phase transition reorganizes the atomic structure of the amorphous layers, transforming them into polycrystalline silicon. This structural change is fundamental to creating a layer capable of efficient charge carrier transport.
Dopant Diffusion via Nanopinholes
Beyond structural changes, the furnace facilitates the critical movement of chemical dopants.
The thermal energy drives dopants already present in the polycrystalline silicon to migrate. Specifically, the heat forces these dopants through nanopinholes in the interfacial oxide layer.
This process creates local high-doping regions within the silicon substrate directly beneath the oxide. These regions allow for current flow (carrier transport) across the interface while preserving the passivation properties that prevent electron recombination.
Operational Precision and Control
Maintaining Thermal Stability
A high-temperature tube furnace is distinct from standard ovens due to its ability to maintain a stable, uniform temperature profile within a cylindrical cavity.
Heating coils wrapped around the chamber generate intense heat, while internal thermocouples constantly monitor the environment.
This feedback loop ensures the temperature remains strictly within the target range (e.g., 850°C to 925°C), which is vital for uniform crystallization across the sample.
The Importance of the Chamber Environment
The reaction takes place within a tube, typically made of heat-resistant quartz or ceramic.
This design isolates the samples, minimizing contamination while allowing for the precise thermal treatment required to activate the POLO structure without degrading its delicate oxide layers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Temperature Window
The specific range of 850°C to 925°C is not arbitrary; it represents a critical operational window.
If the temperature is too low, the amorphous silicon may fail to fully crystallize, or the dopants may not diffuse sufficiently through the nanopinholes to create a good contact.
Conversely, excessive temperatures could degrade the passivation quality of the oxide layer or cause uncontrolled dopant diffusion, ruining the device's efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the tube furnace in POLO formation, consider your specific fabrication targets:
- If your primary focus is carrier transport: Ensure the furnace temperature is sufficient (closer to the upper limit of the range) to drive dopants effectively through the nanopinholes into the substrate.
- If your primary focus is surface passivation: strictly monitor the thermal budget to ensure the annealing process does not compromise the integrity of the interfacial oxide layer.
The tube furnace is not merely a heater; it is the precision tool that balances crystallization and diffusion to enable high-efficiency silicon contacts.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature Range | Primary Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Crystallization | 850°C - 925°C | Reorganizes amorphous silicon atoms | Formation of conductive polycrystalline silicon |
| Dopant Diffusion | 850°C - 925°C | Drives dopants through oxide nanopinholes | Establishes electrical connectivity with substrate |
| Thermal Stability | Constant Target | Uniform heating via thermocouples | Ensures consistent crystallization across sample |
| Environmental Control | High-Temp Window | Isolate sample in quartz/ceramic tube | Minimizes contamination and protects oxide layers |
Elevate Your Semiconductor Fabrication with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a functional contact and a failed device. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature tube furnaces designed specifically for the rigorous demands of POLO structure activation. Our systems offer the thermal stability and atmospheric control necessary to balance crystallization and passivation perfectly.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Advanced thermal solutions tailored for lab and industrial high-temp needs.
- Versatile Product Line: From Tube and Muffle to Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
- Fully Customizable: We adapt our technology to meet your unique research and production specifications.
Ready to achieve superior charge carrier transport and surface passivation? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your high-temperature furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- William Nemeth, Paul Stradins. Self‐Assembled Monolayer Templating for Engineered Nanopinholes in Passivated Contact Solar Cells. DOI: 10.1002/solr.202500200
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you power on and operate a multi zone tube furnace? Master Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What are the differences between solid tube and split type tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What role does a tube furnace play in the carbonization of porous carbon? Master Precise Thermal Control
- What is the main benefit of tube furnaces compared to chamber furnaces? Superior Atmosphere Control for Purity
- What are the key components of a tubular furnace? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the advantages of vertical tube furnaces? Achieve Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace ensure the quality of carbon materials? Precision Control for Hydrochar to Pyrochar Conversion
- What is the purpose of a stepper motor equipped with a 100:1 reducer in a tube furnace? Achieve Precision Control



















