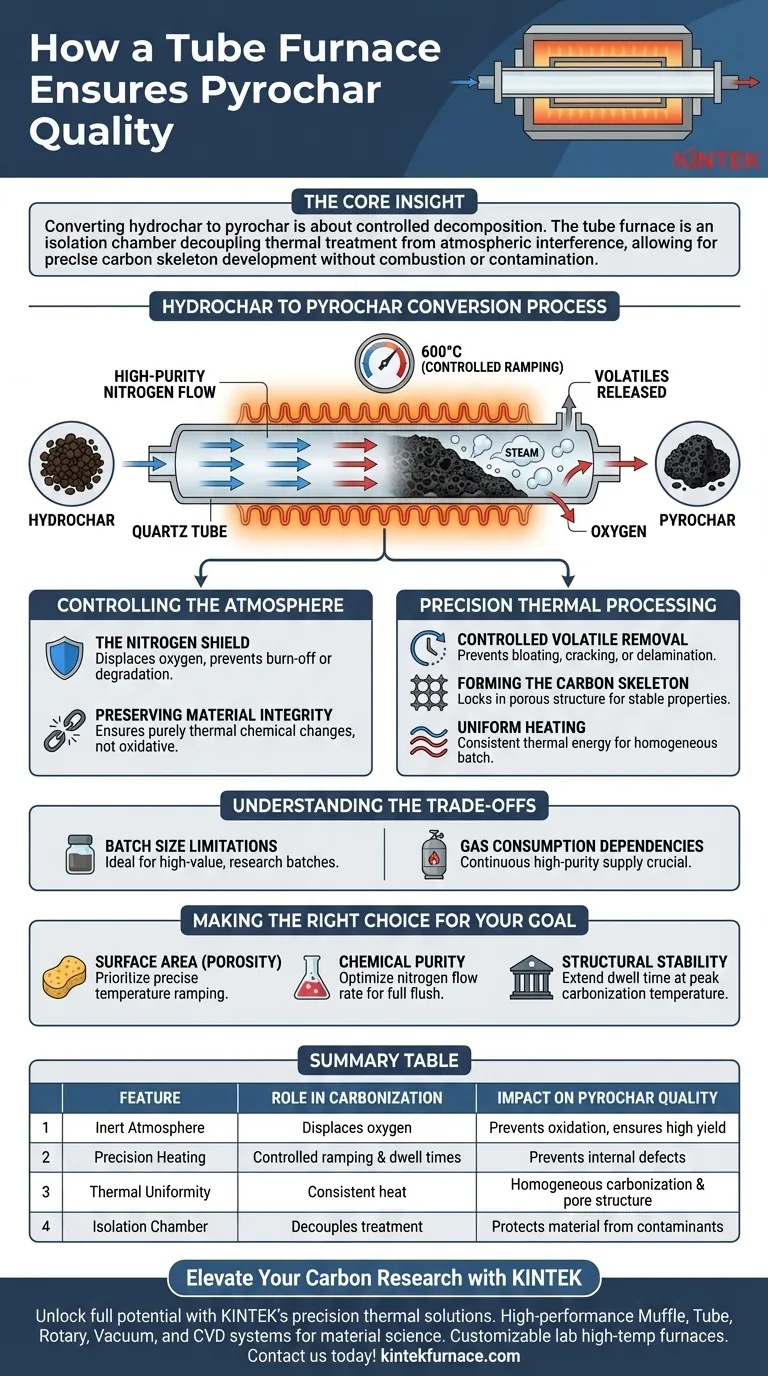
A tube furnace ensures the quality of carbon materials during the conversion of hydrochar to pyrochar primarily by creating a strictly controlled, inert processing environment. By maintaining a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen gas and regulating the pyrolysis temperature (e.g., 600°C), the furnace prevents oxidation while precisely managing the removal of volatiles to form a stable, porous carbon structure.
The Core Insight Converting hydrochar to pyrochar is not just about heating; it is about controlled decomposition. The tube furnace acts as an isolation chamber that decouples thermal treatment from atmospheric interference, allowing for the precise development of a stable carbon skeleton without the risk of combustion or contamination.

Controlling the Atmosphere
The Nitrogen Shield
The most critical function of the tube furnace in this process is the prevention of oxidation. By pumping a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen into the chamber, the furnace displaces oxygen that would otherwise cause the carbon to burn away or degrade.
Preserving Material Integrity
This inert atmosphere ensures that the chemical changes occurring are strictly thermal, not oxidative. Without this protection, the high temperatures required for carbonization would destroy the material's surface properties and significantly reduce the yield of useful pyrochar.
Precision Thermal Processing
Controlled Volatile Removal
The furnace allows for specific temperature settings, such as 600°C, to drive off volatile components at a controlled rate. This controlled heating prevents rapid gas release, which can otherwise cause internal defects like bloating, cracking, or delamination within the material.
Forming the Carbon Skeleton
The quality of pyrochar is defined by its porous, skeletal structure. By sustaining specific temperatures for a set duration, the tube furnace facilitates the "locking in" of this structure, converting the raw hydrochar into a material with stable physical and chemical properties.
Uniform Heating
Resistive heating elements surrounding the tube ensure the sample is subjected to consistent thermal energy. This uniformity is essential for homogeneity, ensuring that the entire batch of hydrochar converts to pyrochar with the same degree of carbonization and porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Batch Size Limitations
While tube furnaces offer exceptional control, the geometry of the tube limits the volume of material you can process at once. They are ideal for research and high-value batch processing but may act as a bottleneck for high-throughput industrial production.
Gas Consumption Dependencies
The quality of the final product is directly tied to the purity and consistency of the nitrogen supply. Any interruption or contamination in the gas flow can compromise the inert environment, leading to immediate oxidation and a failed batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your pyrochar, align your furnace settings with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is Surface Area (Porosity): Prioritize precise temperature ramping to ensure volatiles escape slowly, preventing pore collapse or bloating.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the nitrogen flow rate is optimized to flush out all oxygen before heating begins and maintain positive pressure throughout the process.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Extend the dwell time at the peak carbonization temperature to ensure complete conversion and skeletal reinforcement.
True quality in carbonization is achieved not by the heat itself, but by the precision with which that heat is applied and controlled.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Carbonization | Impact on Pyrochar Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Displaces oxygen using high-purity Nitrogen | Prevents oxidation and ensures high material yield |
| Precision Heating | Controlled ramping and dwell times | Prevents internal defects like cracking or bloating |
| Thermal Uniformity | Consistent heat from resistive elements | Ensures homogeneous carbonization and pore structure |
| Isolation Chamber | Decouples treatment from atmosphere | Protects material integrity from external contaminants |
Elevate Your Carbon Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your carbon materials with KINTEK’s precision thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you are converting hydrochar to pyrochar or developing advanced porous structures, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces offer the atmospheric control and thermal uniformity you need for repeatable, high-quality results.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs with our technical specialists.
Visual Guide
References
- Ria Yolanda Arundina, Bambang Subiyanto. Preparation of nitrogen-doped activated carbon from palm oil empty fruit bunches for electrodes in electric double-layer capacitance-type supercapacitors: effect of pyrolysis temperature. DOI: 10.1093/ce/zkae100
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace system play in the catalytic pyrolysis of LLDPE? Enhancing Yield and Precision
- What is a tubular furnace? Precision Heating for Lab and Industrial Applications
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace serve during Si/Al2O3/RGO synthesis? Precise Thermal Reduction & Bonding
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in two-stage pyrolysis? Precision Thermal Control
- How do three-zone tube furnaces support scalability? Bridge Lab to Industrial Production Seamlessly
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace form Nitrogen-doped Porous Carbon (RMF)? Precision Thermal Synthesis Guide
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for the in-situ reduction of NiO/Al2O3 catalysts? Optimize Your Lab Results
- What is the significance of the heating zone in a vertical tube furnace? Unlock Precision for Material Processing



















