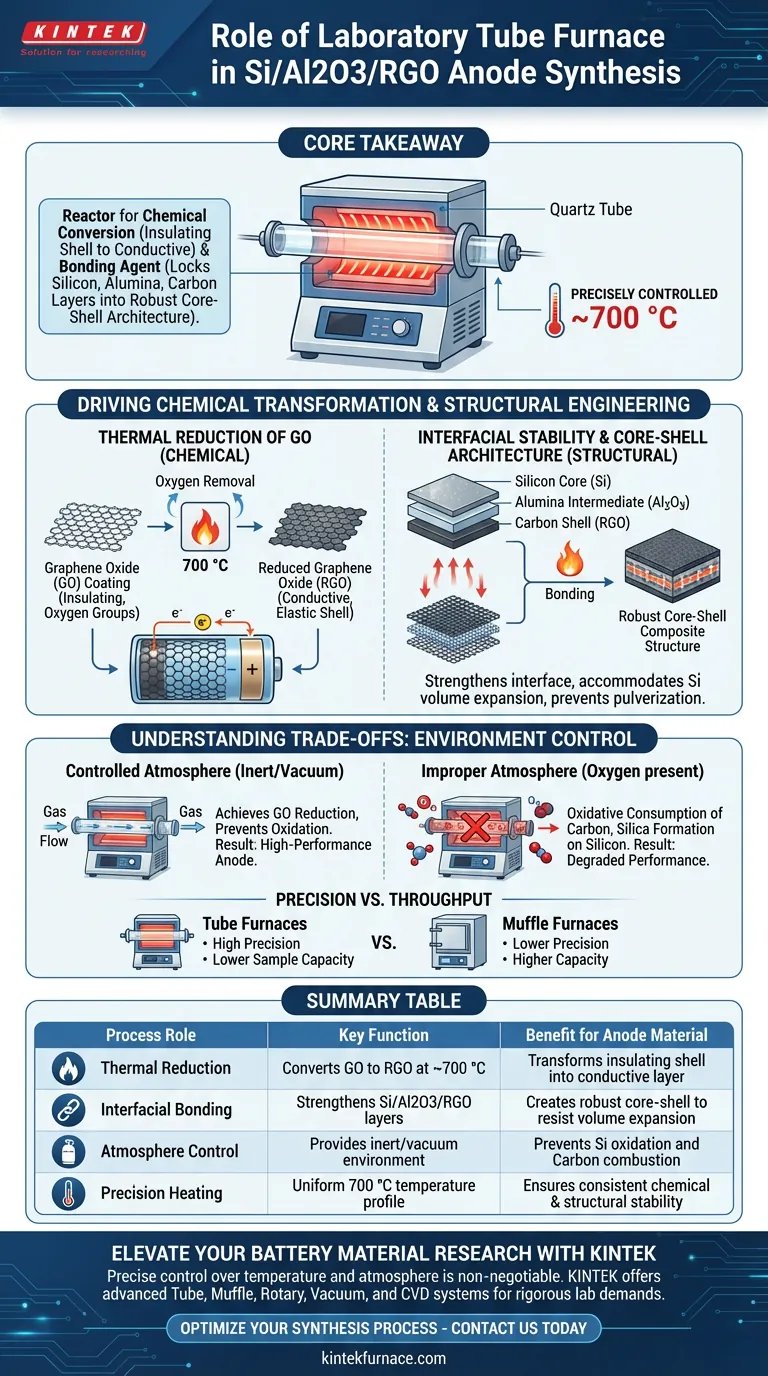
The primary role of a laboratory tube furnace in this synthesis is to provide a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment around 700 °C. This thermal energy drives the reduction of graphene oxide (GO) into reduced graphene oxide (RGO), transforming a passive coating into a conductive, elastic carbon shell. Furthermore, the heat treatment solidifies the interface between the silicon core, the alumina (Al2O3) intermediate layer, and the external RGO shell, ensuring structural integrity.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace is not merely a heating source; it is a reactor that facilitates the chemical conversion of the composite's shell from insulating to conductive. It simultaneously acts as a bonding agent, locking the silicon, alumina, and carbon layers into a robust core-shell architecture capable of withstanding battery cycling.
Driving Chemical Transformation
Thermal Reduction of Graphene Oxide
The most critical chemical reaction occurring within the furnace is the thermal reduction of graphene oxide (GO).
At temperatures reaching approximately 700 °C, the furnace removes oxygen-containing functional groups from the GO coating.
Creating a Conductive Shell
This reduction process converts the GO into reduced graphene oxide (RGO).
This transformation is essential because RGO serves as a highly conductive and elastic outer shell, allowing the anode material to conduct electrons efficiently during battery operation.
Structural Engineering and Stability
Enhancing Interfacial Stability
The heat treatment does more than change the surface chemistry; it creates a stable bond between the material's layers.
The high-temperature environment strengthens the interface between the internal silicon core, the intermediate alumina (Al2O3) layer, and the external carbon shell.
Forming the Core-Shell Architecture
The result of this thermal processing is a robust core-shell composite structure.
This architecture is critical for accommodating the volume expansion of silicon during charging while preventing the material from pulverizing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Environment Control
The Necessity of Atmosphere Control
While the primary reference focuses on heat, the choice of a tube furnace specifically implies the need for a controlled atmosphere.
To achieve the reduction of GO (removing oxygen) rather than the combustion of the carbon or oxidation of the silicon, the furnace likely operates under an inert gas flow or vacuum.
Risks of Improper Atmosphere
If the tube furnace fails to maintain a strictly controlled environment (inerting), oxygen may remain in the chamber.
This would lead to the oxidative consumption of the carbon shell or the formation of unwanted silica on the silicon surface, degrading the anode's performance.
Precision vs. Throughput
Tube furnaces offer exceptional control over temperature profiles and atmospheric purity, which is vital for this precise chemical reduction.
However, they typically have lower sample capacity compared to muffle furnaces, making them ideal for high-precision synthesis but a bottleneck for mass production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of your Si/Al2O3/RGO composite, ensure your heat treatment protocol is aligned with your specific structural requirements.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize maintaining a stable temperature at 700 °C to ensure the complete reduction of GO into conductive RGO.
- If your primary focus is Structural Longevity: Verify that the furnace atmosphere is perfectly inert to prevent oxidation of the silicon core, preserving the integrity of the Al2O3 interface.
The success of this composite relies on using the furnace not just to heat the material, but to precisely engineer its surface chemistry and layer adhesion.
Summary Table:
| Process Role | Key Function | Benefit for Anode Material |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Reduction | Converts GO to RGO at ~700 °C | Transforms insulating shell into a highly conductive carbon layer |
| Interfacial Bonding | Strengthens Si/Al2O3/RGO layers | Creates a robust core-shell architecture to resist volume expansion |
| Atmosphere Control | Provides inert or vacuum environment | Prevents silicon oxidation and carbon shell combustion |
| Precision Heating | Uniform 700 °C temperature profile | Ensures consistent chemical conversion and structural stability |
Elevate Your Battery Material Research with KINTEK
Precise control over temperature and atmosphere is non-negotiable for high-performance Si/Al2O3/RGO composite synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory. Whether you need specialized atmosphere control for chemical reduction or customizable high-temperature profiles, our furnaces are engineered to ensure your core-shell architectures remain robust and conductive.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact us today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Xiangyu Tan, Xin Cai. Reduced graphene oxide-encaged submicron-silicon anode interfacially stabilized by Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> nanoparticles for efficient lithium-ion batteries. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra00751d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace combustion system function in food waste analysis? Master Ultimate Analysis
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace during Ce-NiCoP phosphorization? Achieve Precise Catalyst Synthesis
- How does the positioning of the substrate within a tube furnace affect the in-situ growth of SnSe2 and SnSe?
- What are the key features of an alumina tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in Ti3AlC2 synthesis? Achieve Pure MAX Phase Precursor Powders
- What is the specific role of a Tube Furnace in the synthesis of sodium cobalt borate (NCBO)? Achieve Pure Crystals
- Why is a secondary high-temperature activation process in a tube furnace necessary? Converting Biochar into CBAC



















