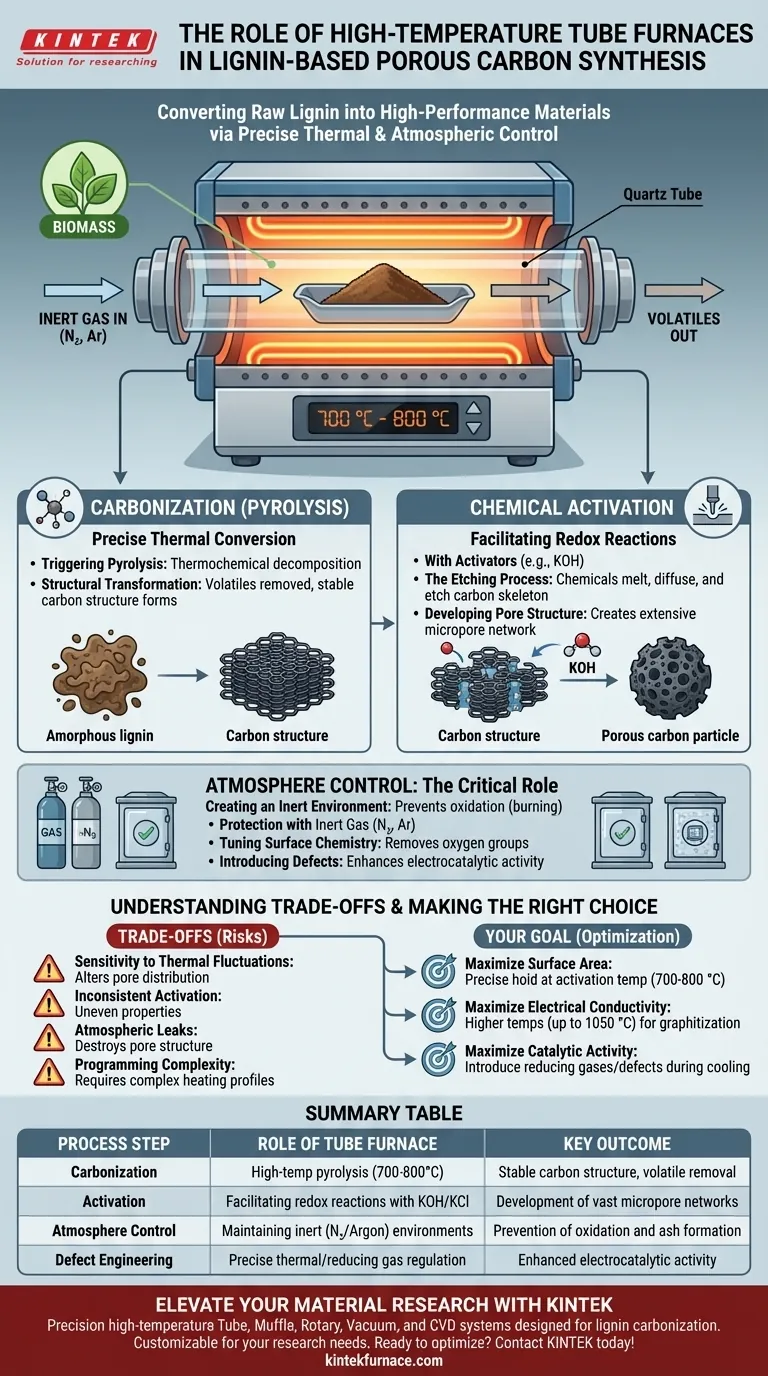
High-temperature tube furnaces serve as the precise thermal reactors required to convert raw lignin into functional, high-performance porous carbon. By providing a strictly controlled thermal environment—often around 700 °C—and a regulated atmosphere, these furnaces facilitate the simultaneous pyrolysis of lignin and the chemical activation needed to develop extensive pore networks.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace is not merely a heating device; it is a precision instrument for atmospheric and thermal regulation. Its stability allows chemical activators (like KOH) to predictably etch the carbon skeleton, ensuring the consistency of specific surface area and pore size distribution that defines the material's quality.
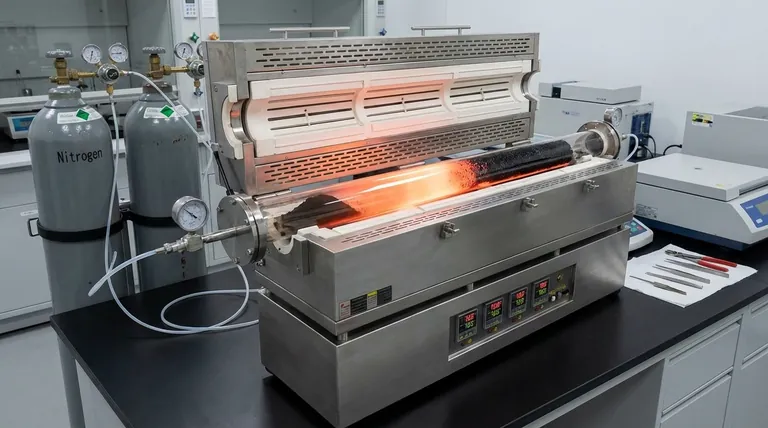

The Mechanics of Carbonization and Activation
Precise Thermal Conversion
The primary function of the furnace is to elevate the lignin to critical temperatures, typically in the range of 700 °C to 800 °C.
Triggering Pyrolysis
At these specific temperatures, the furnace triggers pyrolysis, a thermochemical decomposition that strips away volatile components.
Structural Transformation
This heat treatment transforms the organic polymer network of lignin into a stable, conductive carbon structure.
Facilitating Chemical Activation
When lignin is processed alongside chemical activators like Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) or Potassium Chloride (KCl), the furnace drives a redox reaction.
The Etching Process
Under the furnace's heat, these chemicals melt and diffuse, "etching" the carbon skeleton.
Developing Pore Structure
This controlled etching creates a vast network of micropores, directly resulting in the high specific surface area required for advanced applications.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Creating an Inert Environment
To prevent the lignin from simply burning away (oxidizing) into ash, the tube furnace maintains a sealed environment.
Protection with Inert Gas
Continuous flows of inert gases, such as Nitrogen (N2) or Argon, protect the material during the high-temperature phase.
Tuning Surface Chemistry
By introducing specific reducing gases or maintaining strict inert atmospheres, the furnace helps remove unwanted oxygen-containing functional groups.
Introducing Defects
Precise heating in these atmospheres can induce carbon vacancy defects, which significantly enhance the material's electrocatalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Thermal Fluctuations
The quality of porous carbon is strictly tied to temperature stability; even minor fluctuations can alter the pore size distribution.
Inconsistent Activation
If the furnace cannot maintain a uniform temperature zone, the chemical activation will be uneven, leading to heterogeneous material properties.
Atmospheric Leaks
The tube furnace relies on a perfect seal; any ingress of oxygen during the high-temperature phase will destroy the pore structure and drastically reduce yield.
Programming Complexity
Achieving the best results often requires complex heating programs (e.g., segmented heating rates or specific dwell times) rather than a simple ramp-to-temperature approach.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ideally, the operation of your tube furnace should be dictated by the specific properties you wish to engineer in your lignin-based carbon.
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area: Prioritize precise temperature holding at the activation point (e.g., 700–800 °C) to maximize the etching efficiency of KOH.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Ensure your furnace can reach higher temperatures (up to 1050 °C) to induce graphitization and structural ordering.
- If your primary focus is catalytic activity: Use the furnace's atmosphere controls to introduce reducing gases or create vacancy defects during the cooling phase.
Mastering the thermal and atmospheric controls of the tube furnace is the single most important step in transitioning from raw biomass to high-value carbon nanomaterials.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Role of Tube Furnace | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonization | High-temp pyrolysis (700-800°C) | Removal of volatiles; stable carbon structure |
| Activation | Facilitating redox reactions with KOH/KCl | Development of vast micropore networks |
| Atmosphere Control | Maintaining inert (N2/Argon) environments | Prevention of oxidation and ash formation |
| Defect Engineering | Precise thermal/reducing gas regulation | Enhanced electrocatalytic activity via defects |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of high-performance porous carbon. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of lignin carbonization and chemical activation. Whether you need uniform temperature zones for consistent etching or advanced atmosphere control to engineer specific surface chemistries, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research needs.
Ready to optimize your carbon synthesis? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your customized furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhihao Ding, Suxia Ren. Exploring the Connection Between the Structure and Activity of Lignin-Derived Porous Carbon Across Various Electrolytic Environments. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30030494
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What technological requirements affect tube furnace design? Key Factors for Optimal Performance
- What is the function of sealed quartz ampoules in Se80In5Te6Sb9 synthesis? Ensure Purity and Precision
- What experimental conditions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide for V2AlC MAX phase sintering?
- What Role Does a Tube Reactor Play in Food Waste Pyrolysis? Control Carbonization for High-Quality Biochar
- Why is a high-vacuum tube furnace required for sintering aluminum composites? Achieve Superior Purity and Density
- What is the role of a laboratory tube furnace in the carbonization of peanut shells? Master Biochar Preparation
- What are the key advantages of using a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Dynamic, Uniform Heating for Powders
- What conditions does a tube vacuum furnace provide for zinc sulfide distillation? Optimize Your Zinc Ore Processing



















