In short, the key advantage of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to simultaneously heat and mix materials. This dynamic process ensures every particle is treated uniformly, leading to exceptionally consistent results, higher efficiency, and faster processing times compared to static furnace designs.
A standard furnace simply heats a sample. A rotary tube furnace actively processes it. Its core value lies in creating a dynamic environment that guarantees uniform exposure to both temperature and atmospheric conditions, a critical requirement for advanced material synthesis and analysis.

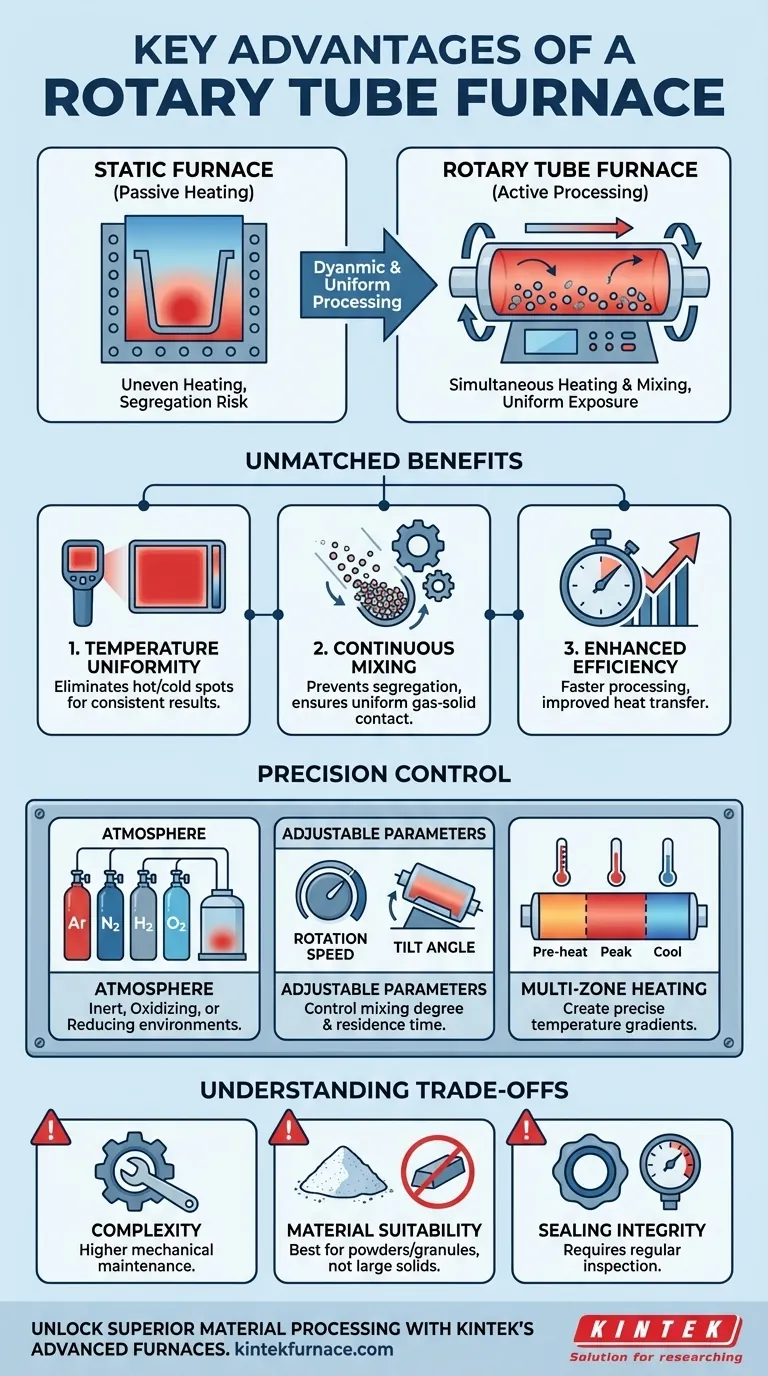
The Core Advantage: Dynamic and Uniform Processing
The defining feature of a rotary tube furnace is the rotation of the process tube. This simple mechanical action fundamentally changes how heat and atmosphere interact with the material inside, providing benefits that are impossible to achieve in a static system.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The constant tumbling and mixing of the material eliminates hot and cold spots. As particles move, they are continuously redistributed throughout the heated zone.
This prevents localized overheating or under-heating, ensuring that the entire batch of material experiences the exact same temperature profile. This uniformity is critical for processes where slight temperature deviations can ruin the final product.
Continuous Material Mixing
For powders, granules, and other bulk solids, the rotation prevents segregation and settling. Every particle is consistently exposed to the controlled atmosphere within the tube.
This is essential for chemical reactions, such as catalyst activation or roasting, where uniform gas-solid contact is necessary for the reaction to proceed evenly and completely.
Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency
By constantly agitating the material, the furnace significantly improves the efficiency of heat transfer. The movement increases the effective surface area exposed to the heat source at any given moment.
This often leads to shorter processing times and lower energy consumption to reach the target temperature compared to heating a static pile of the same material.
Precision Control Over the Processing Environment
Beyond its dynamic nature, a rotary tube furnace offers a high degree of control over every aspect of the thermal process, making it a versatile tool for research and production.
Adaptable Atmosphere Control
These furnaces are designed to operate with a tightly controlled atmosphere. You can introduce inert (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen), oxidizing (e.g., Air, Oxygen), or reducing (e.g., Hydrogen) gases.
This capability is vital for preventing unwanted oxidation or facilitating specific chemical transformations during the heating process.
Adjustable Process Parameters
Modern rotary furnaces allow for precise, intelligent control over key variables. The rotation speed can be adjusted to control the degree of mixing, while the tilt angle of the entire furnace can be changed.
Adjusting the tilt angle influences the residence time of the material within the heated zone, making it ideal for creating continuous or semi-continuous processing workflows.
Multi-Zone Heating
Many models feature multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube. This allows for the creation of precise temperature gradients.
A material can be pre-heated, held at a peak temperature, and then cooled according to a specific profile, all within a single pass through the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary design is not universally superior. Its advantages come with specific considerations.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor, drive system, and rotating seals, adds mechanical complexity compared to a simple, static tube furnace. This can translate to higher initial costs and more demanding maintenance requirements.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are explicitly designed for processing powders, granules, and small, free-flowing solids. They are not suitable for heating single large objects, delicate structures that could be damaged by tumbling, or liquids.
Sealing Integrity
Maintaining a perfect seal on a rotating tube is more challenging than on a static one. While modern designs are highly effective, the seals are a critical component that requires regular inspection and maintenance to ensure atmospheric integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible uniformity for powders or granules: The mixing action of a rotary tube furnace is essential and cannot be replicated in a static system.
- If your primary focus is continuous processing of bulk solids: The ability to control material flow via tilting makes the rotary furnace the superior choice for consistent throughput.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a solid, static sample (e.g., a crucible, wafer, or solid bar): A standard, non-rotating tube or chamber furnace is simpler, more cost-effective, and better suited for the task.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary tube furnace is a decision to prioritize dynamic processing and uniformity over simplicity.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Processing | Simultaneously heats and mixes materials for uniform exposure to temperature and atmosphere. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Eliminates hot/cold spots through constant tumbling, ensuring consistent results. |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Improves heat transfer, reducing processing times and energy consumption. |
| Precise Control | Adjustable rotation speed, tilt angle, and multi-zone heating for tailored workflows. |
| Atmosphere Versatility | Supports inert, oxidizing, or reducing gases for specific chemical reactions. |
Unlock Superior Material Processing with KINTEK's Advanced Rotary Tube Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our rotary tube furnaces are designed to deliver dynamic, uniform heating and mixing for powders and granules, ensuring consistent results and higher efficiency in your material synthesis and analysis. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Ready to enhance your lab's performance? Contact us today to discuss how our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, can be tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















