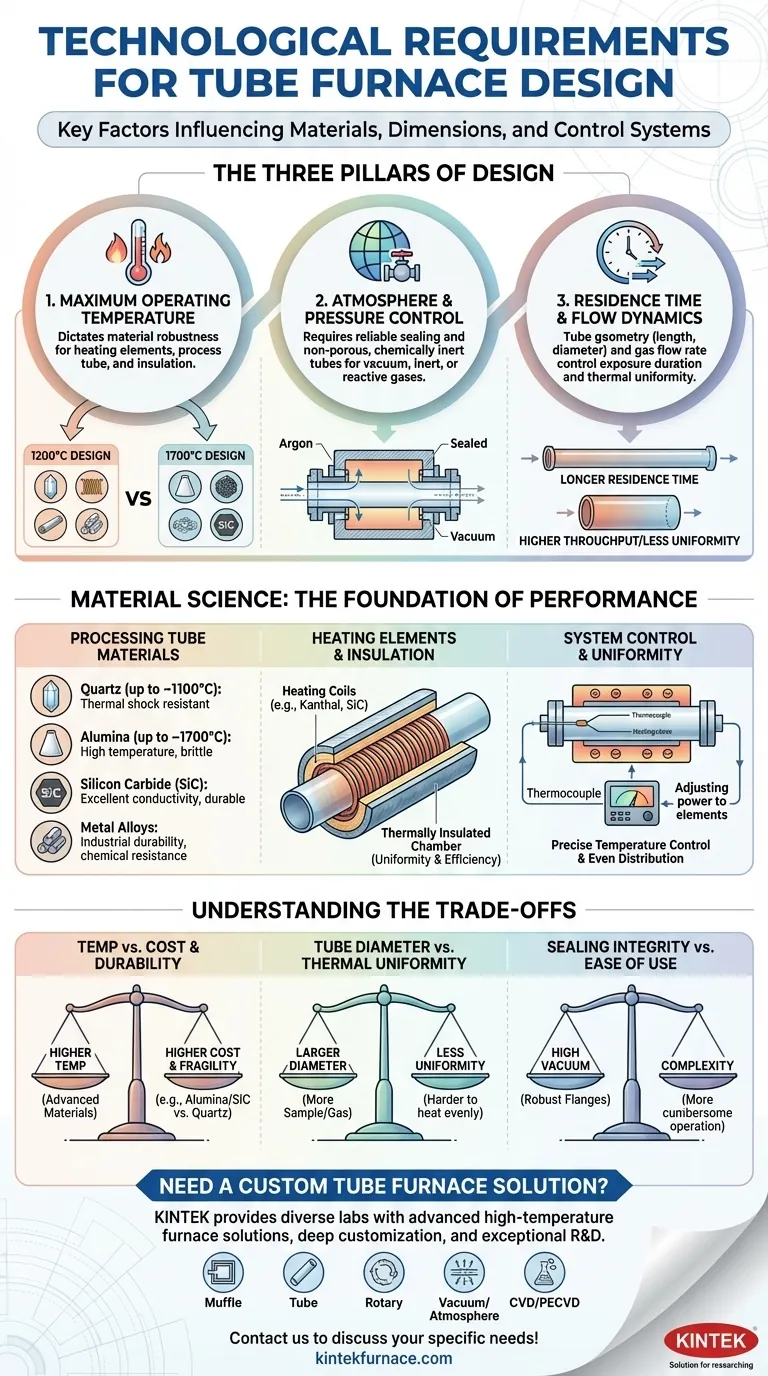
At its core, a tube furnace’s design is dictated by three primary technological requirements: the maximum operating temperature, the control of the internal atmosphere, and the desired residence time for the material being processed. These factors directly influence the choice of tube materials, heating elements, and the furnace's physical dimensions, with higher performance demands necessitating advanced alloys and more complex control systems.
The design of a tube furnace is not simply about generating heat. It is a calculated balance between achieving a specific, uniform thermal environment and respecting the physical and chemical limitations of the materials used to create it.
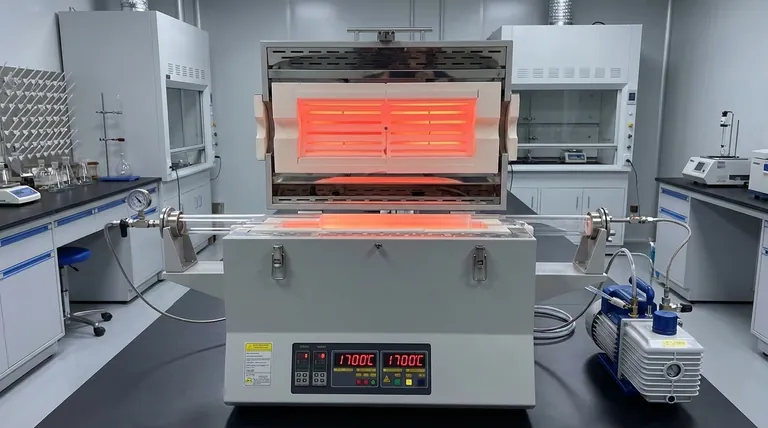

The Three Pillars of Tube Furnace Design
Every element of a tube furnace is a solution to a specific technological challenge. The design process centers on three fundamental parameters that define the furnace's purpose and capabilities.
1. Maximum Operating Temperature
The single most significant factor is the target temperature. This requirement has a cascading effect on every other component of the furnace.
Higher temperatures demand more robust materials for the heating elements, the process tube itself, and the thermal insulation that contains the energy. A furnace designed for 1200°C will use different materials than one built for 1700°C.
2. Atmosphere and Pressure Control
A tube furnace is designed to create an isolated, controlled environment. This involves more than just heat.
The ability to maintain a vacuum, introduce specific inert or reactive gases, or manage pressure is a critical design requirement. This dictates the need for reliable sealing at the tube ends and a process tube material that is non-porous and chemically inert to the desired atmosphere.
3. Residence Time and Flow Dynamics
Residence time—the duration a sample or gas is exposed to the heat—is controlled by the furnace tube's geometry and the flow rate of any gas.
A longer tube can increase reaction efficiency for continuous processes. The tube's diameter affects gas velocity and thermal uniformity, influencing how evenly the material is heated. These dimensions are not arbitrary; they are engineered to achieve a specific process outcome.
Material Science: The Foundation of Performance
The technological requirements can only be met if the right materials are used. The choice of material is a direct consequence of the temperature, chemical, and physical stresses the furnace must endure.
The Processing Tube
This is the heart of the furnace. The material must withstand the target temperature without degrading and remain inert to the chemicals being processed.
- Quartz is common for temperatures up to ~1100°C, offering excellent thermal shock resistance and high purity.
- Alumina is used for higher temperatures (up to ~1700°C) but is more brittle.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) offers excellent thermal conductivity and durability at very high temperatures.
- High-temperature metal alloys are used in industrial applications where durability and resistance to specific chemical attacks are paramount.
Heating Elements and Insulation
The system for generating and containing heat is just as critical as the tube.
Heating coils, often made of materials like Kanthal or SiC, are positioned around the tube to generate heat. The entire assembly is housed within a thermally insulated chamber to ensure energy efficiency and achieve high thermal uniformity along the tube's length.
System Control and Uniformity
Achieving a stable, uniform temperature is a key design goal. This prevents temperature gradients that could ruin an experiment or industrial process.
This is accomplished through a feedback loop. A thermocouple measures the temperature inside the furnace, and a controller adjusts the power to the heating elements to maintain the setpoint precisely. The physical arrangement of these elements is engineered to distribute heat evenly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or designing a tube furnace involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making an informed decision.
Temperature vs. Cost and Durability
The desire for higher operating temperatures directly increases cost. Materials like high-purity alumina or silicon carbide are significantly more expensive than quartz. They can also be more susceptible to thermal shock, requiring more careful operating procedures.
Tube Diameter vs. Thermal Uniformity
While a larger diameter tube allows for processing larger samples or higher gas throughput, it presents a challenge for heating. It is inherently more difficult to maintain a perfectly uniform temperature across a wider cross-section, which can impact process consistency.
Sealing Integrity vs. Ease of Use
Achieving a high-vacuum or perfectly controlled atmosphere requires complex, robust sealing flanges. While effective, these systems can be more cumbersome and time-consuming to operate than simpler end caps used for ambient pressure applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final design or purchasing decision must be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material synthesis: Prioritize furnaces with alumina or silicon carbide tubes and high-performance heating elements capable of reaching and sustaining your target temperature.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control for sensitive reactions: Scrutinize the quality of the end flanges and sealing system, and choose a non-porous tube material like high-purity quartz.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput continuous processing: Carefully consider the tube length and diameter to optimize for residence time and flow dynamics, accepting potential trade-offs in absolute thermal uniformity.
Ultimately, a well-designed tube furnace is one where the materials, dimensions, and control systems are all chosen in service of a specific technological goal.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Impact on Design | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Determines materials for tubes, heating elements, and insulation | Higher temps require advanced alloys, increasing cost and complexity |
| Atmosphere and Pressure Control | Influences sealing systems and tube material choice | Critical for vacuum, inert, or reactive gas environments |
| Residence Time and Flow Dynamics | Affects tube length, diameter, and heating uniformity | Optimizes for continuous processing and reaction efficiency |
Need a custom tube furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on high-temperature synthesis, precise atmosphere control, or high-throughput processing, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















