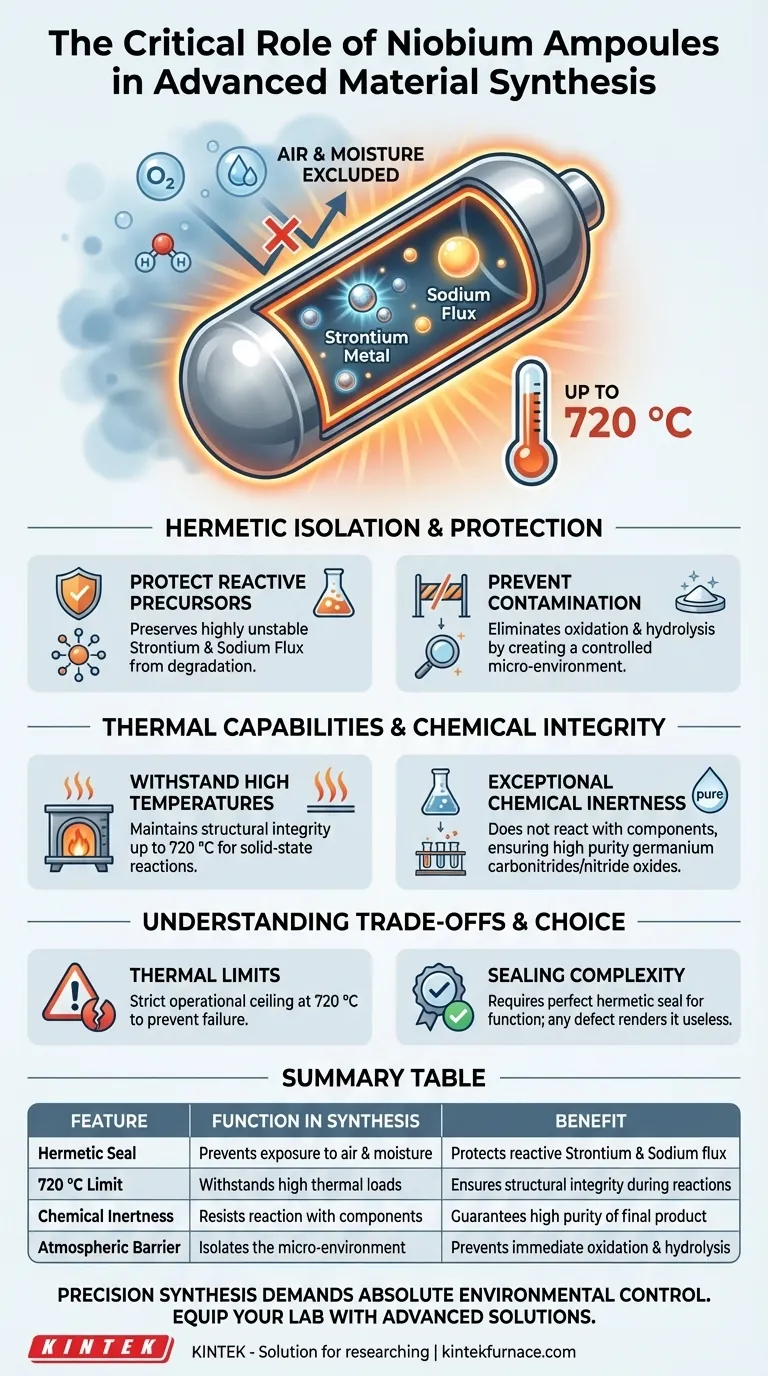
Niobium ampoules act as specialized, hermetically sealed reaction vessels essential for the high-temperature synthesis of sensitive materials like strontium germanium nitride oxides. Their primary role is to physically isolate highly reactive components—specifically strontium metal and sodium flux—from the external environment while enduring synthesis temperatures up to 720 °C.
Core Takeaway Niobium ampoules provide a chemically inert, hermetic environment that is critical for preventing the oxidation and hydrolysis of reactive precursors. Without this isolation, starting materials like strontium would degrade upon contact with air, making the synthesis of pure nitride oxides impossible.
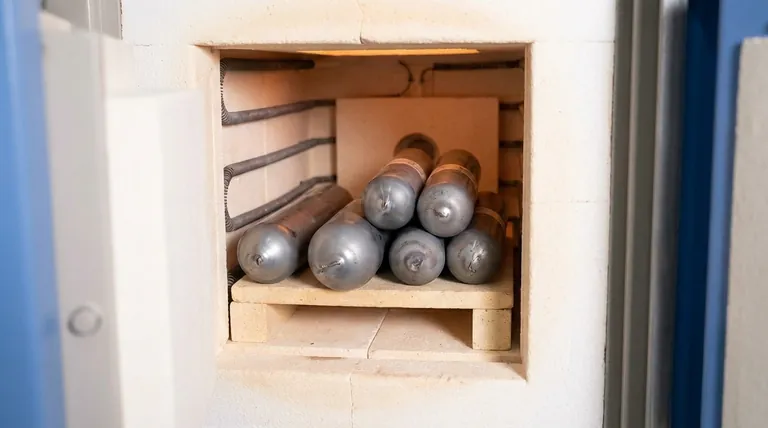

The Necessity of Hermetic Isolation
Protecting Reactive Precursors
The synthesis of strontium germanium nitride oxides requires the use of highly reactive starting materials. Specifically, strontium metal and sodium flux are unstable when exposed to standard atmospheric conditions. Niobium ampoules serve as a barrier that preserves the chemical integrity of these raw materials.
Preventing Environmental Contamination
The most significant threat to this synthesis is exposure to air and moisture. If the reaction mixture contacts the atmosphere, oxidation or hydrolysis will occur immediately. The hermetic seal of the Niobium ampoule creates a controlled micro-environment, ensuring that the reaction proceeds solely between the intended reactants.
Thermal Capabilities and Material Integrity
Withstanding High Synthesis Temperatures
Solid-state reactions often require significant thermal energy to proceed. Niobium ampoules are selected for their ability to maintain structural integrity at synthesis temperatures up to 720 °C. This allows researchers to heat the materials sufficiently without risking vessel failure.
Chemical Inertness
Beyond temperature resistance, the reaction vessel must not contaminate the sample. Niobium offers exceptional chemical inertness, meaning it does not react with the strontium, germanium, or nitrogen components inside. This ensures the final product is a pure germanium carbonitride or nitride oxide, rather than a compound contaminated by the vessel wall.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Limitations
While robust, these vessels have a defined operational ceiling. The synthesis protocols are strictly limited to temperatures up to 720 °C when using these specific ampoules. Exceeding this limit risks compromising the vessel's mechanical strength or seal integrity.
Sealing Complexity
The effectiveness of a Niobium ampoule relies entirely on a perfect hermetic seal. Unlike standard laboratory glassware, these vessels must be sealed completely to function. Any defect in the closure renders the ampoule useless for protecting moisture-sensitive fluxes like sodium.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure successful synthesis of these complex nitrides, align your vessel choice with your specific processing needs:
- If your primary focus is Purity: Prioritize the hermetic sealing process to ensure absolutely no air contacts the strontium metal or sodium flux.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Planning: Verify that your reaction protocol does not require temperatures exceeding the 720 °C threshold of the Niobium ampoules.
By utilizing Niobium ampoules, you effectively remove environmental variables, allowing for the precise and reproducible synthesis of air-sensitive solid-state compounds.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Synthesis | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hermetic Seal | Prevents exposure to air and moisture | Protects reactive Strontium and Sodium flux |
| 720 °C Limit | Withstands high thermal loads | Ensures structural integrity during solid-state reactions |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists reaction with internal components | Guarantees high purity of the final carbonitride product |
| Atmospheric Barrier | Isolates the micro-environment | Prevents immediate oxidation and hydrolysis |
Precision synthesis requires more than just high temperatures—it demands absolute environmental control. KINTEK provides the advanced lab solutions necessary for sensitive material research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a full range of customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the purity and integrity of your most reactive precursors. Whether you are synthesizing complex nitrides or high-performance oxides, our high-temp furnaces are built to meet your unique specifications. Contact KINTEK today to equip your laboratory with the tools for your next breakthrough!
Visual Guide
References
- Lukas Link, Rainer Niewa. Nitridogermanates(IV): The Germanide Oxide Sr<sub>15</sub>Ge[GeN<sub>4</sub>]<sub>3</sub>O, the Carbodiimide Ba<sub>5</sub>[GeN<sub>4</sub>][CN<sub>2</sub>], and the Oxidonitridogermanate Sr<sub>6</sub>[Ge<sub>2</sub>N<sub>6</sub>O]. DOI: 10.1002/zaac.202500068
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is rhenium selected as a material for sample capsules? Key Benefits for High-Temperature Experimental Success
- What are the mechanical and chemical advantages of alumina ceramic tubes? Discover Durability for High-Temp and Corrosive Environments
- Why are fume hoods and sealed quartz tubes mandatory for BiF3 and SbF3? Safety in High-Temp Fluoride Reactions
- Where are water circulating vacuum pumps commonly used? Essential for Lab and Industrial Vapor Handling
- Why is a Mass Flow Controller (MFC) important for gas-phase corrosion research? Ensure Data Integrity & Precision
- Why is Internal Radiation Baffle (IRB) technology used in mold designs? Enhance Directional Solidification Quality
- Why is a high-pressure MFC necessary for CHP systems? Achieve Precision in Catalytic Hydropyrolysis Data
- What are the roles of rotameters and digital flow controllers in pneumatic systems? Enhance Precision and Testing

















