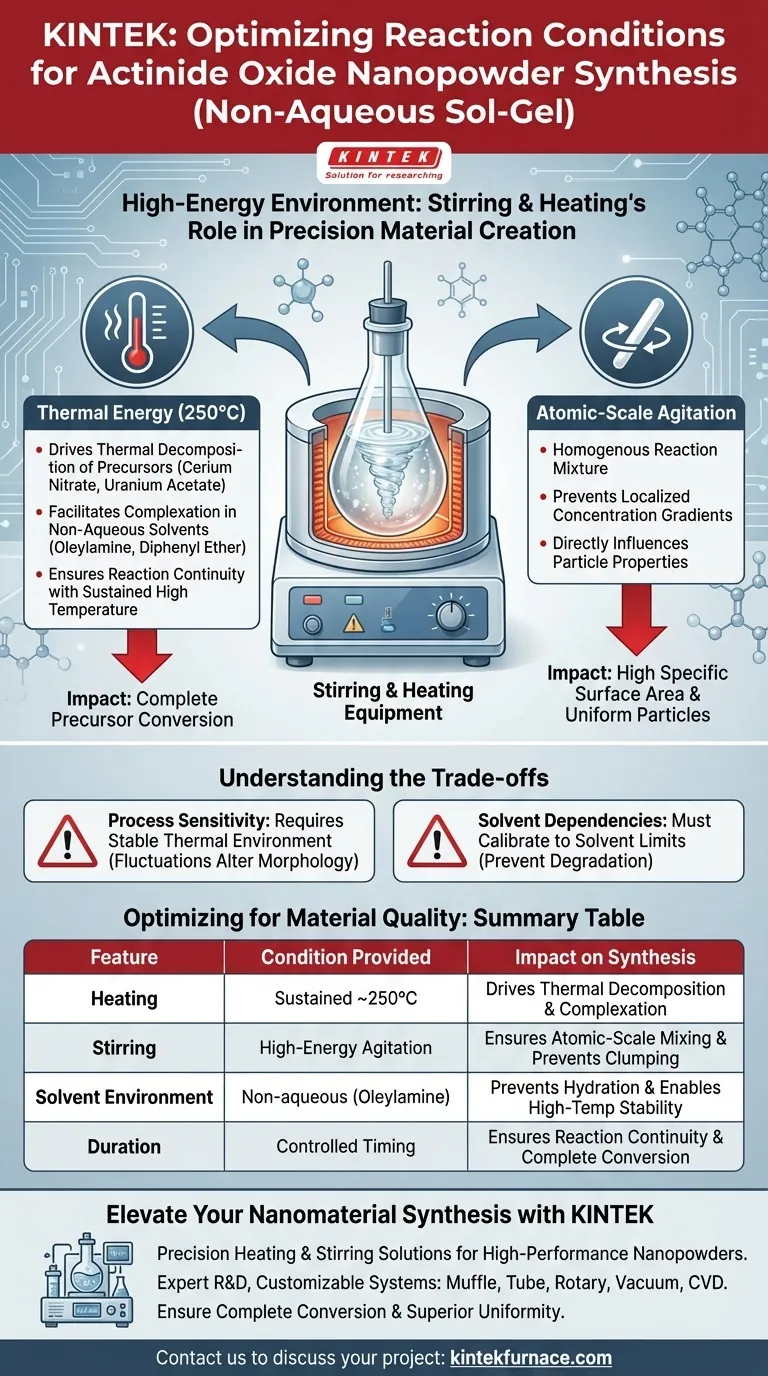
Stirring and heating equipment establishes a precise, high-energy environment essential for the successful non-aqueous sol-gel synthesis of actinide oxide nanopowders. Specifically, this equipment maintains a steady temperature, such as 250°C, to provide the thermal energy required for the decomposition and complexation of precursor salts within a solvent medium.
The core function of this setup is to facilitate atomic-scale mixing and thermal decomposition. By strictly controlling the temperature and agitation duration, the process transforms precursors like cerium nitrate or uranium acetate into nanoparticles with a high specific surface area.
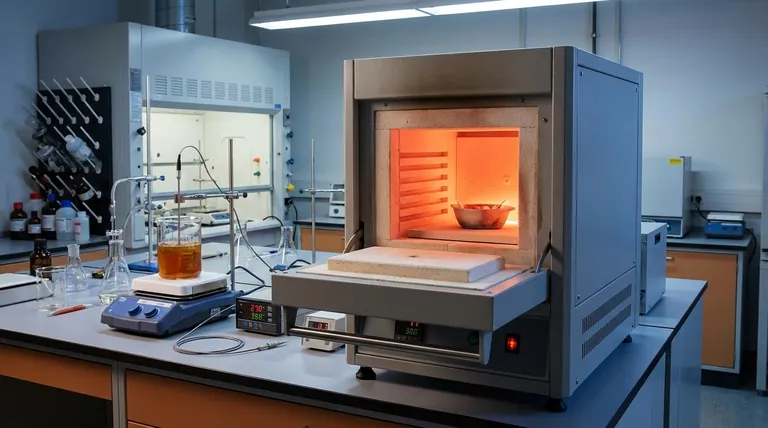

The Role of Thermal Energy
Driving Thermal Decomposition
The primary condition provided by the heating element is a sustained high temperature, typically around 250°C. This thermal energy is the catalyst that forces precursor salts, such as cerium nitrate or uranium acetate, to break down (decompose) chemically.
Facilitating Complexation
Beyond simple breakdown, the heat enables complexation, a process where the chemical components reassemble into new structures. This reaction occurs within specific non-aqueous solvents, notably oleylamine and diphenyl ether.
Ensuring Reaction Continuity
The equipment does not merely reach a peak temperature; it maintains this environment for a specific duration. This sustained input of energy ensures that the reaction proceeds to completion rather than stopping partially through the synthesis.
Achieving Atomic Precision
Atomic-Scale Mixing
Stirring equipment is responsible for creating a homogenous reaction mixture. This agitation ensures that the components are mixed at the atomic scale, preventing localized concentration gradients that could lead to uneven particle growth.
Determining Particle Properties
The combination of precise heating and continuous stirring directly influences the physical properties of the final product. These conditions induce the formation of nanoparticles that possess a high specific surface area, a critical quality for actinide oxide powders.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Sensitivity
While this method yields high-quality nanoparticles, it relies heavily on the stability of the thermal environment. Any fluctuation in temperature away from the target (e.g., 250°C) can disrupt the decomposition rate and alter the final particle morphology.
Solvent Dependencies
The success of these reaction conditions is intrinsically linked to the choice of solvent. The heating equipment must be calibrated to work within the thermal limits of solvents like oleylamine and diphenyl ether to prevent solvent degradation while still achieving the necessary activation energy for the precursors.
Optimizing Synthesis for Material Quality
To ensure the best results in your sol-gel synthesis, align your equipment settings with your specific material goals:
- If your primary focus is Particle Uniformity: Prioritize the consistency of your stirring mechanism to ensure atomic-scale mixing throughout the solvent.
- If your primary focus is Complete Precursor Conversion: Ensure your heating element can maintain exactly 250°C without fluctuation for the entire required duration.
Mastering these reaction conditions is the key to producing actinide oxide nanopowders with consistent, high-performance characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Condition Provided | Impact on Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Sustained ~250°C | Drives thermal decomposition and precursor complexation |
| Stirring | High-energy Agitation | Ensures atomic-scale mixing and prevents particle clumping |
| Solvent Environment | Non-aqueous (Oleylamine) | Prevents hydration and enables high-temperature stability |
| Duration | Controlled Timing | Ensures reaction continuity and complete conversion |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the cornerstone of successful non-aqueous sol-gel synthesis. KINTEK provides the advanced heating and stirring solutions necessary to maintain the strict 250°C environments and atomic-scale agitation required for high-performance actinide oxide nanopowders.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements. Ensure complete precursor conversion and superior particle uniformity with equipment designed for high-temperature stability.
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Lee Shelly, Shmuel Hayun. Unveiling the factors determining water adsorption on CeO <sub>2</sub> , ThO <sub>2</sub> , UO <sub>2</sub> and their solid solutions. DOI: 10.1007/s12598-025-03393-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an industrial-grade rapid heating furnace? Maximize Glass-Ceramic Debinding Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using an RTA system for CBTSe films? Precision Heating for Superior Thin Film Stoichiometry
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in CMS synthesis? Ensure High-Purity Precursor Integrity
- How are heat treatment furnaces utilized in the automotive industry? Enhance Component Durability and Performance
- What are the main types of sintering methods for metals, ceramics, and refractory intermetallic compounds powders? Optimize Your Material Processing
- What are the advantages of a benchtop industrial oven in terms of usability? Enhance Lab Efficiency with Compact Design
- How do industrial cameras and CNN improve surface defect detection? Revolutionize QC with 95%+ Accuracy
- Why is it necessary to dry Industrial EAF slag before hydrogen reduction? Crucial Safety and Accuracy Prep



















