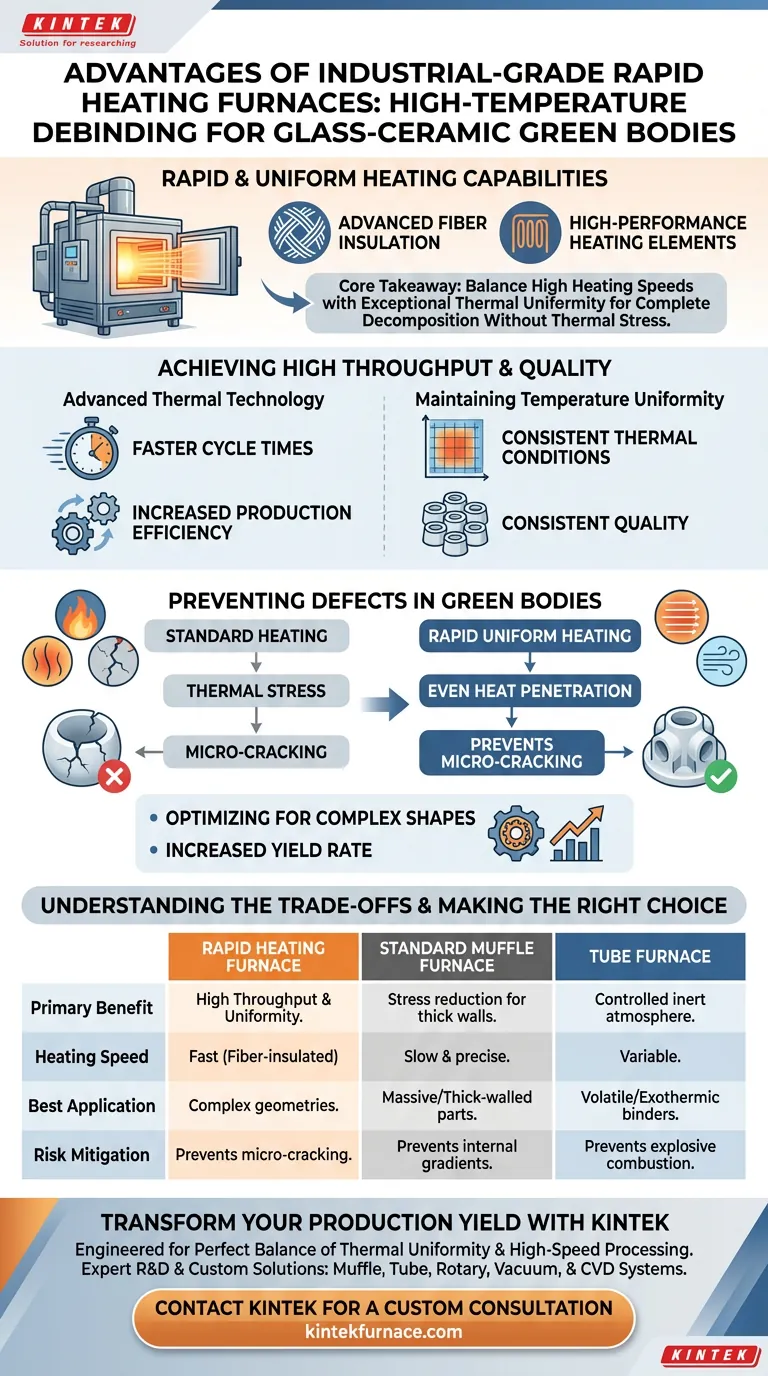
Rapid and uniform heating capabilities distinguish this equipment. An industrial-grade rapid heating furnace utilizes advanced fiber insulation and high-performance heating elements to reach debinding temperatures quickly without sacrificing internal consistency. This technology significantly improves production throughput while ensuring the structural integrity of complex glass-ceramic parts.
Core Takeaway By balancing high heating speeds with exceptional thermal uniformity, these furnaces allow for the complete decomposition of organic binders without inducing the thermal stress that typically leads to micro-cracking in complex green bodies.
Achieving High Throughput and Quality
Advanced Thermal Technology
The core advantage of an industrial-grade rapid heating furnace lies in its construction. It employs advanced fiber insulation and high-performance heating elements.
These components allow the chamber to reach the necessary debinding temperatures much faster than standard kilns. This directly translates to shorter cycle times and increased production efficiency.
Maintaining Temperature Uniformity
Rapid heating often risks creating hot spots, but this equipment is engineered to maintain excellent temperature uniformity throughout the chamber.
This consistency is critical for glass-ceramic green bodies. It ensures that every part of the component experiences the same thermal conditions simultaneously, regardless of its position in the furnace.
Preventing Defects in Green Bodies
Eliminating Thermal Stress
A major risk during debinding is the creation of temperature gradients between the interior and exterior of the ceramic body.
If the outside heats too fast relative to the inside, thermal stress occurs. The industrial-grade furnace mitigates this by ensuring the heat penetrates the body evenly, preventing the gradients that cause structural failure.
Preventing Micro-Cracking
When thermal stress is uncontrolled, it manifests as micro-cracking, which ruins the part.
By stabilizing the temperature gradient, this furnace type prevents these microscopic fissures. This is essential for maintaining the mechanical strength of the final product.
Optimizing for Complex Shapes
Complex geometries are particularly susceptible to cracking during binder removal.
The precise control and uniformity provided by this furnace increase the yield rate for these difficult components. It ensures organic binders decompose and are removed smoothly, even from intricate features.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Rapid vs. Slow Processing
While rapid heating is excellent for efficiency and complex shapes, it may not be suitable for every application.
For extremely large-scale or thick-walled structures, a standard high-precision muffle furnace may be preferable. These units often run programs lasting up to 48 hours to ensure very slow binder discharge, which is safer for massive parts.
Atmosphere Limitations
Industrial rapid heating furnaces typically focus on thermal efficiency in an oxidizing environment.
If your binders are prone to violent exothermic reactions, a tube furnace with an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen) might be required. This converts combustion into a controlled pyrolysis process, preventing explosive cracking that rapid heating might trigger in specific resin systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace for your glass-ceramic application, consider your specific constraints:
- If your primary focus is production speed and complex geometries: Choose the industrial-grade rapid heating furnace to maximize yield and minimize cycle times through superior uniformity.
- If your primary focus is extremely thick-walled parts: Opt for a muffle furnace to utilize long, slow ramp times that minimize internal stress during binder release.
- If your primary focus is volatile binder safety: Select a tube furnace to utilize an inert atmosphere, transforming violent combustion into controlled pyrolysis.
Selecting the right furnace technology transforms debinding from a production bottleneck into a precise, yield-enhancing step.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rapid Heating Furnace | Standard Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Benefit | High throughput & uniformity | Stress reduction for thick walls | Controlled inert atmosphere |
| Heating Speed | Fast (Fiber-insulated) | Slow & precise | Variable |
| Best Application | Complex geometries | Massive/Thick-walled parts | Volatile/Exothermic binders |
| Risk Mitigation | Prevents micro-cracking | Prevents internal gradients | Prevents explosive combustion |
Transform Your Production Yield with KINTEK
Don't let debinding become a bottleneck in your manufacturing process. KINTEK’s industrial-grade rapid heating solutions are engineered to provide the perfect balance of thermal uniformity and high-speed processing for complex glass-ceramic components.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your specific lab or industrial high-temperature requirements. Whether you need to eliminate micro-cracking in intricate shapes or manage volatile binders in an inert environment, our technical team is ready to design your ideal thermal cycle.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and precision?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Custom Consultation
Visual Guide
References
- Tao Shang, Xuebing Zhao. A Novel Low-Density-Biomass-Carbon Composite Coated with Carpet-like and Dandelion-Shaped Rare-Earth-Doped Cobalt Ferrite for Enhanced Microwave Absorption. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29112620
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA/DTG) provide industrial guidance? Optimize Blast Furnace Dust Treatment
- What is the purpose of bottom-entry argon injection? Enhance Lithium-ion Battery Safety & Purge Efficiency
- Why is industrial-grade isostatic pressing necessary for zirconia? Achieve Uniform Density & Structural Integrity
- Why is a vibratory mill used for ultra-fine grinding when preparing magnesite samples for zeta potential tests?
- How does low-temperature volatilization equipment function? Efficient Electrolyte Removal for Battery Recycling
- What is the primary role of an industrial-grade oven in the preparation of chitosan-modified soil samples?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for purifying zinc oxide nanoparticles? Superior Material Quality
- Why is rapid water quenching necessary after thermal compression? Capture True Microstructures in Medium-Mn Steel



















