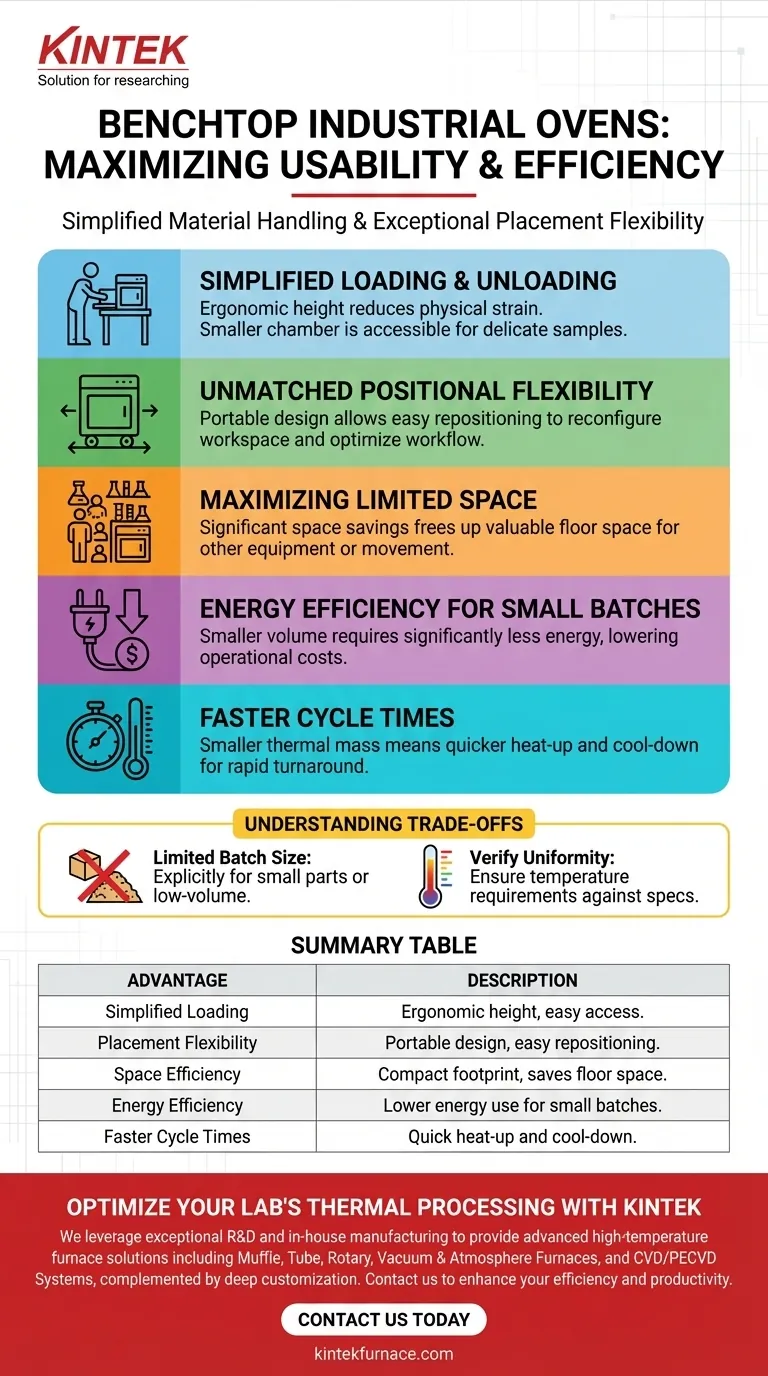
In terms of usability, a benchtop industrial oven's primary advantages are its simplified material handling and exceptional placement flexibility. Its compact size makes it significantly easier to load and unload samples compared to larger floor-standing units, and its portability allows it to be easily repositioned to optimize lab workflow as needs change.
The core value of a benchtop oven is not just its small footprint, but how that compact scale directly enhances day-to-day operations. It aligns the tool's size and energy consumption with the demands of small-batch, dynamic laboratory work, creating a more efficient and user-friendly process.

Optimizing Workflow with a Compact Footprint
The most immediate benefits of a benchtop design are physical and logistical. These ovens are engineered to integrate seamlessly into an existing workspace without causing major disruptions.
Simplified Loading and Unloading
Because these ovens are placed on a standard workbench, they are at an ergonomic height. This position reduces the physical strain of loading and unloading materials, which is particularly beneficial for technicians who perform these tasks frequently.
The smaller chamber door and accessible interior make placing and retrieving small, delicate samples a much simpler and more controlled action.
Unmatched Positional Flexibility
Unlike large, stationary ovens, a benchtop model is not a permanent fixture. This allows labs to reconfigure their workspace as projects evolve or as new equipment is introduced.
This mobility is a key usability feature for dynamic R&D environments where workflow is not always static and space must be adaptable.
Maximizing Limited Laboratory Space
The most obvious advantage is the significant space savings. For laboratories with a crowded floor plan or those operating in smaller facilities, a benchtop oven frees up valuable floor space for other critical equipment or movement.
This allows for the addition of thermal processing capabilities without requiring a major and costly lab redesign.
Beyond Physical Handling: The Efficiency Advantage
True usability extends beyond ergonomics to include operational efficiency. A benchtop oven excels when its use case is properly matched to its design.
Energy Efficiency for Small Batches
Heating a large oven chamber for a small number of samples is highly inefficient. A benchtop oven's smaller volume requires significantly less energy to reach and maintain a target temperature.
This directly translates to lower operational costs and is a more environmentally responsible choice for labs that primarily run small-scale tests.
Faster Cycle Times for Quick Turnaround
A smaller thermal mass allows a benchtop oven to heat up and cool down more quickly than a larger unit.
For labs needing rapid turnaround on quality control checks or experimental samples, this faster thermal cycling is a critical usability benefit that boosts overall productivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly usable in the right context, the benchtop design has inherent limitations that must be considered. Objectivity requires acknowledging where this tool is not the right fit.
The Constraint of Batch Size
The most significant trade-off is limited capacity. These ovens are explicitly designed for small parts or low-volume sample batches.
Attempting to use a benchtop oven for medium- to high-volume production will create a major bottleneck, negating any of its usability advantages.
Verifying Process Uniformity
While well-engineered, the smaller chamber size means that temperature uniformity must be carefully verified against your process requirements.
Always check the manufacturer's specifications for temperature deviation and ensure it meets the tolerance needed for your specific application, as an overloaded or poorly designed small oven can exhibit temperature gradients.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right oven depends entirely on the scale and goals of your work.
- If your primary focus is lab flexibility and frequent workflow changes: A benchtop oven is the ideal choice due to its portability and small footprint.
- If your primary focus is processing a high variety of small-batch samples: The energy efficiency and rapid cycle times of a benchtop oven will maximize your lab's productivity.
- If your primary focus is medium- to large-volume processing or treating large parts: A benchtop oven is unsuitable, and you should investigate larger, floor-standing batch or conveyor ovens.
Ultimately, choosing a benchtop oven is a strategic decision to align your equipment's scale perfectly with the demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplified Loading | Ergonomic height reduces strain; easy access for small samples. |
| Placement Flexibility | Portable design allows easy repositioning to optimize lab workflow. |
| Space Efficiency | Compact footprint saves floor space, ideal for crowded labs. |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy use for small batches, cutting operational costs. |
| Faster Cycle Times | Quick heat-up and cool-down for rapid sample turnaround. |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you require the usability of a benchtop oven or other specialized equipment, we can help enhance your efficiency and productivity. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do high-precision laboratory ovens play in assessing the energy potential of MSW? Enhancing Biomass Accuracy
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- What is the purpose of ashing furnaces? Achieve Precise Ash Analysis for Material Quality
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in eggshell powder pretreatment? Optimize AA6061 Composites
- What is a high-temperature vacuum furnace and where is it commonly used? Essential for Purity in Materials Science



















