At its core, an ashing furnace is a high-temperature oven designed for a specific analytical purpose: to completely burn away the combustible components of a sample. This process isolates the non-combustible inorganic residue, known as ash, allowing for its precise measurement. Common materials tested include petroleum products, coal, and lubricating oils, where ash content is a critical quality indicator.
The true purpose of an ashing furnace is not simply to burn a material, but to perform a precise quantitative analysis. By isolating a sample's inorganic content, it provides a crucial data point for evaluating material quality, purity, and performance characteristics.

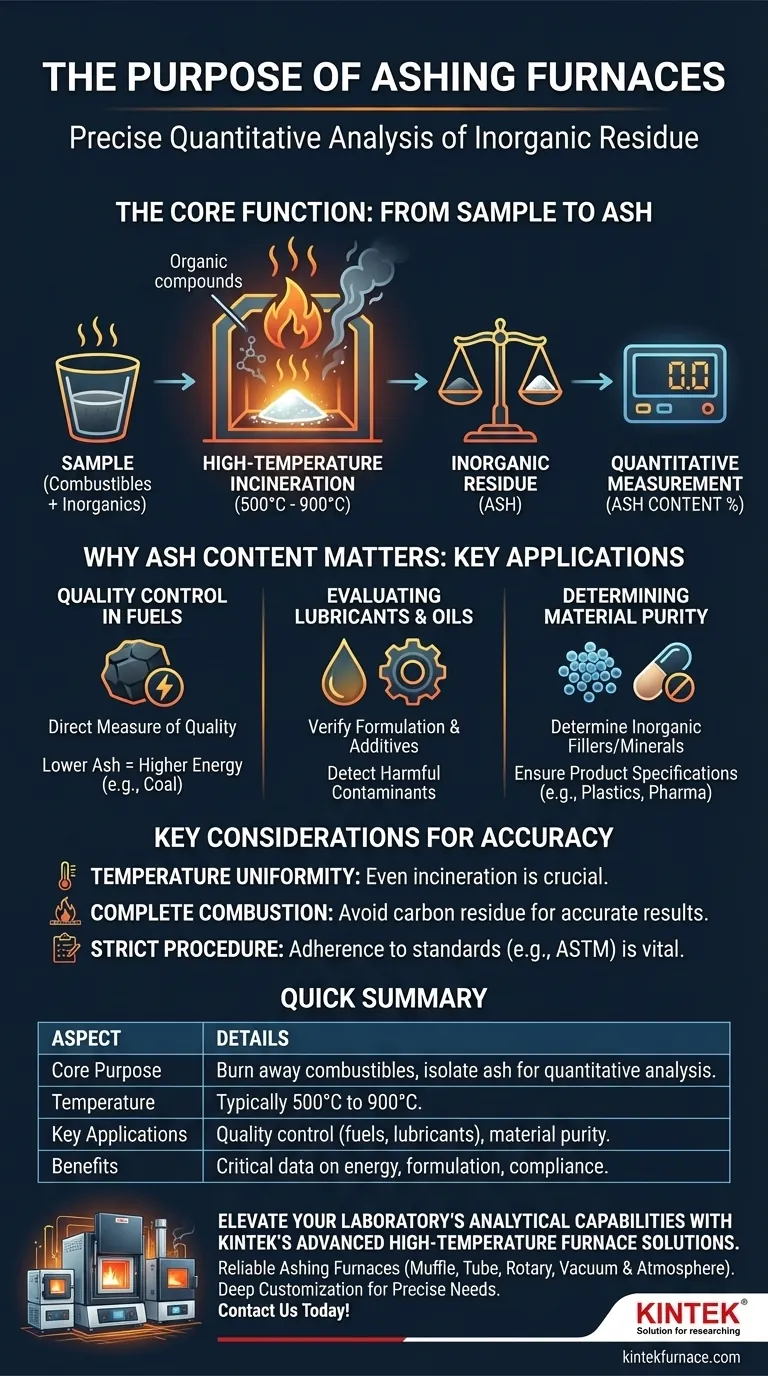
The Core Function: From Sample to Ash
An ashing furnace executes a controlled thermal decomposition process known as incineration or "ashing." This is a foundational technique in many analytical laboratories.
The Process of Complete Combustion
The furnace heats a sample to a specified high temperature, typically between 500°C and 900°C, in the presence of air. This controlled environment ensures that all organic or carbon-based substances in the sample are fully oxidized and burn away.
Isolating the Inorganic Residue
Once the combustion is complete, the only thing remaining is the ash. This residue consists of the inorganic components of the original sample, such as minerals, salts, and metallic compounds.
The Goal: Quantitative Measurement
The primary output is a number. The process involves carefully weighing a sample before it goes into the furnace and then weighing the remaining ash afterward. The difference, expressed as a percentage, is the ash content of the material.
Why Ash Content Matters: Key Applications
Determining ash content is rarely an academic exercise. It is a vital quality control metric across numerous industries that directly impacts performance, compliance, and cost.
Quality Control in Fuels
For materials like coal, ash content is a direct measure of quality. A lower ash percentage indicates more combustible material, meaning it will produce more energy per unit of weight. High ash content means less energy and more waste to manage.
Evaluating Lubricants and Oils
In lubricating oils, ash can signify the presence of metallic additives (like detergents or anti-wear agents) or harmful contaminants. Ashing tests help verify that the formulation is correct and free from abrasive impurities that could damage an engine.
Determining Material Purity
In plastics, food science, and pharmaceuticals, ashing is used to determine the total amount of inorganic fillers, minerals, or contaminants. This helps ensure a product meets its design specifications or regulatory standards.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the concept is simple, achieving accurate and repeatable results requires understanding the nuances of the equipment and process.
Ashing vs. General-Purpose Furnaces
An ashing furnace is specifically designed for this task. It must provide exceptional temperature uniformity to ensure the entire sample incinerates evenly. Many are also equipped with specialized ventilation to safely handle the fumes produced during combustion.
The Risk of Incomplete Combustion
If the temperature is too low or the duration is too short, combustion may be incomplete, leaving behind carbon residue that is not actually ash. This will artificially inflate the final measurement and lead to incorrect conclusions.
The Importance of Procedure
The accuracy of the analysis is highly dependent on strict adherence to standardized procedures (like those from ASTM). Factors like sample preparation, crucible type, and cooling processes must be carefully controlled to ensure the result is valid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Interpreting the results of an ashing test depends entirely on the material and your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is fuel efficiency: A lower ash percentage is almost always better, as it indicates a higher concentration of energy-producing material.
- If your primary focus is material composition: Ash content reveals the total amount of inorganic additives or fillers, which is essential for verifying product specifications.
- If your primary focus is lubricant quality: Ash content helps quantify the concentration of metallic detergent packages and can identify inorganic contamination.
Ultimately, using an ashing furnace provides a powerful and definitive tool for assessing the fundamental composition and quality of a material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Purpose | Burn away combustible components to isolate inorganic ash for quantitative analysis |
| Temperature Range | Typically 500°C to 900°C for complete combustion |
| Key Applications | Quality control in fuels (e.g., coal), lubricants, and material purity assessment |
| Benefits | Provides critical data on energy content, formulation accuracy, and compliance with standards |
| Considerations | Requires temperature uniformity, proper ventilation, and adherence to standardized procedures (e.g., ASTM) |
Elevate your laboratory's analytical capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable ashing furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering accurate ash content measurements for fuels, lubricants, and materials. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your quality control and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature laboratory oven play in catalyst activation? Boost Surface Area and Performance
- What is a high-temperature vacuum furnace and where is it commonly used? Essential for Purity in Materials Science
- Why is it necessary to dry glassware in a 140 °C oven overnight before GTP? Ensure Precise Anhydrous Polymerization
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- How are a muffle furnace and ceramic crucible used for MoO3? Master High-Purity Synthesis Today



















