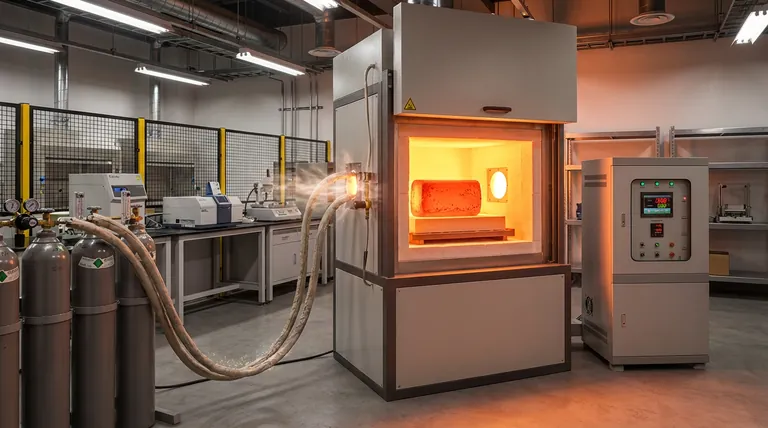
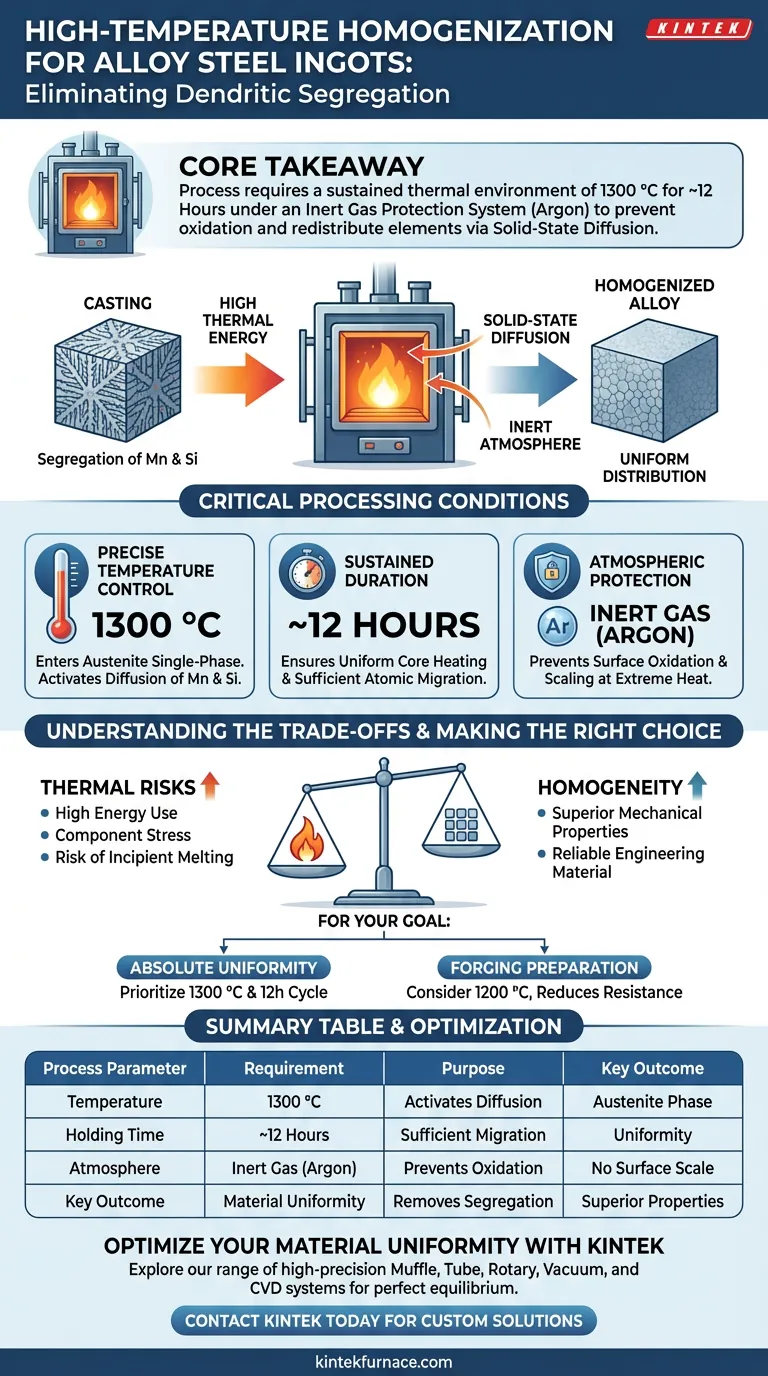
To eliminate dendritic segregation in alloy steel ingots, a high-temperature homogenization furnace must provide a sustained thermal environment of approximately 1300 °C for a duration of roughly 12 hours. Crucially, the system must be equipped with an inert gas protection system, typically using argon, to prevent excessive surface oxidation during this prolonged heating cycle.
Core Takeaway The homogenization process relies on solid-state diffusion to redistribute segregated elements like Manganese and Silicon. By maintaining high temperatures within an inert atmosphere, the furnace allows these elements to migrate from dendritic boundaries to a uniform distribution without degrading the material's surface.

The Mechanics of Homogenization
Targeting Dendritic Segregation
During the initial casting of alloy steel, the material creates a dendritic (tree-like) structure. This naturally leads to segregation, where certain elements cluster rather than mixing evenly.
Specifically, substitutional solute elements such as Manganese (Mn) and Silicon (Si) tend to concentrate in specific areas during solidification. The homogenization furnace is the primary tool used to correct this non-uniformity.
Activating Solid-State Diffusion
The core principle behind this process is solid-state diffusion. At room temperature, atoms are relatively static.
However, by raising the thermal energy, the furnace increases atomic mobility. This allows the segregated atoms (Mn and Si) to migrate through the crystal lattice, moving from areas of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Critical Processing Conditions
Precise Temperature Control
To be effective, the furnace must reach temperatures sufficient to enter the austenite single-phase region.
According to rigorous standards, this requires a temperature of 1300 °C. This extreme heat reduces the material's resistance to plastic deformation and provides the activation energy necessary for heavy substitutional elements to diffuse effectively.
Sustained Duration
Diffusion is not instantaneous. The furnace must maintain this peak temperature for an extended period, typically 12 hours.
This duration ensures that the core of the ingot reaches the same temperature as the surface and that the solute elements have sufficient time to migrate throughout the entire experimental sample.
Atmospheric Protection
Subjecting steel to 1300 °C in standard air would result in severe surface degradation.
Therefore, the furnace must utilize an inert gas protection system, such as argon. This creates a shielded environment that prevents oxygen from reacting with the steel, ensuring the ingot remains free from excessive surface oxidation or scaling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Risks vs. Homogeneity
While higher temperatures accelerate diffusion, they also introduce risks. Operating at 1300 °C places significant stress on the furnace components and energy resources.
Furthermore, if the temperature control fluctuates significantly, there is a risk of incipient melting at grain boundaries, which can permanently damage the alloy's mechanical properties.
Processing Efficiency
The requirement for a 12-hour cycle represents a significant bottleneck in production throughput.
While a lower temperature (e.g., 1200 °C used in forging) helps reduce plasticity resistance and begins the homogenization process, the dedicated 1300 °C cycle is often required for the complete elimination of stubborn dendritic segregation in high-quality alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters you choose depend on the balance between material quality and operational efficiency.
- If your primary focus is Absolute Material Uniformity: Prioritize the full 1300 °C for 12 hours cycle under argon to ensure complete diffusion of Manganese and Silicon.
- If your primary focus is Forging Preparation: A temperature of 1200 °C may be sufficient to lower deformation resistance and enter the austenite phase, though it may not fully resolve severe segregation.
Ultimately, true homogenization requires a commitment to time and temperature protection to transform a cast structure into a reliable engineering material.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1300 °C | Enters austenite phase and activates solid-state diffusion |
| Holding Time | ~12 Hours | Allows sufficient migration of Mn and Si atoms |
| Atmosphere | Inert Gas (Argon) | Prevents surface oxidation and scaling at high heat |
| Key Outcome | Material Uniformity | Removes dendritic structures for superior mechanical properties |
Optimize Your Material Uniformity with KINTEK
Don't let dendritic segregation compromise your alloy performance. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including high-precision lab furnaces fully customizable for your homogenization needs. Whether you require precise 1300 °C stability or advanced argon atmosphere control, our team delivers the technology to ensure your engineering materials achieve perfect equilibrium.
Ready to upgrade your heat treatment precision?
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Monika Krugla, Dave N. Hanlon. Microsegregation Influence on Austenite Formation from Ferrite and Cementite in Fe–C–Mn–Si and Fe–C–Si Steels. DOI: 10.3390/met14010092
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does sintering atmosphere affect aluminum matrix composites? Optimize Hardness and Thermal Conductivity
- What is an atmospheric furnace? Understand the Risks & Efficiency of Your Home Heating
- What are the advantages of a hydrogen reducing atmosphere for stainless steel MIM parts? Achieve Superior Integrity
- What are the common industrial processes performed using an atmosphere box furnace? Discover Key Applications for Material Processing
- How does a high-temperature furnace facilitate the molten salt synthesis of CoNb2O6? Precision Thermal Control Guide
- What is a controlled atmosphere for heat treatment? Prevent Oxidation & Decarburization for Superior Metallurgical Results
- What are the cost considerations when using argon in heat treatment? Maximize Savings and Quality
- What industries commonly use controlled atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Tech Manufacturing



















