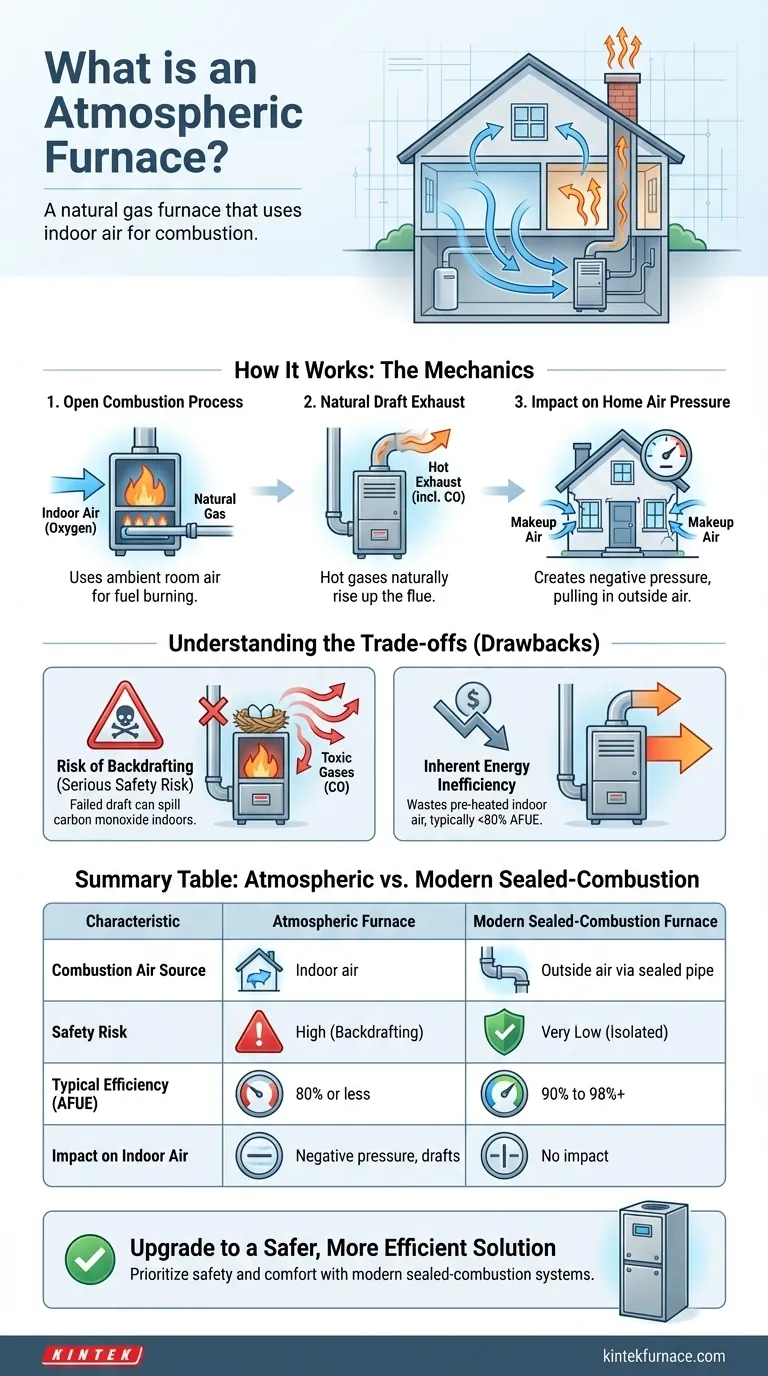
In simple terms, an atmospheric furnace is a type of natural gas furnace that uses the air from inside your home to fuel its combustion process. It draws this air through a grill or vent directly on the unit, mixes it with natural gas at the burner, and ignites the mixture to create heat. This design effectively makes the furnace "breathe" the same air you do.
The defining characteristic of an atmospheric furnace is its reliance on open combustion, using indoor air to burn fuel. While mechanically simple, this design has critical implications for your home's safety, air quality, and energy efficiency when compared to modern alternatives.

How an Atmospheric Furnace Works
Understanding the mechanics of an atmospheric furnace reveals why it's a technology that has been largely superseded in modern home construction. Its operation is based on simple, natural principles.
The Open Combustion Process
An atmospheric furnace features exposed burners, often visible behind a louvered panel. It pulls in surrounding air from the room it's in—typically a basement or utility closet—to provide the oxygen needed to burn natural gas.
This process is "atmospheric" because it uses air at the normal, ambient pressure of the room, without the help of a fan to force air into the burner.
Natural Draft Exhaust
After combustion, the hot, lightweight exhaust gases (including dangerous carbon monoxide) naturally rise. This principle, known as natural draft or convection, carries the fumes up through a metal flue pipe or chimney and vents them outside.
The furnace relies entirely on this passive movement of hot air to safely remove its byproducts.
The Impact on Home Air Pressure
Because the furnace consumes a significant amount of indoor air for combustion and sends it up the flue, it creates a slight negative pressure inside your home.
Your house then tries to equalize this pressure by pulling in "makeup" air from the outside through any available cracks, gaps, or window seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The simple design of an atmospheric furnace comes with significant drawbacks that are critical for any homeowner to understand. These trade-offs are the primary reason this technology is now considered outdated.
The Risk of Backdrafting
The most serious risk is backdrafting. If the natural draft up the flue fails—due to a blockage like a bird's nest, or strong negative pressure from running kitchen or bathroom exhaust fans—the toxic combustion gases can't escape.
Instead, they spill backward out of the furnace and into your living space. This can lead to a dangerous buildup of carbon monoxide (CO), an odorless, poisonous gas.
Inherent Energy Inefficiency
Atmospheric furnaces are inherently inefficient. They use air that you have already paid to heat for the combustion process, only to immediately exhaust it outside.
This constant loss of pre-heated indoor air means the system has to work harder and burn more fuel to maintain your home's temperature. Most atmospheric furnaces have an AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) rating of 80% or less, meaning at least 20 cents of every dollar you spend on fuel is wasted.
Simplicity vs. Modern Reliability
On the positive side, their simple design with fewer moving parts (like a draft-inducer motor) meant they were historically inexpensive and straightforward to service.
However, their performance and safety are highly dependent on external conditions, unlike modern sealed-combustion furnaces which offer more controlled and reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Situation
Whether you currently own an atmospheric furnace or are evaluating heating options, understanding its place in HVAC technology is key to making an informed decision.
- If you currently own an atmospheric furnace: Prioritize safety by installing carbon monoxide detectors on every level of your home and having the unit professionally inspected and cleaned annually.
- If you are replacing an old furnace: Choose a modern, high-efficiency sealed-combustion model. The energy savings and significant safety improvements provide a clear long-term benefit.
- If your primary focus is indoor air quality: A sealed-combustion furnace is the superior choice, as it completely isolates the combustion process from your home's air supply.
Ultimately, knowing what kind of furnace you have empowers you to manage its risks and plan for a safer, more efficient future.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Atmospheric Furnace | Modern Sealed-Combustion Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion Air Source | Indoor air from your home | Outside air through a sealed pipe |
| Safety Risk | High (risk of carbon monoxide backdrafting) | Very Low (combustion is isolated) |
| Typical Efficiency (AFUE) | 80% or less | 90% to 98%+ |
| Impact on Indoor Air | Creates negative pressure, can pull in drafts | No impact on indoor air quality |
Upgrade to a Safer, More Efficient Heating Solution
Your family's safety and comfort are paramount. While atmospheric furnaces represent older technology, modern high-efficiency systems offer unparalleled safety and significant energy savings.
At KINTEK, we leverage our advanced R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide robust, reliable heating solutions. While our core expertise is in high-temperature laboratory furnaces (like Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum Furnaces), our engineering principles of precision, safety, and efficiency are universal.
If you are an HVAC professional or manufacturer looking for advanced thermal system components or custom engineering support, our deep customization capabilities can help you build a better product.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how KINTEK's engineering excellence can meet your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage



















