In essence, an inert atmosphere prevents oxidation by starving the chemical reaction of its key ingredient: oxygen. By actively purging an environment and replacing the ambient air with a non-reactive gas—most commonly nitrogen or argon—you create a protective shield. This shield physically displaces the oxygen, making it impossible for the oxidation reaction to begin, thereby preserving the integrity of the material or process.
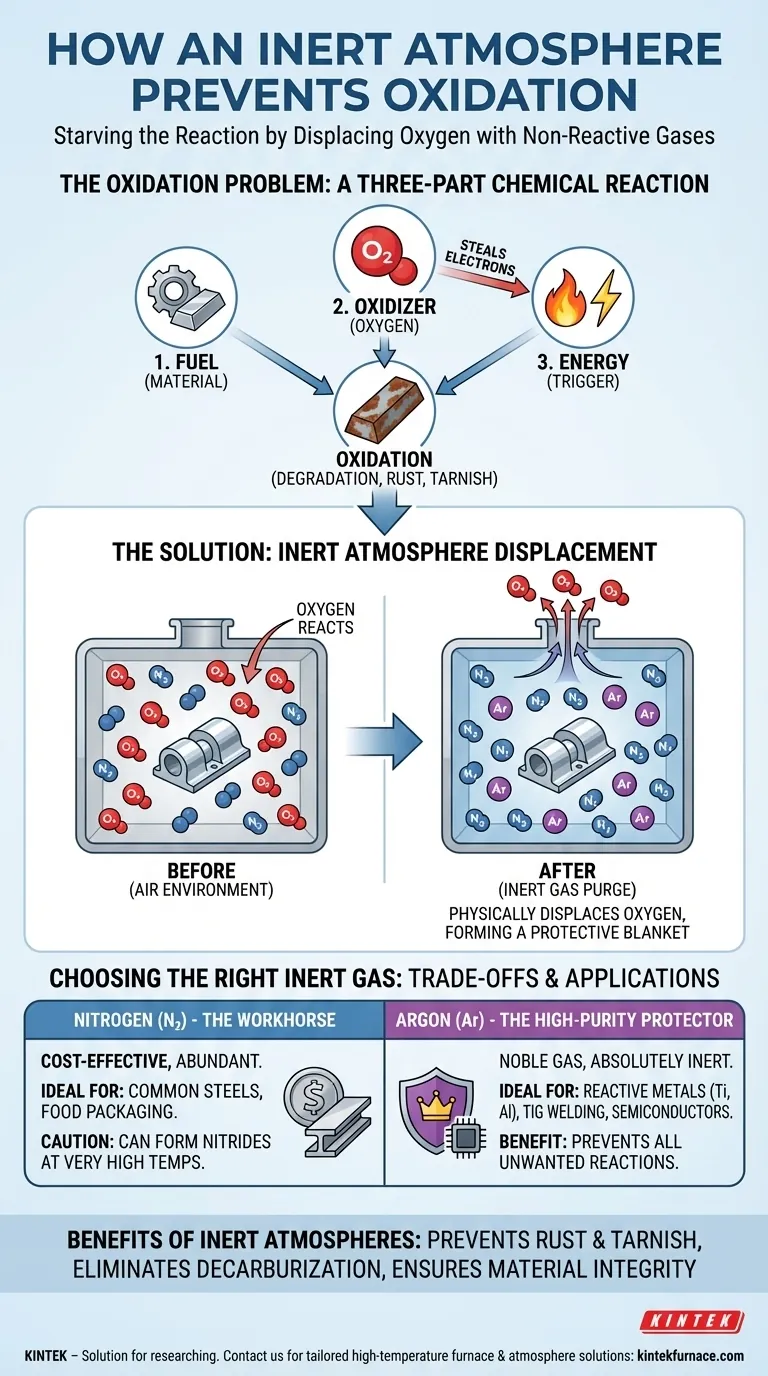
Oxidation is a chemical reaction that requires both a material to act as fuel and an oxidizer, which is typically oxygen. An inert atmosphere is a tool for precisely removing the oxidizer from the equation, giving you control over material integrity during sensitive processes.

The Chemistry of Oxidation: A Three-Part Problem
To understand how an inert atmosphere works, you must first understand what you are trying to prevent. Oxidation is a chemical process that degrades materials, but it depends on a few key components being present.
The Role of the Oxidizer (Oxygen)
Oxygen is a highly reactive element. Due to its atomic structure, it has a strong tendency to "steal" electrons from other substances. This process of losing electrons is what we call oxidation.
In common terms, this reaction manifests as rust on iron, tarnish on silver, or even the browning of a cut apple.
The Role of the Material (The "Fuel")
The material you are trying to protect—be it molten metal, a chemical compound, or a sensitive electronic component—acts as the fuel for the reaction. Its atoms are what surrender electrons to the oxygen.
Without a material susceptible to oxidation, the oxygen has nothing to react with.
The Role of Energy (The Trigger)
While oxidation can happen slowly at room temperature, processes like welding, 3D printing, or heat treating add significant energy in the form of heat. This energy acts as a powerful catalyst, dramatically accelerating the rate of oxidation and causing severe damage in seconds.
How an Inert Atmosphere Breaks the Reaction
An inert atmosphere is an engineered solution that intervenes in this process by removing one of the critical components.
The Principle of Displacement
The fundamental mechanism is physical displacement. By flooding a sealed chamber or a localized area with an inert gas, you physically push the lighter oxygen molecules out of the way.
This process, often called purging, continues until the concentration of oxygen is so low that oxidation cannot meaningfully occur. A continuous, low-pressure flow can then create a "blanket" that prevents any new oxygen from entering the work area.
The Nature of Inert Gases
Gases like nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar) are called "inert" because they are chemically stable. Their atoms have a full outer shell of electrons, meaning they have no desire to share, gain, or lose electrons.
Unlike reactive oxygen, these gases will not interact with your material, even at high temperatures. They simply serve as a neutral, non-reactive placeholder that occupies the space oxygen otherwise would.
Preventing Secondary Reactions
Beyond just oxidation, an inert atmosphere can prevent other unwanted reactions. For instance, in the heat treatment of steel, it prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the steel's surface—which would otherwise be drawn out by reacting with oxygen.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right Gas
While the principle is simple, the choice of inert gas involves balancing cost against chemical purity. Not all inert gases are equally inert under all conditions.
Nitrogen: The Workhorse
Nitrogen is the most common and cost-effective choice for creating an inert atmosphere. It makes up about 78% of the air we breathe and is easily separated for industrial use.
For the vast majority of applications, such as heat treating common steels or food packaging, nitrogen provides excellent protection against oxidation. However, at very high temperatures, it can react with certain metals like titanium, aluminum, and magnesium to form nitrides, which can make the material brittle.
Argon: The High-Purity Protector
Argon is a noble gas, making it significantly more inert than nitrogen. It will not react with any other element, even under extreme heat and pressure.
This absolute inertness makes it the mandatory choice for processes involving highly reactive metals, such as the TIG welding of titanium or aluminum. It is also used in high-tech applications like semiconductor manufacturing, where even the slightest contamination can ruin a component. This higher degree of protection comes at a higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the sensitivity of your material and the demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general applications: Nitrogen is almost always the most economical and effective choice for preventing oxidation on common steels and most materials.
- If your primary focus is maximum protection for reactive metals or high-purity processes: Argon is the superior choice, as its complete inertness prevents unwanted side-reactions like nitriding at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is handling sensitive electronics or scientific analysis: High-purity argon is essential to guarantee a completely non-reactive environment and avoid any sample contamination.
By understanding that an inert atmosphere is a tool for removing oxygen, you can confidently select the right gas to protect your material's integrity and ensure process success.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Displaces oxygen with non-reactive gases like nitrogen or argon to stop oxidation reactions. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Argon (high-purity for reactive metals). |
| Applications | Welding, 3D printing, heat treating, semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Benefits | Prevents rust, tarnish, decarburization; ensures material integrity in sensitive processes. |
Protect your materials with precision! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're handling reactive metals or need cost-effective oxidation prevention, our expertise ensures optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process with tailored inert atmosphere solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















