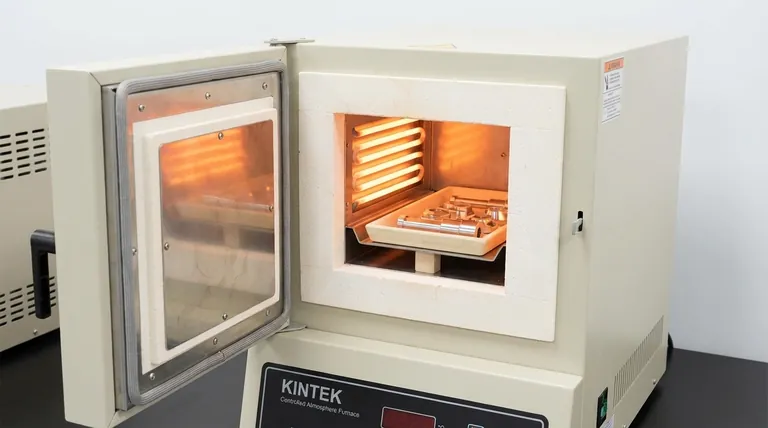
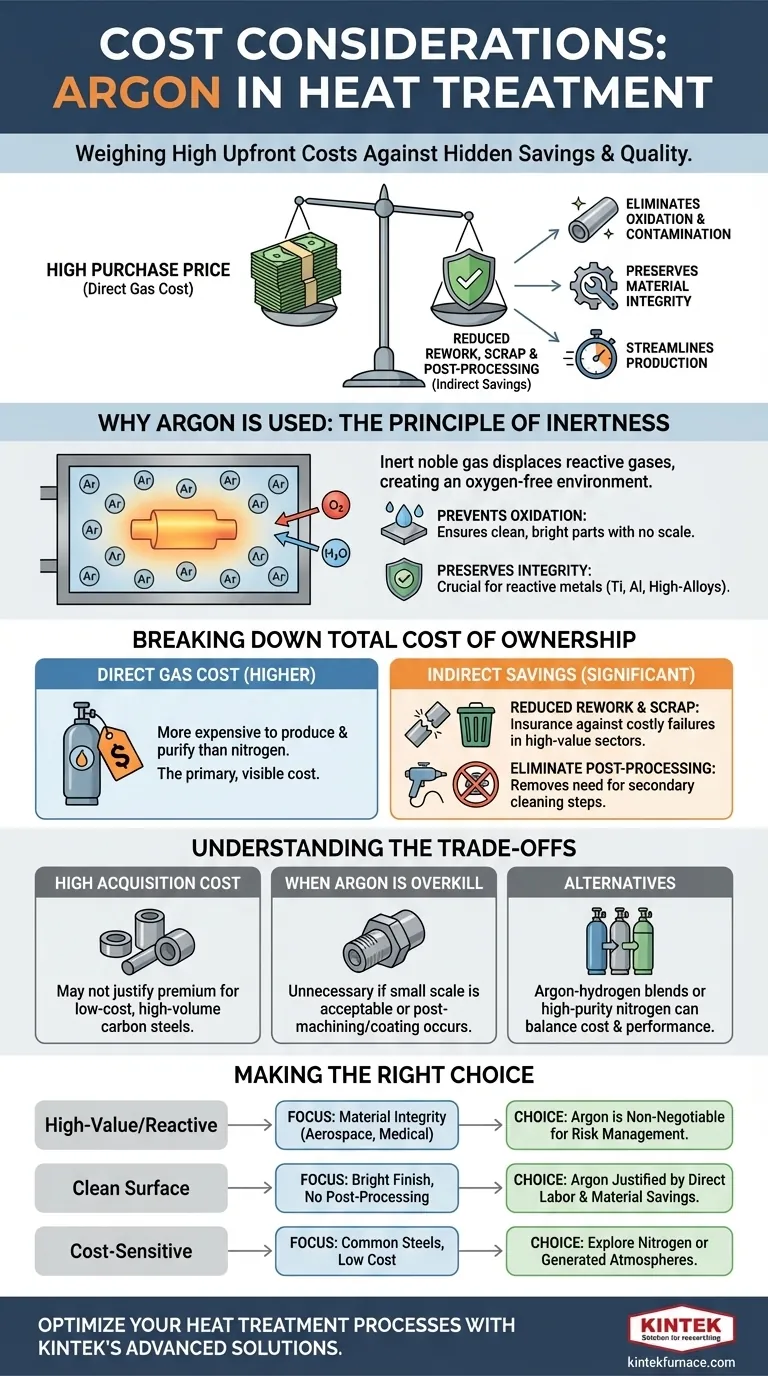
The primary cost consideration when using argon for heat treatment is its high purchase price relative to other atmospheric gases. However, this direct expense is only part of the equation. The true financial impact is understood by weighing this cost against the significant, often hidden, costs of material degradation, rework, and post-processing that argon can eliminate.
While argon presents a higher upfront cost, it is fundamentally an investment in process control and final part quality. The decision to use it hinges on a simple calculation: does the cost of potential material failure, oxidation, or contamination outweigh the cost of the protective gas?

Why Argon Is Used Despite Its Cost
To understand the cost-benefit analysis, we must first understand why argon is so effective. Its value is derived from its fundamental chemical nature.
The Principle of Inertness
Argon is a noble gas, which means it is chemically inert. At the high temperatures typical of heat treatment, it does not react with metals or other elements in the furnace atmosphere.
This inert shield is the foundation of all its benefits, as it displaces reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most immediate benefit is the prevention of oxidation. When hot metal is exposed to oxygen, it forms a layer of scale on the surface, which can compromise dimensional tolerances and surface finish.
Argon creates an oxygen-free environment, ensuring the part emerges from the furnace clean, bright, and free of scale. This is critical for parts with tight specifications.
Preserving Material Integrity
For reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, and certain high-alloy steels, even trace amounts of oxygen or nitrogen can diffuse into the material and alter its mechanical properties. This can lead to brittleness or reduced fatigue life.
Using an argon atmosphere guarantees the chemical and metallurgical purity of the material is preserved throughout the thermal cycle.
Breaking Down the Total Cost of Ownership
Focusing solely on the price per cubic foot of argon is misleading. A proper cost analysis must consider the total impact on the manufacturing process.
The Direct Gas Cost
Argon is more expensive to produce and purify than nitrogen, its most common alternative. This results in a higher direct purchase price, which is the primary and most visible cost factor.
Indirect Savings: Reduced Rework and Scrap
This is where the true value of argon becomes apparent. If a high-value component made of a sensitive alloy is scrapped due to oxidation or contamination, the financial loss can be hundreds or thousands of times the cost of the argon that would have protected it.
Using argon acts as an insurance policy against costly failures, especially in sectors like aerospace, medical, and advanced electronics.
Indirect Savings: Eliminating Post-Processing
Parts heat-treated without a fully inert atmosphere often require secondary operations like sandblasting, acid pickling, or grinding to remove scale.
These steps add significant costs in labor, materials, and production time. By producing a clean part directly from the furnace, argon can completely eliminate this expensive post-processing loop.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Argon is a powerful tool, but it is not the right choice for every application. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations.
The High Acquisition Cost
The most significant trade-off is its upfront expense. For low-cost, high-volume parts made from common carbon steels, the benefits of a perfectly clean surface may not justify the premium price of argon over less expensive nitrogen or endothermic gas atmospheres.
When Argon Is Overkill
If a part's application allows for a small amount of surface scale, or if it will be machined or coated after heat treatment anyway, using argon is likely an unnecessary expense. The key is to match the atmospheric requirements to the final needs of the component.
Alternatives to Pure Argon
In some cases, a mixture of gases can provide a balance of cost and performance. Argon-hydrogen blends can offer enhanced cleaning power, while high-purity nitrogen can be a "good enough" solution for less sensitive materials at a lower cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be based on a clear-eyed assessment of your material, your process, and your final part requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing high-value or reactive materials (e.g., aerospace, medical): Argon is often a non-negotiable requirement to guarantee material integrity and prevent catastrophic component failure.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, clean surface finish to avoid post-processing: The cost of argon can be easily justified by the direct savings from eliminating secondary cleaning and finishing operations.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive heat treatment of common steels: Explore less expensive alternatives like nitrogen or generated atmospheres, as the premium benefits of argon may not outweigh its cost.
Ultimately, viewing argon not as a consumable but as a tool for risk management is the key to making a sound financial decision.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Direct Gas Cost | Higher purchase price compared to alternatives like nitrogen |
| Indirect Savings | Reduces scrap, rework, and eliminates post-processing steps |
| Material Protection | Prevents oxidation and contamination, preserving integrity |
| Application Suitability | Best for high-value, reactive materials; may be overkill for others |
Optimize your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve superior results—let's discuss how our expertise can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a batch type controlled atmosphere furnace operate? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- Why are inert atmosphere furnaces important for graphite and carbon products? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure High-Performance Results
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















