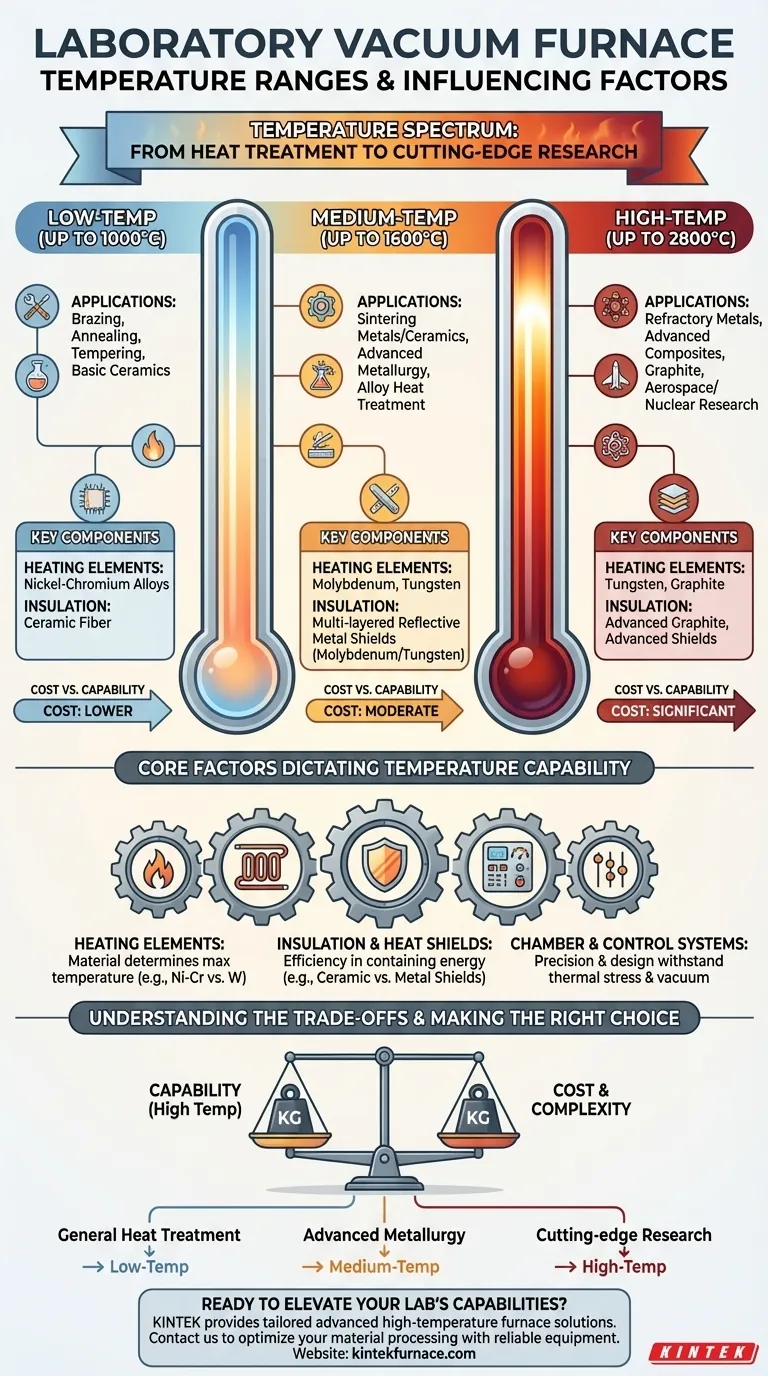
In short, laboratory vacuum furnaces operate across a wide temperature spectrum, typically classified into low-temperature (up to 1000°C), medium-temperature (up to 1600°C), and high-temperature (up to 2800°C) ranges. The furnace's maximum achievable temperature is not an arbitrary number; it is fundamentally determined by the materials used for its core components, especially the heating elements and internal insulation.
The specific temperature range you require is the single most important factor driving a vacuum furnace's design, material composition, and ultimately, its cost. Understanding this relationship is critical to selecting the right instrument for your research or production goals.

The Core Components Dictating Temperature
A vacuum furnace's temperature capability is a direct result of the physical limitations of its constituent parts. Three elements are paramount.
Heating Elements: The Engine of the Furnace
The heating elements are responsible for generating the thermal energy. The material used for these elements directly determines the maximum operating temperature.
Different materials are chosen for specific temperature regimes. For example, nickel-chromium alloys are common for lower temperatures, while molybdenum, tungsten, and graphite are required to reach medium and high temperatures without degrading.
Insulation and Heat Shields: Containing the Energy
Reaching and maintaining extreme temperatures efficiently requires exceptional insulation. This "hot zone" insulation prevents heat from escaping to the water-cooled furnace walls.
Lower-temperature furnaces may use ceramic fiber insulation. High-temperature systems often rely on multi-layered shields made from reflective metals like molybdenum or tungsten, which are more effective at blocking radiant heat transfer in a vacuum.
Chamber Design and Control Systems
The furnace chamber must withstand both high vacuum and intense thermal stress. Its construction and the precision of its control systems also influence performance.
Modern furnaces use sophisticated sensors and computer controls to ensure uniform heat distribution and repeatable thermal cycles, which is critical for achieving consistent material properties. The ability to control temperature precisely is as important as the ability to reach it.
Classifying Furnaces by Temperature Range
To simplify selection, furnaces are generally grouped by their maximum operating temperature, with each class suited for different applications.
Low-Temperature Furnaces (Up to 1000°C)
These furnaces are designed for processes like brazing, annealing, tempering, and firing certain ceramics and porcelain materials. They often provide a cost-effective solution for general-purpose heat treatment where an oxygen-free environment is required.
Medium-Temperature Furnaces (Up to 1600°C)
This range is the workhorse for many advanced metallurgy and materials science applications. It is ideal for sintering various metals and ceramics, heat-treating specialized alloys, and conducting research on a wide array of materials.
High-Temperature Furnaces (Up to 2800°C)
Reserved for the most demanding applications, these furnaces are used to process materials with extremely high melting points. This includes refractory metals, advanced ceramics, carbon composites, and graphite, often for aerospace, nuclear, or cutting-edge research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability with practical constraints. Higher temperatures introduce significant challenges.
Cost vs. Capability
There is a direct and steep correlation between maximum temperature and cost. The exotic materials required for high-temperature heating elements (tungsten, graphite) and insulation are significantly more expensive than those used in lower-temperature models.
Process Control vs. Temperature
Achieving tight temperature uniformity becomes exponentially more difficult at higher temperatures. A high-temperature furnace requires more sophisticated power delivery and control systems to maintain a stable and uniform hot zone.
Operational Complexity
Operating at extreme temperatures demands stricter protocols for safety and maintenance. The risk of component failure and the consequences of a process error are greater, requiring more experienced operators and diligent upkeep.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material processing goal should be the primary driver of your decision.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment, brazing, or basic ceramics: A low-temperature furnace (up to 1000°C) is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced metallurgy or sintering most alloys and technical ceramics: A medium-temperature furnace (up to 1600°C) offers the best balance of capability and cost for a wide range of applications.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge research on refractory metals or advanced composites: A high-temperature furnace (up to 2800°C) is necessary to meet the demands of these specialized materials.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace means precisely matching its temperature capabilities to the specific requirements of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Typical Applications | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1000°C | Brazing, annealing, tempering, basic ceramics | Nickel-chromium heating elements, ceramic fiber insulation |
| Up to 1600°C | Sintering metals/ceramics, heat-treating alloys | Molybdenum/tungsten heating elements, multi-layered metal shields |
| Up to 2800°C | Refractory metals, advanced composites, graphite | Graphite/tungsten heating elements, advanced insulation and controls |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a tailored vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether for general heat treatment or cutting-edge research. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your material processing with reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















