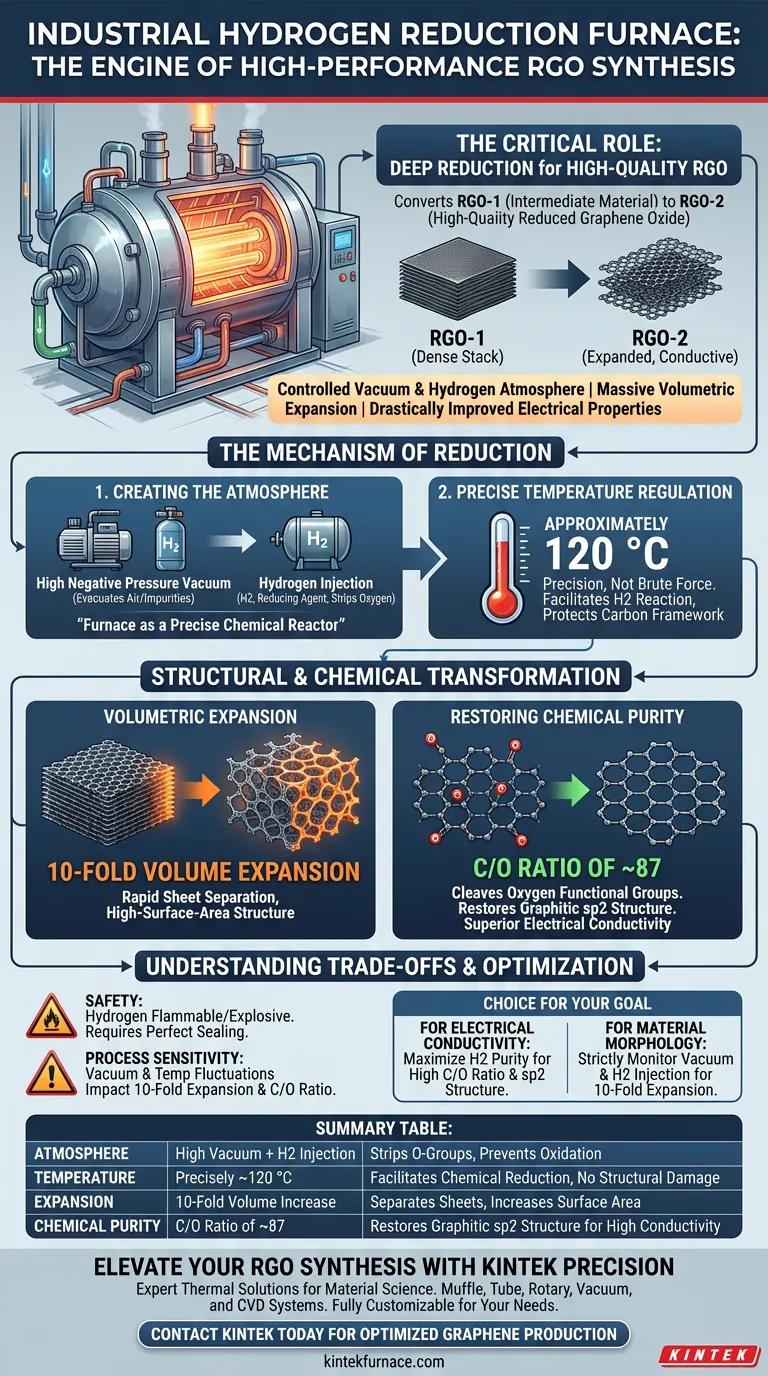
An industrial-grade hydrogen reduction furnace serves as the critical environment for the deep reduction of graphene oxide, specifically aiming to convert intermediate material (RGO-1) into high-quality Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO-2). This equipment provides a controlled vacuum and hydrogen atmosphere to trigger a massive volumetric expansion and drastically improve the material's electrical properties.
The furnace functions not just as a heater, but as a precise chemical reactor. By combining high negative pressure with hydrogen injection, it effectively strips away oxygen functional groups, resulting in a 10-fold volume expansion and a restored carbon structure essential for superior conductivity.
The Mechanism of Reduction
Creating the Reaction Atmosphere
The primary role of the furnace is to establish an isolated environment where oxidation is impossible. It begins by creating a high negative pressure vacuum to evacuate air and impurities.
Once the vacuum is established, the system introduces high-purity hydrogen. This hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, actively seeking out and reacting with oxygen atoms attached to the graphene lattice.
Precise Temperature Regulation
While thermal treatment often implies extreme heat, this specific process relies on precision rather than brute force. The furnace maintains a temperature of approximately 120 °C.
This specific thermal window is sufficient to facilitate the reaction between hydrogen and the oxygen functional groups without damaging the underlying carbon framework.
Structural and Chemical Transformation
Volumetric Expansion
One of the most distinct outcomes of using this specific furnace setup is the physical transformation of the material. As oxygen groups are removed, the graphene sheets undergo a rapid separation.
This results in a 10-fold volume expansion, changing the morphology of the material from a dense stack into a more open, high-surface-area structure.
Restoring Chemical Purity
The ultimate goal of this process is to restore the carbon-to-oxygen (C/O) ratio. The furnace environment effectively cleaves residual oxygen functional groups (such as carboxyl groups).
According to the primary data, this process achieves a C/O ratio of approximately 87. This high carbon purity is directly linked to the restoration of the graphitic sp2 structure, which is what gives RGO its superior electrical conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Safety and Complexity
Using hydrogen as a reducing agent introduces significant safety considerations. The furnace must be perfectly sealed, as hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive when mixed with air.
Process Sensitivity
The "10-fold expansion" and high C/O ratio are dependent on the exact sequence of vacuum and hydrogen injection.
If the negative pressure is insufficient or the temperature fluctuates away from the 120 °C target, the reduction may be incomplete, resulting in a material with lower conductivity and less volume expansion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of an industrial hydrogen reduction furnace for RGO synthesis, align your process parameters with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Ensure the hydrogen atmosphere is of high purity to maximize the restoration of the sp2 carbon structure and achieve a high C/O ratio.
- If your primary focus is material morphology: Strictly monitor the vacuum levels and hydrogen injection timing to guarantee the full 10-fold volume expansion occurs.
Precision in the furnace atmosphere is the defining factor between standard reduced graphene and high-performance RGO.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification/Role | Impact on RGO |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | High Vacuum + H2 Injection | Strips oxygen functional groups; prevents oxidation |
| Temperature | Precisely ~120 °C | Facilitates chemical reduction without structural damage |
| Expansion | 10-Fold Volume Increase | Separates sheets and increases surface area |
| Chemical Purity | C/O Ratio of ~87 | Restores graphitic sp2 structure for high conductivity |
Elevate Your RGO Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precision in atmosphere and temperature control is the defining factor for high-performance Reduced Graphene Oxide. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to your unique research or production needs. Whether you require precise hydrogen injection for 10-fold material expansion or high-vacuum environments for maximum chemical purity, our furnaces deliver consistent, high-quality results.
Ready to optimize your graphene production? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements with our technical experts!
Visual Guide
References
- Zahid Mehmood, Shaukat Saeed. Scalable synthesis of high-quality, reduced graphene oxide with a large C/O ratio and its dispersion in a chemically modified polyimide matrix for electromagnetic interference shielding applications. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra00329b
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why might some industries still require retort-based furnace designs? Ensure Absolute Atmospheric Control for Sensitive Processes
- What are the heating mechanisms used in retort furnaces? Choose the Right Heating for Your Lab or Industry
- What types of industries commonly use box-type atmosphere furnaces? Essential for Metallurgy, Electronics, and More
- What are the key components of an inert atmosphere furnace? Essential Parts for Contamination-Free Heating
- How does the box type annealing atmosphere furnace improve material quality? Enhance Strength, Ductility, and Surface Integrity
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How is an atmosphere box furnace utilized in research on material properties? Unlock Precision in Material Science
- How does a retort furnace differ from a muffle furnace? Uncover Key Design and Function Differences



















