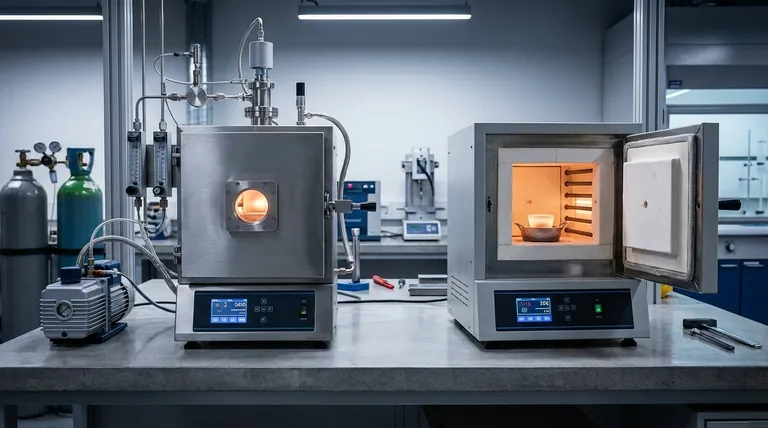
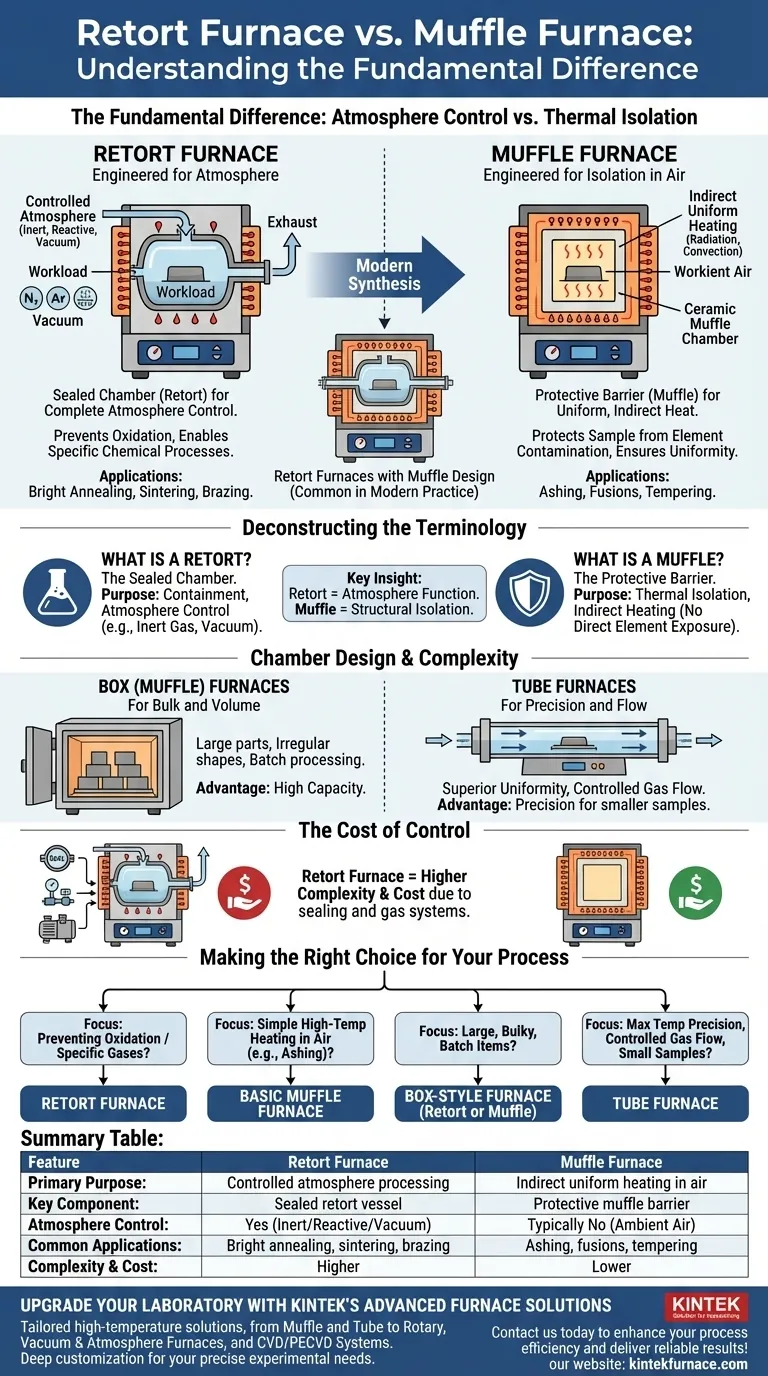
The fundamental difference between a retort furnace and a muffle furnace lies in their primary design purpose. A retort furnace is explicitly designed for heat treatment within a controlled atmosphere inside a sealed vessel (the retort). In contrast, a muffle furnace is defined by its construction, where a "muffle" separates the workload from the heating elements to provide indirect, uniform heat. While the terms are often used interchangeably today, the key distinction is that "retort" describes the function of atmosphere control, while "muffle" describes the structure of thermal isolation.
The distinction is less about two competing furnace types and more about understanding the terminology. A retort is the sealed vessel for atmosphere control, while a muffle is the physical barrier protecting the sample from direct heating. Most modern retort furnaces are, by design, also muffle furnaces.

Deconstructing the Terminology: Retort vs. Muffle
The confusion between these terms stems from their historical origins and modern engineering, where the two concepts have merged. Understanding each component clarifies their purpose.
What is a Retort? The Sealed Chamber
A retort is an airtight vessel placed inside a furnace. Its sole purpose is to contain the material being processed and to allow for the complete control of the gaseous environment.
This means you can introduce inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation, use reactive gases for specific chemical processes, or create a vacuum. The furnace heats the retort, and the retort heats the sample.
What is a Muffle? The Protective Barrier
A muffle is a chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic or alloy, that sits between the furnace's heating elements and the workload. Its primary function is to provide thermal isolation.
This separation ensures uniform, indirect heating via radiation and convection, preventing hot spots. It also protects the sample from any potential contamination coming from the heating elements.
The Modern Synthesis: A Furnace with Both
In modern practice, most furnaces designed for controlled atmosphere applications are retort furnaces that use a muffle design. The "muffle" chamber is simply engineered to be gas-tight, effectively making it a "retort."
Therefore, when a manufacturer labels a furnace as a "retort furnace," they are signaling that its primary feature is atmosphere control. A simple "muffle furnace" may or may not be sealed for atmosphere control and might only operate in ambient air.
The Core Functional Difference: Atmosphere vs. Isolation
While structurally similar, the intended application drives the key difference. The crucial question is: do you need to control the gas around your sample?
Retort Furnaces: Engineered for Atmosphere
A retort furnace is the definitive choice for any process sensitive to air. The ability to create a specific environment is essential for applications like bright annealing, sintering, and brazing, where preventing oxidation is critical to the material's final properties.
Muffle Furnaces: Engineered for Isolation in Air
A basic muffle furnace provides excellent temperature uniformity and protects the sample from direct element radiation, but it operates in ambient air.
This design is perfectly suited for general-purpose lab work and heat treatments where an air atmosphere is acceptable or desired, such as ashing, fusions, or tempering certain steels.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Chamber Design & Complexity
Beyond the atmosphere, the physical shape of the chamber is a critical factor that influences process capability.
Box (Muffle) Furnaces: For Bulk and Volume
A furnace with a large, box-shaped chamber—often called a muffle furnace—is ideal for processing large parts, irregularly shaped components, or multiple samples in a single batch. Its main advantage is capacity.
Tube Furnaces: For Precision and Flow
Tube furnaces, which can also be designed as retort furnaces, use a cylindrical chamber. This geometry allows for superior temperature uniformity along the centerline and precise control over gas flow from an inlet to an outlet. They are ideal for smaller samples, powders, and continuous-flow chemical processes but are limited by their diameter.
The Cost of Control
Implementing atmosphere control adds significant complexity. A retort furnace requires precision-sealed doors, gas-tight ports, flow controllers, and potentially vacuum pumps. This makes a true retort furnace inherently more complex and costly than a simple, air-atmosphere muffle furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Ignore the overlapping terminology and focus on your specific process requirements to select the correct equipment.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or using specific gases: You need a retort furnace with a sealed chamber for atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is simple, high-temperature heating in air (e.g., ashing): A basic, unsealed muffle furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing large, bulky, or batch items: A box-style furnace (either retort or muffle) offers the necessary volume.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature precision and controlled gas flow for small samples: A tube furnace is often the superior technical choice.
Focusing on the demands of your application—atmosphere, sample size, and precision—will guide you to the correct furnace design, regardless of the name on the label.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Retort Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Controlled atmosphere processing | Indirect, uniform heating in air |
| Key Component | Sealed retort vessel | Protective muffle barrier |
| Atmosphere Control | Yes, for inert/reactive gases or vacuum | Typically no, operates in ambient air |
| Common Applications | Bright annealing, sintering, brazing | Ashing, fusions, tempering |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher due to sealing and gas systems | Lower, simpler design |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your specific heat treatment needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you need precise atmosphere control or superior thermal isolation.
Don't let equipment limitations hold back your research or production. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process efficiency and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















