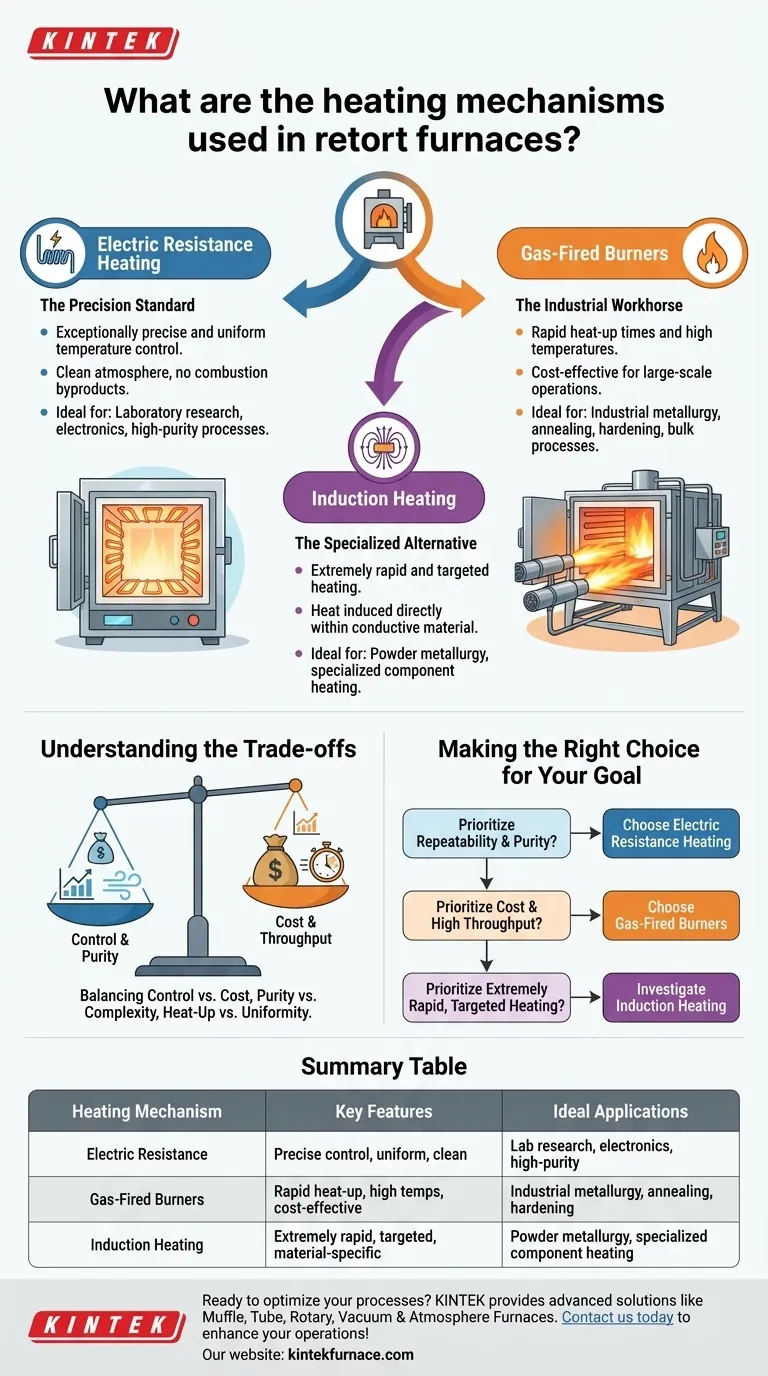
At its core, a retort furnace is heated in one of two primary ways: through electric resistance or with gas-fired burners. Electric heating passes a current through specialized elements to generate precise, uniform heat, making it ideal for controlled environments. Gas heating, by contrast, uses the combustion of fuel to achieve high temperatures rapidly, a common choice for large-scale industrial applications.
The choice between heating mechanisms is not about which is "better," but which best aligns with your specific goals. Electric heating offers unparalleled precision and a clean environment, while gas heating provides raw power and operational efficiency for large-scale processes.
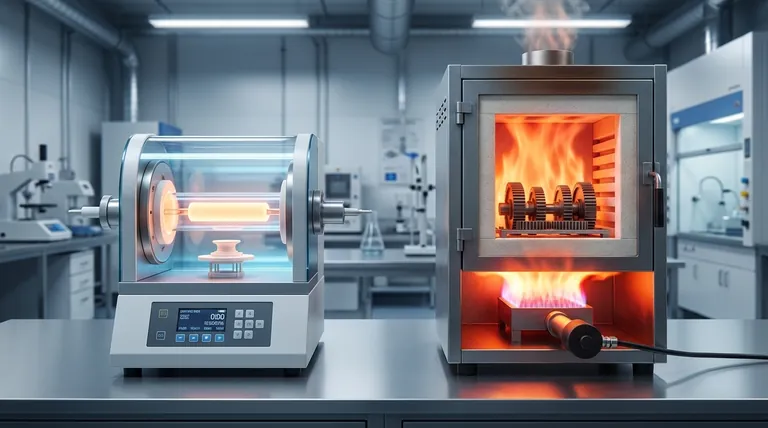

A Closer Look at the Heating Mechanisms
To select the right furnace, you must first understand the fundamental principles, advantages, and ideal use cases for each heating method.
Electric Resistance Heating: The Precision Standard
Electric resistance heating is the most common method for laboratory and high-purity applications. It operates by passing an electrical current through heating elements, which resist the flow of electricity and convert that electrical energy into heat.
This method provides exceptionally precise and uniform temperature control. Because there is no combustion, the furnace atmosphere remains clean, which is critical for sensitive processes like ceramic sintering, electronics manufacturing, and advanced material research.
Gas-Fired Burners: The Industrial Workhorse
Gas-fired systems generate heat through the controlled combustion of a fuel source, such as natural gas or propane. These burners can inject massive amounts of thermal energy into a furnace chamber, enabling rapid heat-up times and very high temperatures.
This power and efficiency make gas heating the standard for high-volume industrial metallurgy. Processes like annealing, hardening, and bulk charcoal development benefit from the speed and lower operational cost associated with gas burners.
Induction Heating: The Specialized Alternative
A less common but powerful third option is induction heating. This method uses a high-frequency electromagnetic field to induce electrical currents directly within a conductive material placed inside the retort.
The material itself becomes the heat source, allowing for extremely rapid and targeted heating. This is a specialized technique often used for unique applications in powder metallurgy or when a specific part of a larger component needs to be heated quickly without affecting the rest of the assembly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every engineering choice involves trade-offs. The decision between electric and gas heating is a classic example of balancing control, cost, and operational complexity.
Control vs. Cost
Electric resistance heating offers superior temperature stability and uniformity, but this precision comes at a higher operational cost due to electricity prices.
Gas heating is typically more cost-effective to run, especially at a large scale, but achieving the same level of granular temperature control as an electric system can be more challenging.
Atmosphere Purity vs. Complexity
Electric heating is an inherently clean process. It introduces no byproducts into the furnace chamber, making it the default choice for applications where material purity is non-negotiable.
Gas combustion, on the other hand, produces byproducts like CO2 and water vapor. While modern retort designs can isolate the heating chamber from combustion gases, it adds a layer of design complexity and a potential point of contamination if not managed perfectly.
Heat-Up Rate vs. Uniformity
Gas burners excel at raising the furnace temperature very quickly, which is a major advantage for high-throughput production lines.
Electric elements often provide a more even and gradual temperature ramp-up, resulting in superior temperature uniformity across the entire workpiece. This is crucial for ensuring consistent material properties in sensitive components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right heating mechanism is the one that best serves your process requirements for precision, purity, speed, and cost.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and atmosphere purity: Choose electric resistance heating for its unmatched temperature control and clean operation, ideal for R&D and electronics.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and high throughput: Choose gas-fired burners for their efficiency and rapid heating capabilities in large-scale industrial settings like metal treatment.
- If your primary focus is extremely rapid heating of a conductive material: Investigate induction heating as a specialized solution that offers targeted, high-speed performance.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating mechanism is the foundational decision that ensures your furnace becomes an asset to your process, not a limitation.
Summary Table:
| Heating Mechanism | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Resistance | Precise temperature control, uniform heating, clean atmosphere | Laboratory research, electronics, high-purity processes |
| Gas-Fired Burners | Rapid heat-up, high temperatures, cost-effective for large scale | Industrial metallurgy, annealing, hardening |
| Induction Heating | Extremely rapid, targeted heating, material-specific | Powder metallurgy, specialized component heating |
Ready to optimize your processes with the perfect high-temperature furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for precise control, cost-efficiency, and rapid heating. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab or industrial operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation



















