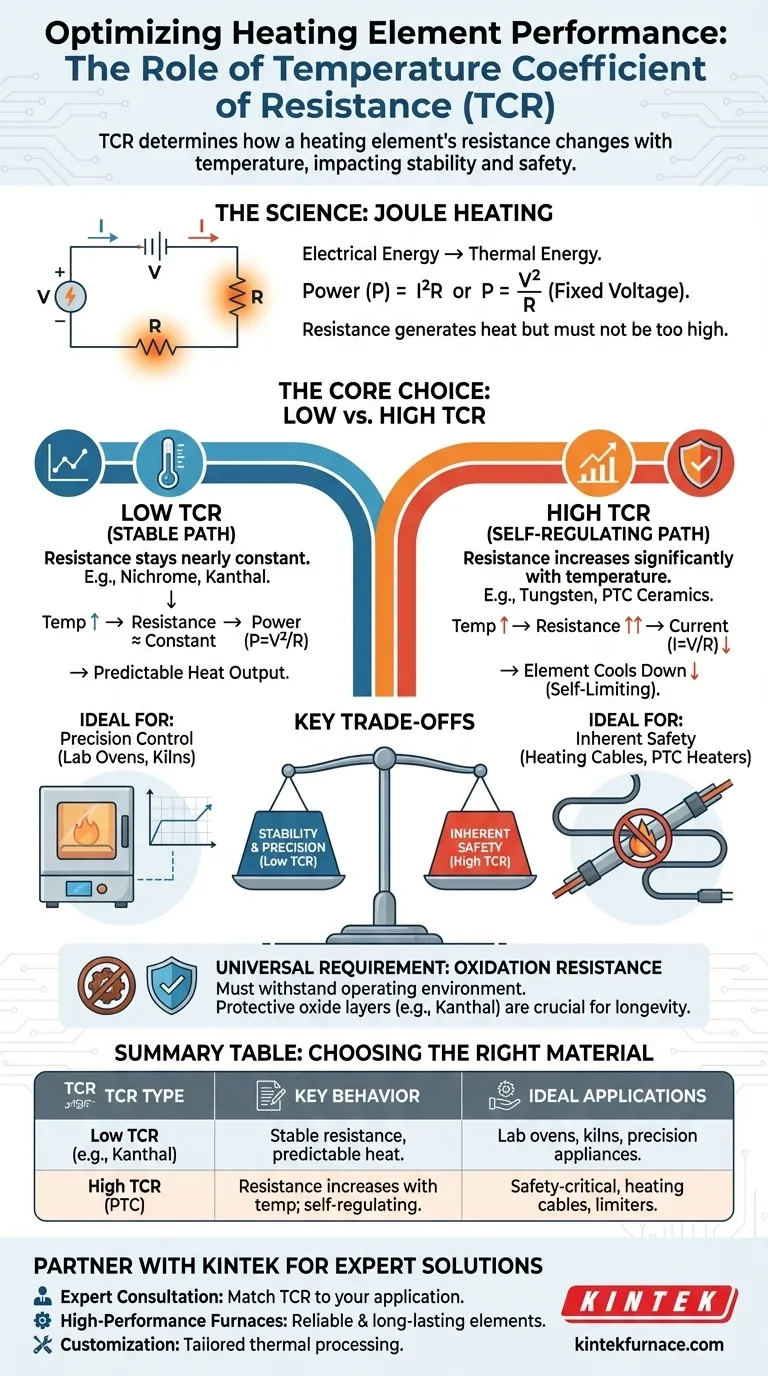
In short, the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) determines how a heating element's performance changes as it heats up. A low TCR means the resistance stays nearly constant, providing stable and predictable heat output. In contrast, a high positive TCR means the resistance increases significantly with temperature, creating a self-regulating effect that can prevent overheating.
The choice of TCR is a fundamental design trade-off. It forces a decision between two distinct goals: the consistent, stable heat output of a low-TCR material versus the inherent safety and self-limiting nature of a high-TCR material.

The Role of Resistance in Generating Heat
The Principle of Joule Heating
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into thermal energy. This process, known as Joule heating, occurs when electric current flows through a material with electrical resistance.
The resistance impedes the flow of electrons, causing collisions that generate heat. For a material to be an effective heating element, it must have high electrical resistivity—enough to produce significant heat, but not so high that it becomes an insulator and prevents current from flowing.
Power, Current, and Resistance
The amount of heat generated is defined by the power formula, often expressed as P = I²R. This shows that power (P) is proportional to the resistance (R) and to the square of the current (I).
While both factors are crucial, this relationship highlights that current has a disproportionately large impact on heat output. However, in most applications with a fixed voltage source (like a wall outlet), the formula P = V²/R is more illustrative. It shows that for a constant voltage (V), power is inversely proportional to resistance.
The Case for a Low TCR: Predictability and Stability
What a Low TCR Means
A material with a low temperature coefficient of resistance maintains a relatively stable resistance value across a wide range of temperatures. Materials like Nichrome (nickel-chromium) and Kanthal (iron-chromium-aluminum) are prized for this characteristic.
Consistent Heat Output
For applications requiring precise temperature control, such as laboratory ovens, kilns, or kitchen appliances, stability is paramount. A low TCR ensures that once the element reaches its operating temperature, its resistance doesn't change significantly.
This stability means the power output (P = V²/R) remains constant, delivering a predictable and easily regulated amount of heat.
Simplified Control Systems
Because the element's behavior is predictable, the control systems can be simpler. They do not need to constantly compensate for a changing resistance value to maintain a target temperature.
The Case for a High TCR: Self-Regulation and Safety
The Self-Limiting Effect
A material with a high positive TCR (PTC), such as tungsten or certain ceramics, behaves very differently. As it gets hotter, its electrical resistance increases dramatically.
In a constant-voltage circuit, this rise in resistance reduces the current flow (I = V/R). This, in turn, lowers the power output (P = V²/R), causing the element to cool down.
Inherent Overheating Protection
This behavior creates a self-regulating or self-limiting feedback loop. The element will naturally settle around a specific temperature and is inherently protected from thermal runaway.
This makes high-TCR materials ideal for applications where safety is critical and precise temperature control is secondary, such as in self-regulating heating cables, PTC heaters, and inrush-current limiters.
Key Trade-offs and Other Critical Factors
Stability vs. Inherent Safety
The primary trade-off is clear: low-TCR elements provide stable, predictable heat, while high-TCR elements offer built-in protection against overheating at the cost of stable power output. The "better" choice is entirely dependent on the goals of the application.
The Imperative of Oxidation Resistance
Regardless of its TCR, a heating element must withstand its operating environment. At high temperatures, materials react with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation, which can cause them to degrade and fail.
Effective heating elements like Kanthal and silicon carbide form a thin, protective layer of oxide on their surface. This layer shields the underlying material from further oxidation, ensuring a long and reliable service life. Materials without this property, such as graphite, must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection depends entirely on the primary goal of your heating application.
- If your primary focus is precise and stable temperature control: Choose a material with a low TCR, such as Nichrome or Kanthal, to ensure consistent and predictable heat output.
- If your primary focus is inherent safety and preventing overheating: Choose a material with a high positive TCR, like a PTC ceramic, to leverage its self-regulating properties.
- If your primary focus is longevity and performance in open air: Prioritize materials with excellent oxidation resistance that form a stable, protective oxide layer.
Ultimately, understanding the temperature coefficient of resistance empowers you to select a material whose behavior perfectly aligns with your specific design requirements.
Summary Table:
| TCR Type | Material Examples | Key Behavior | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low TCR | Nichrome, Kanthal | Stable resistance & predictable heat output | Lab ovens, kilns, appliances requiring precise temperature control |
| High TCR (PTC) | Tungsten, PTC Ceramics | Resistance increases with temperature; self-regulating | Safety-critical applications, heating cables, inrush-current limiters |
Need a Heating Element with Precise Performance?
Selecting the right heating element material is critical to your project's success. Whether your priority is stable, predictable heat output for precise control or inherent safety with self-regulating properties, KINTEK's expertise can guide you to the optimal solution.
We provide:
- Expert Consultation: Our team will help you analyze your application's requirements to select the ideal TCR material.
- High-Performance Furnaces: Our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems incorporate heating elements engineered for reliability and longevity.
- Customization: Every solution is tailored to your unique thermal processing needs, backed by our expert R&D and manufacturing.
Let's discuss your project and build a heating solution that delivers on performance, safety, and durability.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















