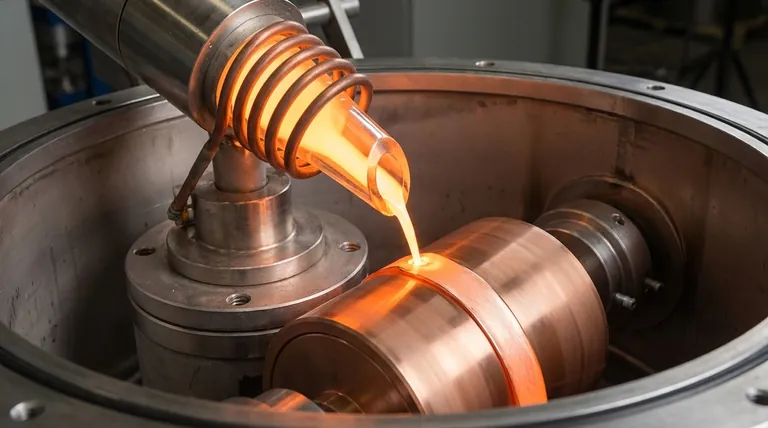
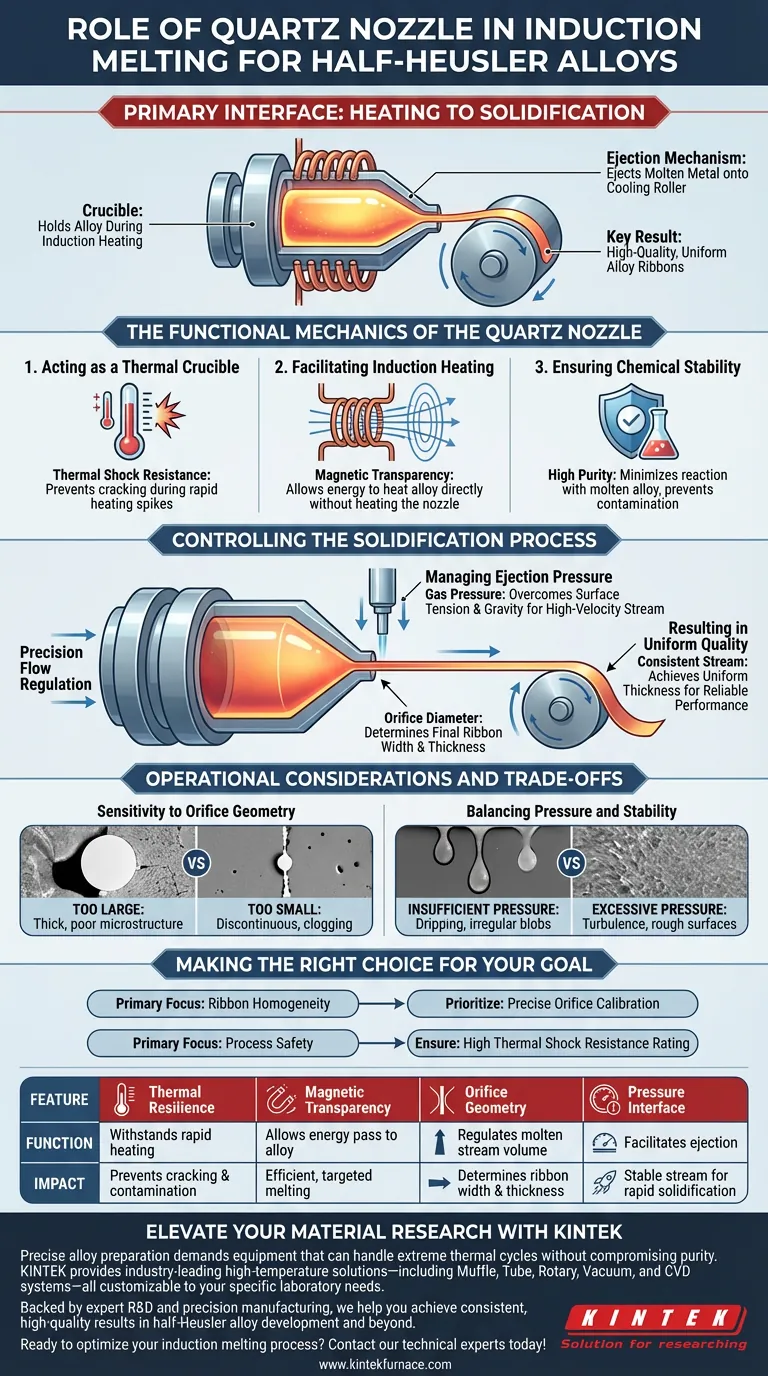
The quartz nozzle acts as the primary interface between the heating element and the solidification stage. It serves as a specialized crucible that holds the half-Heusler alloy during induction heating and functions as the precision delivery mechanism that ejects the molten metal onto the cooling roller. Its role is fundamental to converting bulk ingots into high-quality, uniform alloy ribbons.
The quartz nozzle’s value lies in its combination of thermal resilience and flow control. It withstands the extreme thermal shock of rapid heating while ensuring a stable, continuous ejection stream—the determining factor for achieving consistent thickness and quality in the final alloy ribbon.

The Functional Mechanics of the Quartz Nozzle
To understand the nozzle's role, we must look at how it interacts with both the heat source and the molten material.
Acting as a Thermal Crucible
The nozzle functions as the containment vessel for the alloy melt.
Because induction melting involves rapid temperature spikes, the container requires exceptional thermal shock resistance. This prevents the nozzle from cracking or shattering under the stress of sudden heating.
Facilitating Induction Heating
The nozzle works directly in conjunction with the induction heating coils.
Quartz is electrically insulating and transparent to magnetic fields. This allows the induction coils to heat the alloy inside the nozzle efficiently without heating the nozzle itself directly, ensuring the energy is focused solely on melting the metal.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
Mainting the purity of half-Heusler alloys is critical.
The quartz material offers high chemical stability at elevated temperatures. This minimizes the risk of the container reacting with the molten alloy, ensuring the chemical composition of the sample remains uncontaminated during the melting phase.
Controlling the Solidification Process
Once the alloy is molten, the nozzle shifts roles from a container to a precision tool for ejection.
Precision Flow Regulation
The nozzle dictates the physical characteristics of the molten stream.
By precisely controlling the orifice diameter at the tip of the nozzle, researchers can regulate the volume of metal released. This geometry is the primary variable that determines the final width and thickness of the ribbon.
Managing Ejection Pressure
The nozzle is the vessel through which gas pressure is applied.
To overcome surface tension and gravity, gas pressure forces the melt through the nozzle. This creates a stable, high-velocity stream essential for rapid solidification.
Resulting in Uniform Quality
The ultimate goal of the nozzle is consistency.
A stable stream, achieved through the correct balance of orifice size and pressure, results in ribbons with uniform thickness. This uniformity is essential for the reliable performance of the final half-Heusler material.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
While the quartz nozzle is effective, its implementation requires careful parameter management to avoid process failures.
Sensitivity to Orifice Geometry
The process is highly sensitive to the nozzle's opening size.
If the orifice is too large, the ribbon may become too thick to cool rapidly, losing its desired microstructure. If it is too small, the flow may become discontinuous or prone to clogging.
Balancing Pressure and Stability
There is a delicate trade-off regarding the gas pressure applied through the nozzle.
Insufficient pressure results in a dripping effect rather than a stream, leading to irregular blobs of metal. Conversely, excessive pressure can cause turbulence, resulting in ribbons with rough surfaces or inconsistent edges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The quartz nozzle is a consumable but critical component. Your setup should depend on the specific requirements of your alloy sample.
- If your primary focus is Ribbon Homogeneity: Prioritize precise calibration of the orifice diameter to ensure the melt flow rate matches the speed of the cooling roller perfectly.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Ensure the quartz material is rated for high thermal shock resistance to prevent containment failure during rapid heating cycles.
By meticulously controlling the nozzle parameters, you transform a chaotic melting process into a precise manufacturing technique for high-performance materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Process | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resilience | Withstands rapid induction heating | Prevents crucible cracking & contamination |
| Magnetic Transparency | Allows energy to pass to the alloy | Ensures efficient, targeted melting |
| Orifice Geometry | Regulates molten stream volume | Determines ribbon width and thickness |
| Pressure Interface | Facilitates gas-driven ejection | Ensures a stable stream for rapid solidification |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise alloy preparation demands equipment that can handle extreme thermal cycles without compromising purity. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to your specific laboratory needs. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, we help you achieve consistent, high-quality results in half-Heusler alloy development and beyond.
Ready to optimize your induction melting process? Contact our technical experts today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Effect of Sb Doping on the Thermoelectric Properties of MNiSn (M=Ti, Zr, Hf) Half-Heusler Alloys Fabricated by a Rapid Solidification Process. DOI: 10.3365/kjmm.2025.63.4.243
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the vacuum chamber in an induction-heated vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Performance in Materials Processing
- What role does the induction coil play in an induction melting furnace? It's the Engine of Efficient Melting
- What role do medium frequency induction furnaces play in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Properties
- What role does an induction vacuum furnace play in Yttrium-modified H13 steel? Master Precision Alloy Melting
- Why is cold crucible induction levitation melting utilized for TNZTSF alloys? Achieve Pure & Homogeneous Synthesis
- What is the role of a vacuum arc furnace in the synthesis of AlCrFeNi HEAs? Achieve High-Purity Material Homogeneity
- What is the objective of using a high-power induction heating system? Optimize High-Entropy Alloy Melting
- What is the function of a vacuum arc furnace in the preparation of high-entropy alloy ingots? Achieve Perfect Homogeneity



















