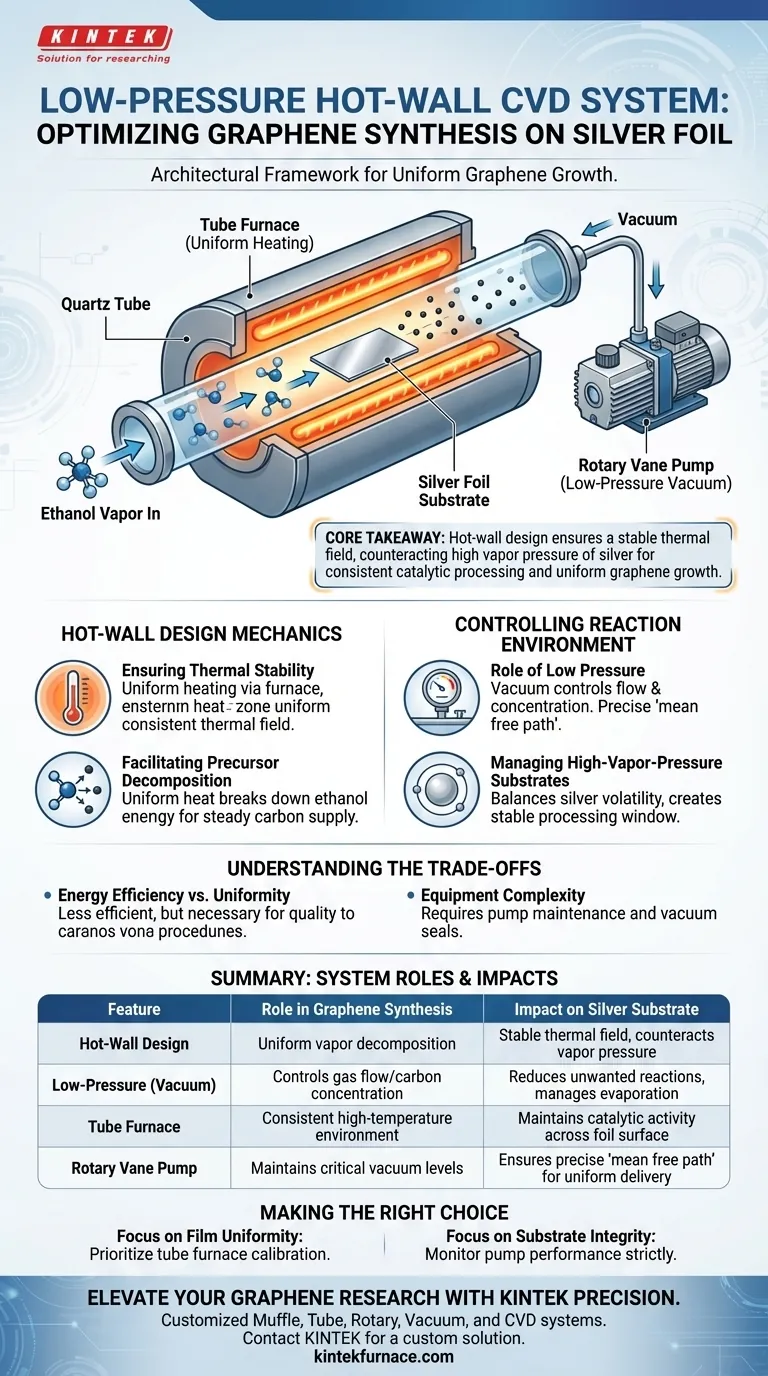
A low-pressure hot-wall Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system functions as the critical architectural framework for synthesizing graphene, specifically when using silver foil as a substrate. This system orchestrates a high-temperature, vacuum-controlled environment using a quartz tube, tube furnace, and rotary vane pump to facilitate the uniform decomposition of ethanol vapor.
Core Takeaway While many systems can induce chemical reactions, the specific role of the low-pressure hot-wall design is to maintain a stable thermal field that counteracts the high vapor pressure of silver, ensuring consistent catalytic processing and uniform graphene growth.

The Mechanics of the Hot-Wall Design
Ensuring Thermal Stability
The "hot-wall" designation refers to the system's method of heating the entire reaction chamber—specifically the quartz tube—via an external tube furnace.
This design creates a uniform temperature field throughout the processing zone. Unlike systems that only heat the substrate, this ensures that the thermal environment surrounding the silver foil is consistent from all angles.
Facilitating Precursor Decomposition
The uniform heat provided by the hot-wall design is essential for the chemistry of the process.
It ensures that the ethanol vapor, which serves as the carbon source, decomposes evenly. This uniform breakdown provides a steady supply of carbon atoms necessary for the catalytic reaction on the silver surface.
Controlling the Reaction Environment
The Role of Low Pressure
The system utilizes a rotary vane pump to create and maintain a low-pressure (vacuum) environment within the quartz tube.
This vacuum level is critical for controlling the flow and concentration of the ethanol vapor. It allows for a precise "mean free path" for gas molecules, reducing unwanted gas-phase reactions before the carbon hits the substrate.
Managing High-Vapor-Pressure Substrates
Silver foil presents a unique challenge in CVD processes because it has a high vapor pressure at elevated temperatures.
The combination of the low-pressure environment and the stable thermal field helps manage this characteristic. It creates a processing window where the silver remains stable enough to act as a catalyst without evaporating or degrading unpredictably.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Energy Efficiency vs. Uniformity
A hot-wall system heats the entire reactor volume, which is generally less energy-efficient than cold-wall systems that heat only the substrate.
However, for silver-based graphene synthesis, this energy expenditure is a necessary trade-off to achieve the thermal homogeneity required for high-quality growth.
Equipment Complexity
The requirement for a rotary vane pump and a sealed quartz tube assembly adds mechanical complexity to the setup.
Maintenance of vacuum seals and pump oil becomes a critical operational factor, as any leak or fluctuation in pressure can disrupt the stability needed for the silver catalyst.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of this CVD system for your project, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is film uniformity: Prioritize the calibration of the tube furnace to ensure the "hot zone" extends well beyond the edges of your silver foil.
- If your primary focus is substrate integrity: Monitor the rotary vane pump performance strictly to ensure the vacuum level effectively balances the vapor pressure of the silver.
By strictly controlling the thermal field and vacuum pressure, you transform the volatile nature of silver from a liability into a controllable catalytic asset.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Graphene Synthesis | Impact on Silver Substrate |
|---|---|---|
| Hot-Wall Design | Ensures uniform decomposition of ethanol vapor | Provides stable thermal field to counteract vapor pressure |
| Low-Pressure (Vacuum) | Controls gas flow and carbon concentration | Reduces unwanted gas-phase reactions and manages evaporation |
| Tube Furnace | Creates a consistent high-temperature environment | Maintains catalytic activity across the entire foil surface |
| Rotary Vane Pump | Maintains critical vacuum levels | Ensures a precise 'mean free path' for uniform carbon delivery |
Elevate Your Graphene Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let substrate volatility compromise your materials research. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to give you absolute control over your thermal environment.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet the unique challenges of high-vapor-pressure substrates like silver foil. Partner with KINTEK to transform complex catalytic processes into repeatable, high-quality results.
Ready to optimize your synthesis? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Hikaru Iwatani, Fumihiko Maeda. Graphene Synthesis on Silver Foil by Chemical Vapor Deposition Using Ethanol. DOI: 10.1380/ejssnt.2025-026
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of CVD in the automotive industry? Boost Vehicle Performance with Advanced Coatings
- What protective functions does a circulating water cooling system provide during CVD? Secure Vacuum Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of CVD coatings? Achieve Superior Performance for Complex Geometries
- How do industrial-grade vacuum CVD reactors achieve precise precursor control? Mastering Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Growth
- How are CVD furnaces used in nanomaterial synthesis? Unlock High-Purity Materials for Advanced Applications
- What is a CVD furnace? A Precision Tool for Building Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Unlock High-Performance Thin Films
- What is Chemical Vapor Infiltration (CVI)? Build Dense, High-Performance Composites



















