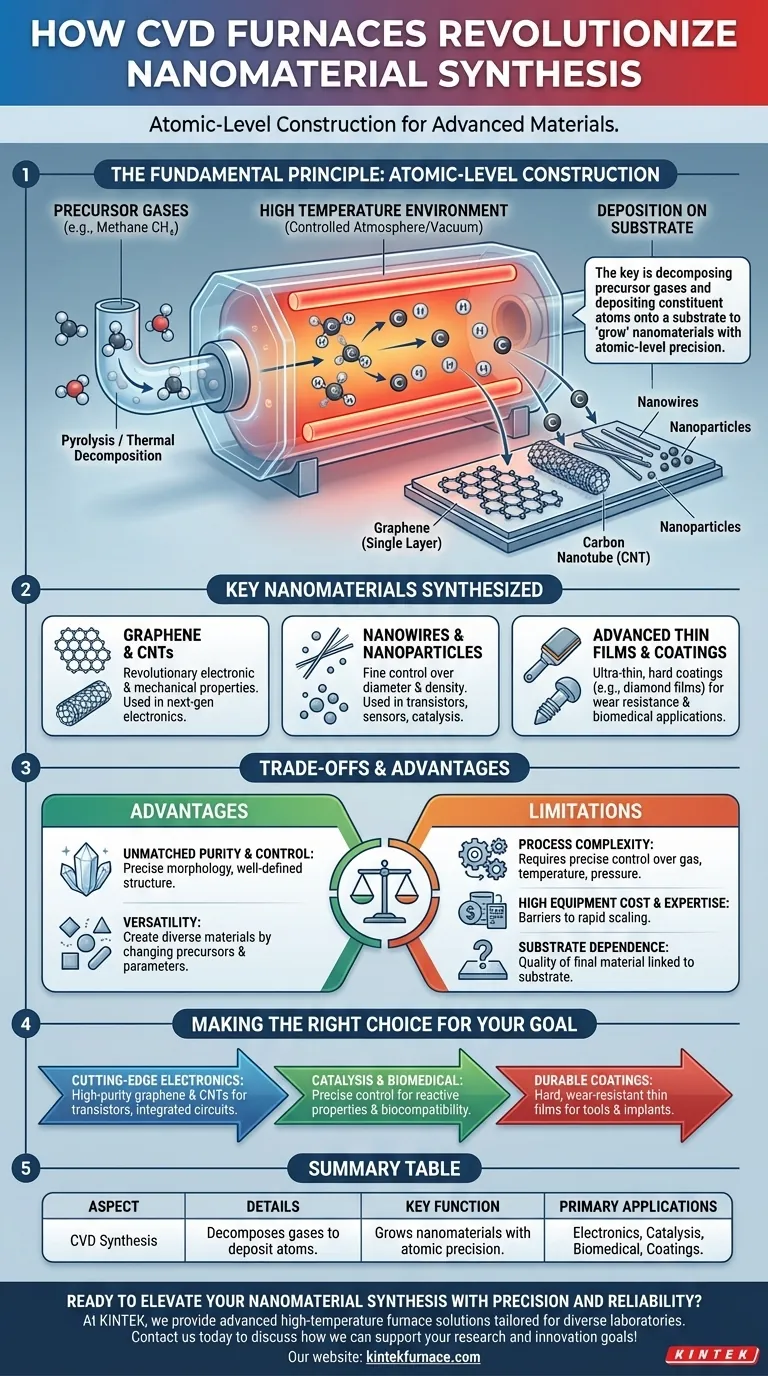
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnace is used in nanomaterial synthesis to create exceptionally pure, high-performance materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes from gaseous raw materials. It provides a highly controlled high-temperature environment where chemical reactions are triggered, allowing atoms to deposit onto a surface and self-assemble into precise nanostructures. This process is fundamental to creating components for advanced electronics, catalysts, and biomedical devices.
The key function of a CVD furnace is not just to heat materials, but to use that thermal energy to decompose precursor gases and deposit their constituent atoms onto a substrate, effectively "growing" a nanomaterial with atomic-level precision.
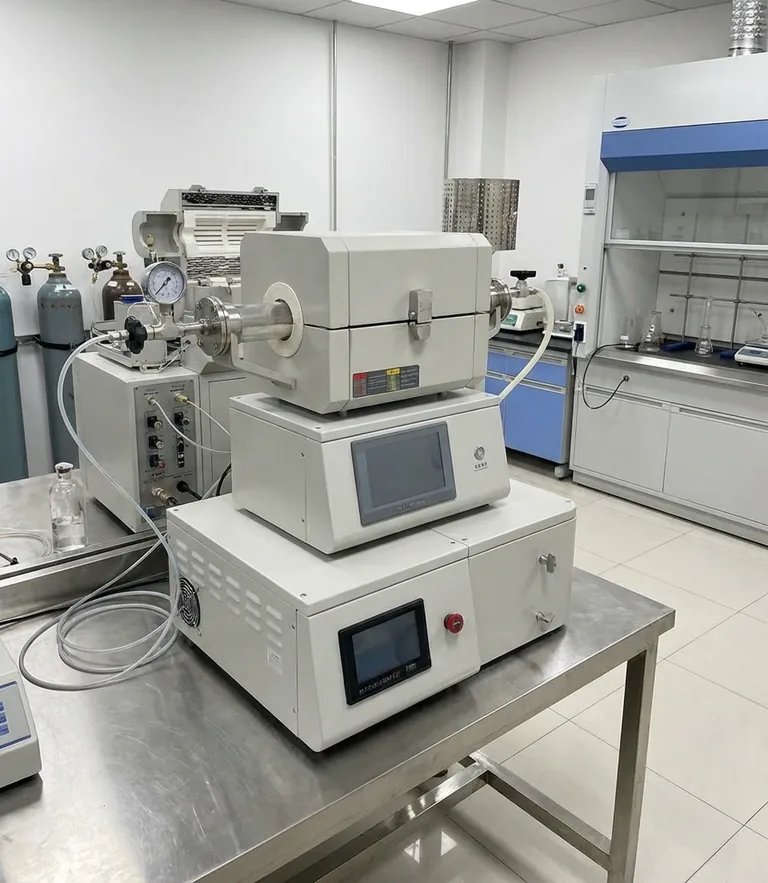

The Fundamental Principle: How CVD Builds Nanomaterials
Understanding the CVD process is about seeing it as a form of atomic-level construction. Instead of carving a material down, you are building it up, atom by atom.
The Role of Precursor Gases
The process begins with precursor gases, which are volatile compounds containing the elements needed for the final material. For example, to create carbon-based nanomaterials, a gas like methane (CH₄) is often used as the carbon source.
The Power of High Temperature
The furnace provides the critical energy, typically at very high temperatures, to initiate a chemical reaction. This heat causes the precursor gases to break down in a process called pyrolysis or thermal decomposition, releasing the desired atoms (e.g., carbon atoms from methane).
Deposition onto a Substrate
These freed atoms then travel through the chamber and land on a prepared surface called a substrate. Under precisely controlled conditions, these atoms bond with the substrate and each other, forming a highly ordered crystalline structure, such as a single layer of graphene or a rolled-up carbon nanotube.
The Critical Controlled Atmosphere
CVD furnaces are atmosphere furnaces, meaning the internal environment is meticulously controlled. Often operating under a vacuum or filled with inert gases, this oxygen-free atmosphere is crucial for preventing contamination and unwanted side reactions, ensuring the final nanomaterial is exceptionally pure.
Key Nanomaterials Synthesized via CVD
The versatility of the CVD process allows for the creation of a wide range of valuable nanomaterials by simply changing the precursor gases, temperature, and pressure.
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
These are the most prominent examples of CVD-synthesized nanomaterials. By decomposing a carbon-containing gas, researchers can grow a single atomic layer of carbon (graphene) on a substrate or encourage it to form seamless cylinders (carbon nanotubes), both of which have revolutionary electronic and mechanical properties.
Nanowires and Nanoparticles
By using different precursors, other structures can be grown. For instance, silicon-containing gases can be used to grow silicon nanowires for use in transistors and sensors. The process allows for fine control over the diameter, length, and density of these wires.
Advanced Thin Films and Coatings
The applications extend beyond standalone nanostructures. CVD is a primary method for depositing ultra-thin, hard coatings like diamond films on cutting tools or wear-resistant layers on biomedical implants. These films are technically nanomaterials due to their controlled, nanometer-scale thickness and structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While powerful, CVD is a sophisticated technique with specific strengths and limitations that determine its suitability for a given application.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Control
The greatest strength of CVD is the ability to produce materials with extremely high purity and a well-defined crystalline structure. This control over morphology and size is what makes the resulting nanomaterials so valuable for high-performance applications in electronics and catalysis.
Advantage: Versatility
The process is highly flexible. A single CVD furnace can be used to create dozens of different materials—from graphene to refractory metal coatings—simply by changing the precursor gases and process parameters.
Limitation: Process Complexity
CVD systems require precise control over gas flow rates, temperature profiles, and chamber pressure. This complexity makes the equipment expensive and requires significant expertise to operate, posing a barrier to rapid scaling and widespread adoption.
Limitation: Substrate Dependence
The quality of the final nanomaterial is often directly linked to the quality and type of the substrate it is grown on. Finding the right substrate and preparing its surface can be a significant challenge in itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for using a CVD furnace will dictate which aspects of the process are most important.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge electronic materials: CVD is the definitive method for producing the high-purity graphene and carbon nanotubes required for next-generation transistors, transparent conductors, and integrated circuits.
- If your primary focus is catalysis or biomedical applications: CVD's precise control over nanoparticle and nanowire morphology is essential for engineering surfaces with specific reactive properties or biocompatibility.
- If your primary focus is creating durable, high-performance coatings: CVD is the industry standard for depositing hard, wear-resistant, and chemically inert thin films on tools, implants, and optical components.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a CVD furnace is about precisely controlling a chemical reaction to transform simple gases into some of the most advanced materials known to science.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Key Function | Decomposes precursor gases to deposit atoms on a substrate, growing nanomaterials with atomic precision. |
| Common Nanomaterials | Graphene, carbon nanotubes, nanowires, nanoparticles, thin films. |
| Primary Applications | Advanced electronics, catalysts, biomedical devices, durable coatings. |
| Key Advantages | High purity, precise control over morphology, versatility in material synthesis. |
| Limitations | High complexity, expensive equipment, substrate dependence. |
Ready to elevate your nanomaterial synthesis with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're developing cutting-edge electronics, catalysts, or biomedical devices, our expertise ensures optimal performance and purity. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















