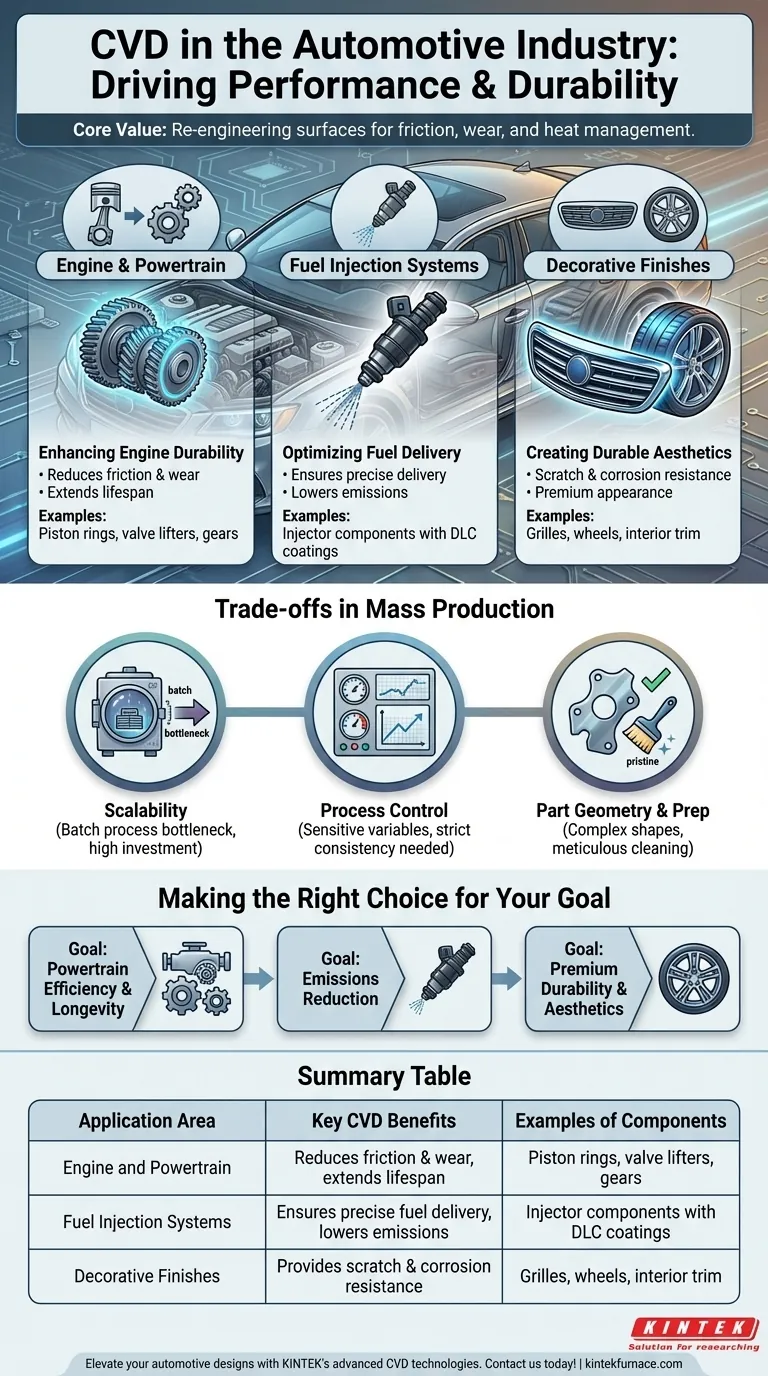
In the automotive industry, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a critical process used to apply high-performance coatings on key components. These applications range from wear-resistant layers on engine parts and hard carbon coatings for fuel injection systems to durable, premium decorative finishes, all contributing to improved vehicle performance, efficiency, and longevity.
The core value of CVD in the automotive sector is not just applying a surface layer; it's about fundamentally re-engineering a component's surface to solve critical challenges related to friction, wear, and heat management, which are central to building more efficient and reliable vehicles.

Why CVD is Essential for Modern Vehicles
The relentless push for greater fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and longer vehicle life has forced engineers to find solutions at the material science level. CVD provides a powerful method for enhancing the properties of conventional materials without changing the bulk component.
Enhancing Engine Durability and Performance
Internal combustion engine components operate under extreme stress, friction, and heat. CVD applies ultra-thin, incredibly hard coatings to parts like piston rings, valve lifters, and gears.
These wear-resistant coatings dramatically reduce friction between moving parts. This not only extends the operational life of the engine but also directly contributes to better fuel economy by minimizing energy lost to heat.
Optimizing Fuel Injection Systems
Modern fuel injection systems operate at exceptionally high pressures. Components within these systems are susceptible to intense wear and corrosion from aggressive fuel additives.
CVD is used to apply hard carbon coatings, such as Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), to injector components. This creates an extremely durable and low-friction surface that ensures precise fuel delivery over the vehicle's lifetime, which is critical for maintaining optimal combustion, fuel efficiency, and low emissions.
Creating Durable and Aesthetic Finishes
Beyond the powertrain, CVD is used for exterior and interior trim pieces. It provides a finish that is far more durable than traditional chrome plating or paint.
These coatings offer superior resistance to scratches, corrosion, and UV degradation. This ensures that grilles, wheels, and interior accents maintain their premium appearance for years, enhancing the vehicle's perceived quality and value.
Understanding the Trade-offs: CVD in Mass Production
While its benefits are clear, integrating CVD into a high-volume automotive production line presents distinct engineering and financial challenges. It is not a universally applicable solution.
The Challenge of Scalability
CVD is often a batch process performed in a vacuum chamber. This can create a bottleneck compared to faster, continuous processes like electroplating. Achieving the high throughput required for automotive manufacturing demands significant investment in large-scale, automated equipment.
The Importance of Process Control
The quality of a CVD coating is highly sensitive to process variables like temperature, pressure, and gas composition. Maintaining strict process control is essential for coating consistency and performance, which adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing line.
Limitations of Part Geometry and Preparation
Achieving a uniform coating on highly complex shapes can be difficult. Furthermore, the success of any CVD coating depends entirely on pristine surface preparation. Parts must be meticulously cleaned and handled to ensure proper adhesion, adding extra steps and quality checks to the production flow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
CVD is a strategic technology applied to solve specific problems. Your implementation should be directly tied to the primary engineering objective you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is powertrain efficiency and longevity: Target internal engine and transmission components with wear-resistant and low-friction CVD coatings to reduce parasitic losses.
- If your primary focus is emissions reduction: Implement hard carbon coatings on fuel system components to guarantee precise operation and clean combustion over the long term.
- If your primary focus is premium durability and aesthetics: Utilize CVD for decorative finishes on high-visibility trim and wheels that must withstand environmental exposure.
Ultimately, CVD is a strategic tool that allows automotive engineers to solve critical material science challenges at the microscopic level, leading to macroscopic improvements in vehicle performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key CVD Benefits | Examples of Components |
|---|---|---|
| Engine and Powertrain | Reduces friction and wear, extends lifespan | Piston rings, valve lifters, gears |
| Fuel Injection Systems | Ensures precise fuel delivery, lowers emissions | Injector components with DLC coatings |
| Decorative Finishes | Provides scratch and corrosion resistance | Grilles, wheels, interior trim |
Ready to elevate your automotive designs with precision coatings? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures deep customization to meet your unique requirements, enhancing component durability and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our CVD technologies can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















