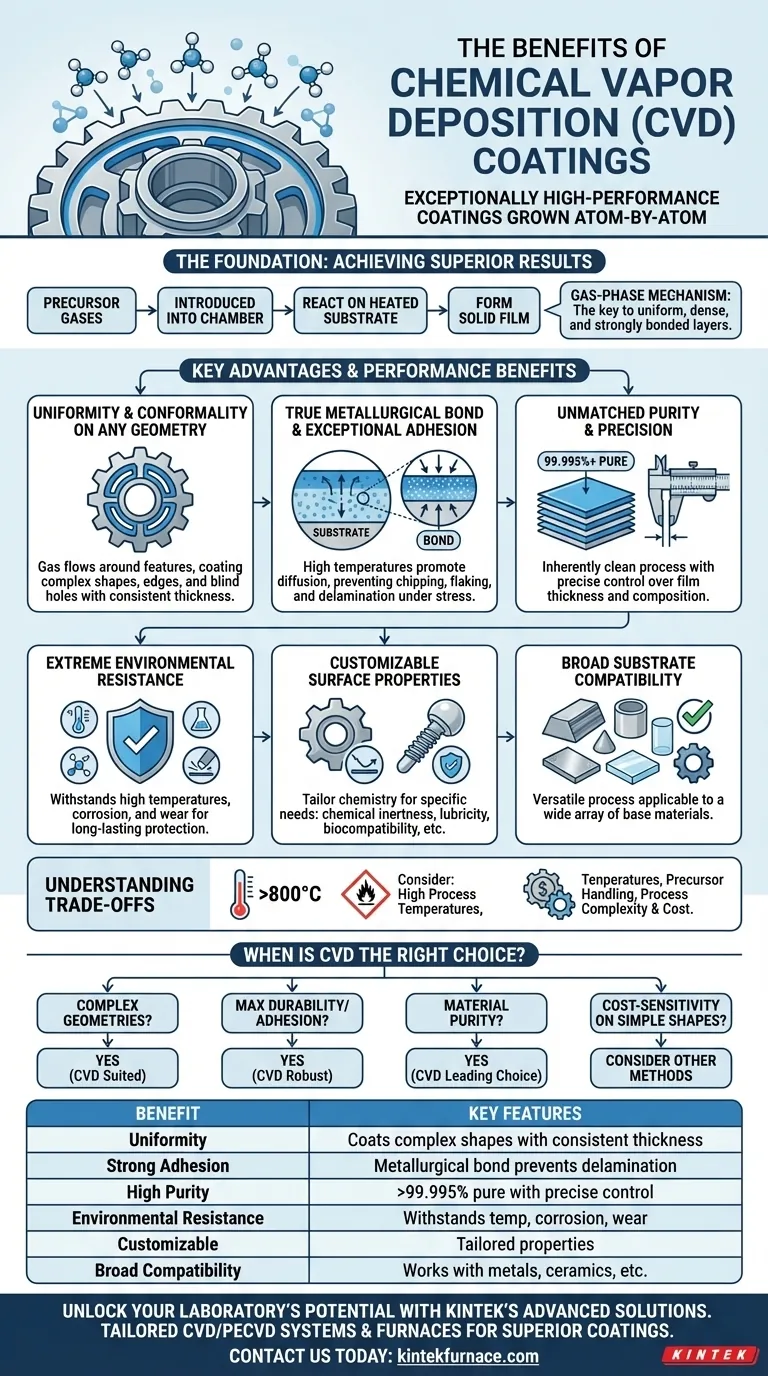
At its core, the primary benefit of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is its ability to produce exceptionally high-performance coatings. These films are not simply layered on top of a surface; they are grown atom-by-atom, resulting in a dense, uniform, and strongly bonded layer that is tailored for specific properties like wear resistance, chemical inertness, and high-temperature stability.
CVD is the definitive choice when performance on complex geometries is non-negotiable. Its fundamental advantage is using a gas to deposit a film, allowing it to uniformly coat intricate surfaces where line-of-sight methods would fail, while creating an exceptionally pure and durable layer.

The Foundation of CVD: How It Achieves Superior Results
To understand the benefits, you must first understand the process. CVD involves introducing precursor gases into a chamber, which then react and decompose on a heated substrate surface to form a solid film. This gas-phase mechanism is the source of its key advantages.
Uniformity and Conformality on Any Geometry
The most distinct advantage of CVD is its ability to create a perfectly conformal and uniform coating. Because the precursor is a gas, it flows around and into any feature on a part's surface.
This allows CVD to coat complex shapes, sharp edges, internal channels, and even blind holes with consistent thickness, something that is difficult or impossible for line-of-sight processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Creating a True Metallurgical Bond
CVD coatings are not just "stuck on" the surface. The high temperatures of the process promote diffusion between the coating and the substrate, creating a true metallurgical bond.
This inter-diffusion zone results in exceptional adhesion. The coating becomes an integral part of the substrate, ensuring it will not chip, flake, or delaminate even under high mechanical stress or extreme temperature variations.
Unmatched Purity and Precision
The CVD process is inherently clean and controllable. Precursor gases can be refined to incredibly high purity levels, allowing for the deposition of films that are often over 99.995% pure.
Furthermore, because the film is grown layer by layer, operators have precise control over its final thickness and composition, ensuring repeatable results for demanding applications in fields like semiconductors and aerospace.
Key Performance Benefits in Application
The unique process characteristics of CVD translate directly into tangible performance benefits for a wide range of industries.
Extreme Environmental Resistance
The strong atomic bonds and dense structure of CVD coatings make them highly resilient. They can withstand both low and high temperatures and survive rapid thermal cycling without degradation.
This durability also provides excellent corrosion and wear resistance, protecting the underlying substrate from harsh chemicals and mechanical abrasion.
Customizable Surface Properties
By changing the chemistry of the precursor gases, the properties of the final coating can be precisely tailored to a specific need.
A coating can be optimized for properties like chemical inertness for lab equipment, high lubricity (low friction) for moving parts, or biocompatibility for medical implants.
Broad Substrate Compatibility
CVD is a remarkably versatile process that is not limited to a single type of base material. It can be successfully applied to a wide array of substrates.
This includes metals, metal alloys, ceramics, glass, and in some low-temperature variations of the process, even certain polymers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. To make an informed decision, it is critical to weigh the benefits of CVD against its inherent requirements and limitations.
High Process Temperatures
Traditional thermal CVD requires high temperatures (often >800°C) to initiate the chemical reactions. This can be a significant limitation, as it may alter the properties of or even damage heat-sensitive substrates.
While lower-temperature variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) exist, they represent a different set of process complexities.
Precursor Material Handling
The precursor gases used in CVD can be toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates sophisticated and often expensive gas handling systems and robust safety protocols, which can increase the overall operational cost.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD equipment is specialized and can represent a significant capital investment. The process itself requires precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates, making it more complex and often more expensive than simpler coating methods like painting or electroplating.
When is CVD the Right Choice?
Your decision should be driven by the primary requirement of your component. CVD excels where other methods fall short, but it may be overkill for less demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries: CVD's gas-phase deposition is uniquely suited for achieving uniform coverage where line-of-sight methods fail.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and adhesion: The diffusion bond created by CVD provides the most robust solution for high-stress, high-load, and high-temperature environments.
- If your primary focus is material purity for sensitive applications: CVD is the leading choice for creating the ultra-pure films required in semiconductor, optical, or biomedical fields.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitivity on simple shapes: You should evaluate other technologies like PVD or electroplating, as CVD's complexity may be unnecessary for the task.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if CVD technology aligns with your specific engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Uniformity and Conformality | Coats complex shapes, sharp edges, and internal channels with consistent thickness |
| Strong Adhesion | Metallurgical bond prevents chipping, flaking, and delamination under stress |
| High Purity and Precision | Films over 99.995% pure with precise thickness and composition control |
| Environmental Resistance | Withstands high/low temperatures, corrosion, and wear for long-lasting protection |
| Customizable Properties | Tailored for chemical inertness, lubricity, or biocompatibility as needed |
| Broad Substrate Compatibility | Works with metals, alloys, ceramics, glass, and some polymers |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored CVD/PECVD systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior coatings for complex geometries, enhanced durability, and high purity. Ready to elevate your research and production? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs and drive innovation in your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision



















