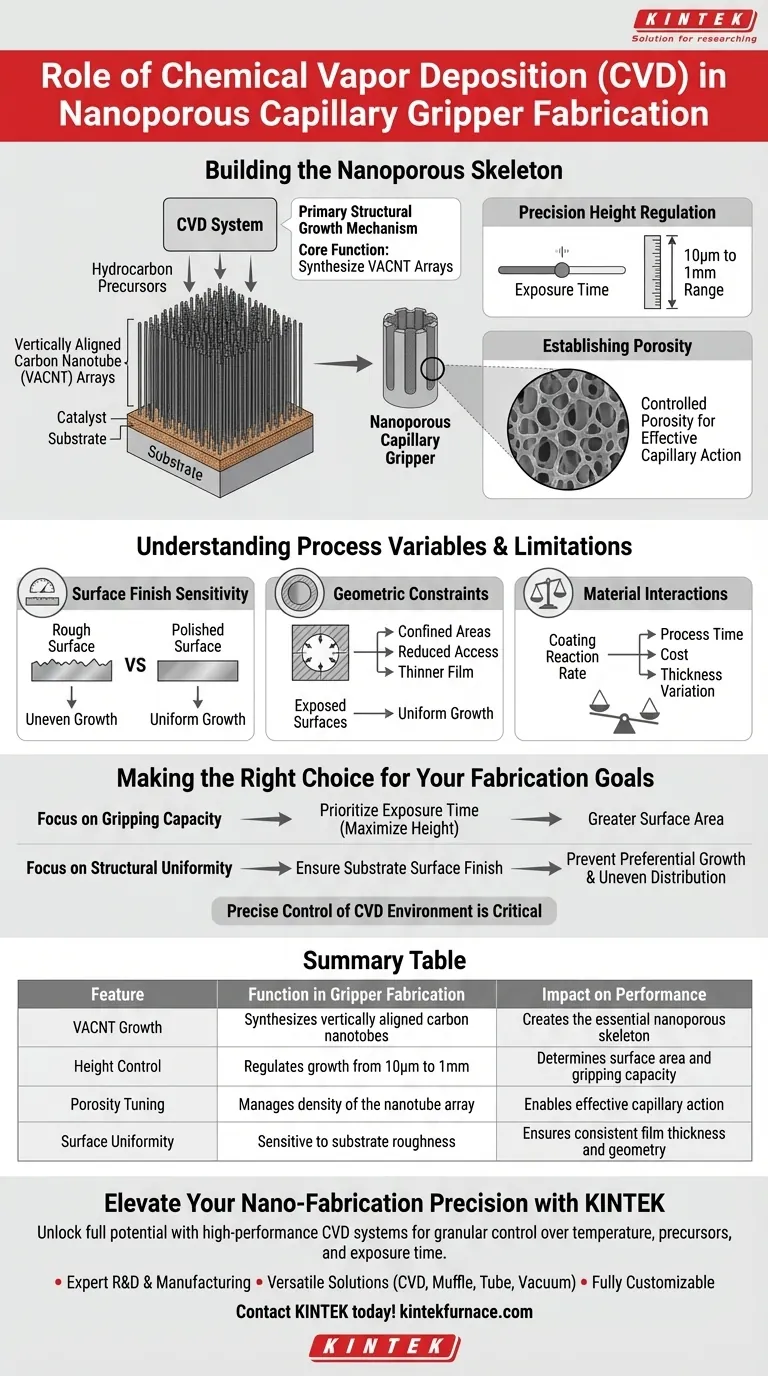
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system serves as the primary mechanism for structural growth in the fabrication of nanoporous capillary grippers. Its specific function is to grow vertically aligned carbon nanotube (VACNT) arrays on a substrate that has been prepared with a catalyst. This step creates the essential physical framework required for the device's operation.
The CVD system enables the precise construction of an initial nanoporous skeleton by regulating the height and density of carbon nanotubes. This process establishes the high specific surface area and controlled porosity necessary for effective capillary action.
Building the Nanoporous Skeleton
Growth of VACNT Arrays
The core function of the CVD system is to synthesize vertically aligned carbon nanotube (VACNT) arrays.
This occurs after the catalyst deposition phase. The system introduces hydrocarbon precursors which react to form the nanotubes directly on the substrate.
Precision Height Regulation
The CVD system offers granular control over the physical dimensions of the gripper's structure.
By precisely manipulating the exposure time of the hydrocarbon precursors, the system can regulate the height of the nanotubes. This allows for a fabrication range spanning from 10 micrometers to 1 millimeter.
Establishing Porosity
The result of this process is an initial skeleton characterized by controlled porosity.
This structure provides a high specific surface area, which is the defining feature enabling the capillary forces used for gripping.
Understanding Process Variables and Limitations
Surface Finish Sensitivity
The condition of the substrate surface significantly influences the uniformity of the CVD process.
Rough surfaces can lead to uneven growth. Specifically, peaks on a rough surface may be coated preferentially compared to valleys, potentially altering the intended geometry of the gripper.
Geometric Constraints
The configuration of the part being processed plays a critical role in the quality of the film or growth.
Small, confined areas, such as internal bores, may experience reduced access to the chemical precursors. This often results in a thinner film or less dense growth in those areas compared to exposed surfaces.
Material Interactions
The underlying base material and its surface condition can affect the coating reaction rate.
This introduces a trade-off between process time, cost, and thickness variation. Operators must balance these factors to achieve a consistent structure without incurring excessive fabrication costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Fabrication Goals
To optimize the fabrication of nanoporous capillary grippers, consider how your design requirements interact with CVD capabilities:
- If your primary focus is gripping capacity: Prioritize the exposure time to maximize the height of the VACNT arrays (up to 1 mm) for greater surface area.
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Ensure the substrate surface finish is highly polished to prevent preferential growth on peaks and uneven distribution.
Precise control of the CVD environment is the single most critical factor in defining the performance characteristics of the final capillary gripper.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Gripper Fabrication | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| VACNT Growth | Synthesizes vertically aligned carbon nanotubes | Creates the essential nanoporous skeleton |
| Height Control | Regulates growth from 10µm to 1mm | Determines surface area and gripping capacity |
| Porosity Tuning | Manages density of the nanotube array | Enables effective capillary action |
| Surface Uniformity | Sensitive to substrate roughness | Ensures consistent film thickness and geometry |
Elevate Your Nano-Fabrication Precision with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your research and manufacturing with KINTEK’s high-performance CVD systems. Whether you are growing VACNT arrays for capillary grippers or developing advanced semiconductor materials, our equipment delivers the granular control over temperature, precursors, and exposure time you need for superior results.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Backed by years of expertise in high-temperature lab technology.
- Versatile Solutions: From standard CVD to Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems.
- Fully Customizable: Tailored configurations to meet your specific porosity and geometry requirements.
Don't let geometric constraints or material interactions compromise your output. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our customizable CVD and furnace solutions can optimize your fabrication workflow!
Visual Guide
References
- Seong Jae Kim, Sanha Kim. Nanoporous Capillary Gripper for Ultragentle Micro‐Object Manipulation. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202508338
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- In which fields are CVD furnaces widely applied? Essential for Semiconductors, Aerospace, and More
- What assurances are provided regarding the quality and reliability of CVD furnaces? Ensure Precision and Durability for Your Lab
- What is the basic principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Unlock High-Purity Thin-Film Synthesis
- How do PVD and CVD differ in terms of coating conformity? Uncover the Best Method for Complex Parts
- What is the primary purpose of a water trap device in CVD? Ensure Safe Carbon Nitride Synthesis
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What are the different types of CVD systems? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab's Needs
- How is CVD used in the aerospace industry? Enhance Engine Performance with Protective Coatings



















